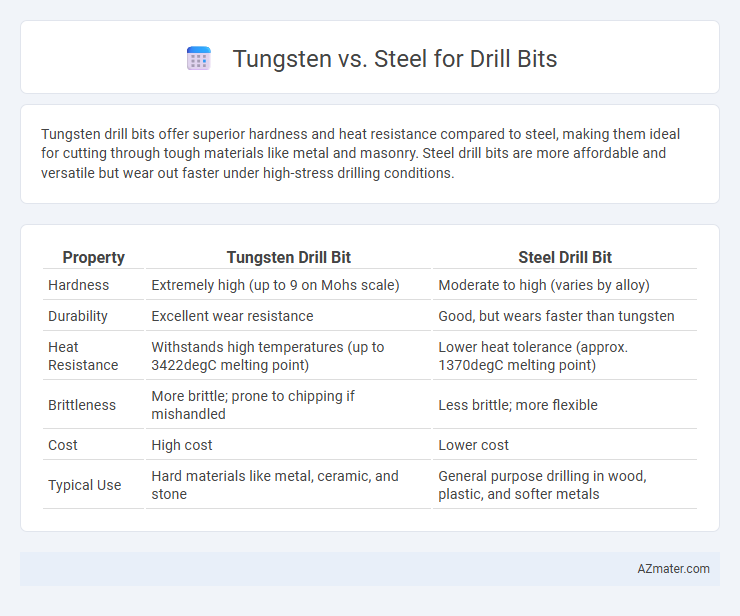
Tungsten drill bits offer superior hardness and heat resistance compared to steel, making them ideal for cutting through tough materials like metal and masonry. Steel drill bits are more affordable and versatile but wear out faster under high-stress drilling conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tungsten Drill Bit | Steel Drill Bit |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Extremely high (up to 9 on Mohs scale) | Moderate to high (varies by alloy) |
| Durability | Excellent wear resistance | Good, but wears faster than tungsten |
| Heat Resistance | Withstands high temperatures (up to 3422degC melting point) | Lower heat tolerance (approx. 1370degC melting point) |
| Brittleness | More brittle; prone to chipping if mishandled | Less brittle; more flexible |
| Cost | High cost | Lower cost |
| Typical Use | Hard materials like metal, ceramic, and stone | General purpose drilling in wood, plastic, and softer metals |
Introduction to Drill Bit Materials
Tungsten and steel are two primary materials used in the manufacturing of drill bits, each offering distinct advantages in terms of hardness and durability. Tungsten carbide drill bits provide superior wear resistance and can maintain a sharper edge for longer, making them ideal for drilling through tough materials such as metal and masonry. Steel drill bits, especially high-speed steel (HSS), are more cost-effective, flexible, and suitable for general-purpose drilling in wood, plastic, and softer metals.
Overview of Tungsten Drill Bits
Tungsten drill bits, typically made from tungsten carbide, offer superior hardness and wear resistance compared to standard steel bits, making them ideal for drilling through tough materials like metal, masonry, and ceramics. Their exceptional durability ensures longer tool life and maintains sharpness under high-stress conditions, which enhances drilling precision and efficiency. Tungsten drill bits outperform high-speed steel (HSS) bits in heat resistance, reducing the risk of deformation during high-speed drilling applications.
Overview of Steel Drill Bits
Steel drill bits, primarily made from high carbon or high-speed steel (HSS), offer excellent durability and heat resistance for general-purpose drilling. Their ability to maintain sharpness and withstand higher temperatures makes them suitable for drilling into softer metals, wood, and plastics. Steel drill bits provide a cost-effective option with reliable performance for a wide range of household and industrial applications.
Hardness Comparison: Tungsten vs Steel
Tungsten drill bits exhibit significantly higher hardness compared to steel, with tungsten carbide reaching hardness levels of approximately 1600-1800 HV (Vickers Hardness), whereas high-speed steel (HSS) typically ranges around 600-700 HV. This superior hardness enables tungsten carbide bits to maintain sharp cutting edges longer and resist wear during drilling in tough materials like stainless steel and ceramics. Steel drill bits, while more affordable and flexible, lack the durability of tungsten carbide, making them less suitable for heavy-duty or precision drilling tasks.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Tungsten drill bits offer superior durability and wear resistance compared to steel, retaining sharpness longer when drilling through hard materials like metal and masonry. The high hardness of tungsten carbide enables it to withstand elevated temperatures and abrasive conditions without significant degradation. Steel drill bits, while more affordable and tougher against impact, typically wear out faster under heavy-duty or continuous use, requiring more frequent replacement.
Performance in Different Applications
Tungsten drill bits offer superior hardness and heat resistance, making them ideal for drilling through tough materials like ceramics, glass, and hardened steel. Steel drill bits, particularly high-speed steel (HSS), provide excellent toughness and flexibility, suitable for general-purpose drilling in wood, plastic, and softer metals. In high-performance applications requiring durability and precision, tungsten carbide bits outperform steel by maintaining sharpness and reducing wear during prolonged use.
Cost and Affordability Analysis
Tungsten drill bits generally cost more than steel ones due to tungsten's hardness and wear resistance, making them ideal for industrial and heavy-duty applications. Steel drill bits, particularly high-speed steel (HSS), are more affordable and widely used in DIY and light to medium drilling tasks. Choosing between tungsten and steel drill bits depends on balancing durability requirements against budget constraints, with steel offering cost-effective performance for non-specialized use.
Maintenance and Longevity
Tungsten drill bits exhibit greater longevity and require less frequent maintenance compared to steel due to their superior hardness and wear resistance. Steel drill bits, while more affordable, tend to dull faster and need regular sharpening to maintain performance. The increased durability of tungsten reduces downtime and replacement costs in industrial and heavy-duty drilling applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Tungsten drill bits have a lower environmental impact due to their longer lifespan and higher durability, which reduces the frequency of replacements and waste generation compared to steel drill bits. Steel drill bits often require more energy-intensive manufacturing processes and tend to corrode faster, leading to increased resource consumption and shorter product life cycles. Recycling tungsten is more efficient and environmentally friendly, as the metal can be recovered and reused without significant loss of quality, enhancing sustainability in industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Drill Bit Material
Tungsten drill bits offer superior hardness and heat resistance, making them ideal for drilling through tough materials like metals and ceramics. Steel drill bits, especially high-speed steel (HSS), provide versatility and durability for wood, plastic, and softer metals, often at a lower cost. Choosing the right drill bit material depends on the specific application, material hardness, and budget considerations to ensure optimal performance and tool longevity.
Infographic: Tungsten vs Steel for Drill Bit
 azmater.com
azmater.com