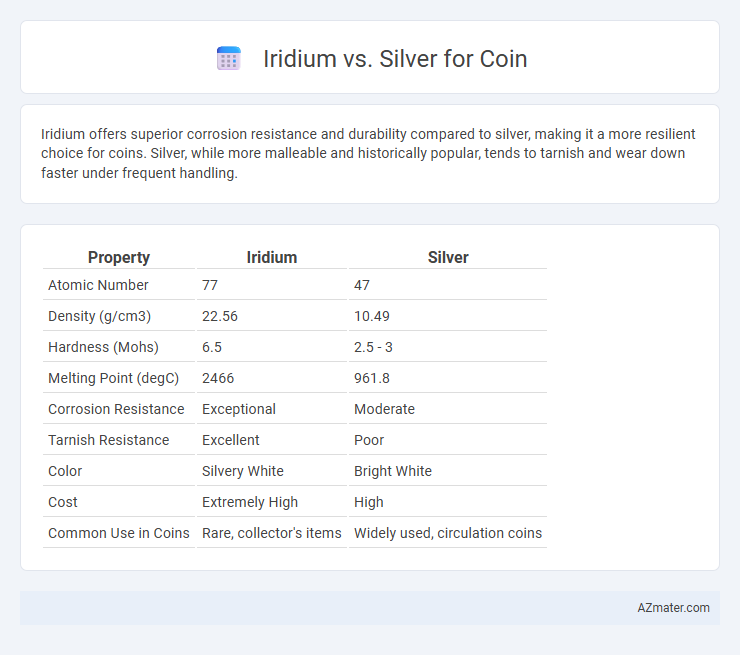
Iridium offers superior corrosion resistance and durability compared to silver, making it a more resilient choice for coins. Silver, while more malleable and historically popular, tends to tarnish and wear down faster under frequent handling.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Iridium | Silver |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 77 | 47 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 22.56 | 10.49 |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 6.5 | 2.5 - 3 |
| Melting Point (degC) | 2466 | 961.8 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Exceptional | Moderate |
| Tarnish Resistance | Excellent | Poor |
| Color | Silvery White | Bright White |
| Cost | Extremely High | High |
| Common Use in Coins | Rare, collector's items | Widely used, circulation coins |
Introduction to Iridium and Silver Coins
Iridium coins are prized for their exceptional hardness, corrosion resistance, and rarity, making them a distinctive choice for collectors and investors seeking durable and unique precious metal pieces. Silver coins, widely recognized for their affordability, high malleability, and historical significance in currency, remain popular due to their excellent conductivity and aesthetic appeal. Both metals offer unique benefits: iridium's extreme durability contrasts with silver's versatility and economic accessibility in numismatic collections.
Historical Use of Iridium and Silver in Coinage
Iridium's historical use in coinage is limited due to its rarity and high melting point, though its exceptional hardness has made it a component in some durable coin alloys. Silver, by contrast, has been a preferred metal for coinage since ancient times owing to its malleability, luster, and intrinsic value, prominently featured in currency from Greek drachmas to modern bullion coins. The contrasting physical properties and availability of iridium and silver have significantly influenced their roles in the economic and numismatic history of coin minting.
Physical and Chemical Properties Compared
Iridium and silver differ significantly in physical and chemical properties relevant to coin use. Iridium exhibits exceptional hardness and corrosion resistance with a melting point of 2,446degC, making it highly durable and resistant to wear, while silver, with a lower melting point of 961.8degC, is much softer and more prone to tarnishing due to oxidation. Chemically, iridium is one of the most chemically inert metals, showing little reaction to acids and environmental factors, whereas silver readily reacts with sulfur compounds in the air, leading to surface darkening over time.
Rarity and Availability in the Market
Iridium is significantly rarer than silver, making it one of the rarest elements on Earth with a scarcity far exceeding that of silver. Silver is more abundant and widely available in the market, often used in coins due to its relative affordability and ease of access. The extreme rarity of iridium drives up its value and limits its use in coinage compared to the commonly accessible silver.
Value and Investment Potential
Iridium, a rare platinum-group metal with high corrosion resistance, offers a unique investment opportunity due to its scarcity and industrial demand, often commanding higher prices than silver per ounce. Silver, widely used in jewelry, electronics, and currency, holds substantial liquidity and historical value but faces price volatility linked to industrial cycles and market speculation. Investors seeking long-term appreciation may favor iridium for its niche applications and limited supply, while silver remains attractive for portfolio diversification and hedge against inflation.
Durability and Tarnish Resistance
Iridium offers exceptional durability and tarnish resistance compared to silver, making it ideal for coins that require long-lasting wear and minimal maintenance. Silver, while popular for its aesthetic appeal, is more prone to tarnishing and scratches due to its softer nature and higher reactivity with sulfur and moisture. Coins made from iridium maintain their luster and structural integrity over time, providing superior performance in harsh environmental conditions.
Collectibility and Popularity Among Numismatists
Iridium coins are highly prized by numismatists for their rarity and durability, often enhancing a collection's uniqueness and long-term value. Silver remains the most popular metal among collectors due to its historical significance, wide availability, and vibrant luster, making silver coins highly sought after in the numismatic market. While silver coins dominate in popularity, iridium's scarcity and resistance to tarnish contribute to a niche but growing interest among advanced collectors seeking distinctive materials.
Industrial Applications Affecting Coin Demand
Iridium's exceptional corrosion resistance and high melting point make it valuable in industrial applications such as electronics and high-temperature equipment, indirectly influencing coin demand by limiting its availability. Silver, widely used in electrical contacts, photovoltaics, and antimicrobial coatings, sustains a steady industrial demand that drives consistent coin investment and recycling trends. The contrasting industrial roles of iridium and silver create distinct market pressures, affecting their coin circulation and hoarding behaviors globally.
Environmental and Ethical Impacts
Iridium mining has a lower environmental footprint compared to silver due to its rarity and extraction from trace deposits in platinum ores, resulting in less surface disruption and habitat loss. Silver extraction often involves open-pit mining and the use of toxic chemicals like cyanide, causing significant soil and water contamination. Ethically, iridium's limited supply reduces large-scale exploitation concerns, while silver mining frequently raises issues related to labor rights and the socio-economic impact on local communities.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Iridium and Silver Coins
Iridium coins offer superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to silver, making them ideal for long-term preservation and investment. Silver coins, prized for their aesthetic appeal and traditional value, provide higher liquidity and are widely recognized in collector and investor markets. Selecting between iridium and silver coins depends on prioritizing longevity and resilience versus market familiarity and liquidity.
Infographic: Iridium vs Silver for Coin
 azmater.com
azmater.com