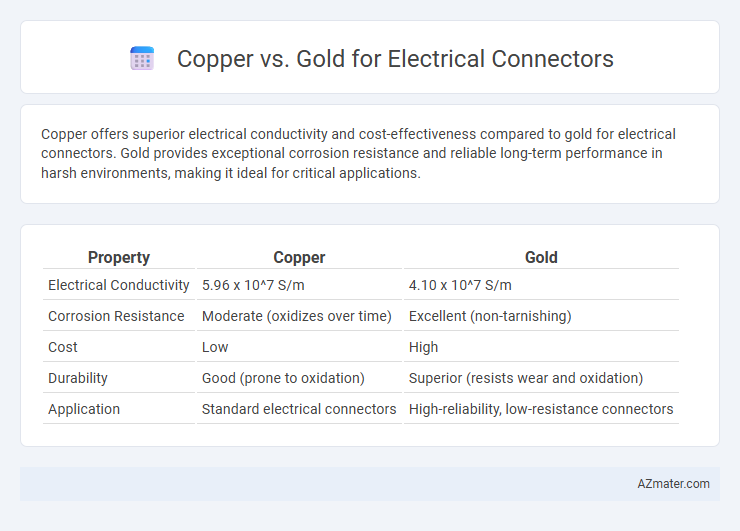
Copper offers superior electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness compared to gold for electrical connectors. Gold provides exceptional corrosion resistance and reliable long-term performance in harsh environments, making it ideal for critical applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Copper | Gold |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 5.96 x 10^7 S/m | 4.10 x 10^7 S/m |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate (oxidizes over time) | Excellent (non-tarnishing) |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Durability | Good (prone to oxidation) | Superior (resists wear and oxidation) |
| Application | Standard electrical connectors | High-reliability, low-resistance connectors |
Introduction to Electrical Connectors
Electrical connectors require materials with excellent conductivity and reliability, where copper and gold are often compared. Copper offers superior electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for most standard electrical connectors. Gold, while less conductive, provides unmatched corrosion resistance and durability, crucial for high-performance or harsh environment connectors.
Importance of Material Selection in Connectors
Selecting copper or gold for electrical connectors significantly impacts conductivity and corrosion resistance, vital for reliable signal transmission and long-term performance. Copper offers excellent electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness but may require protective coatings to prevent oxidation, while gold provides superior corrosion resistance and stable low contact resistance, essential in high-reliability applications. Material selection influences connector durability, signal integrity, and maintenance frequency, making it a critical factor in electrical connector design.
Electrical Conductivity: Copper vs Gold
Copper exhibits superior electrical conductivity with a conductivity rating of approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m, making it one of the best conductors for electrical connectors. Gold, while less conductive at around 4.10 x 10^7 S/m, offers exceptional corrosion resistance, which ensures reliable connections in harsh environments. The choice between copper and gold for electrical connectors depends on the balance between conductivity requirements and long-term durability against oxidation.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Copper offers excellent electrical conductivity but is more prone to oxidation and corrosion over time, especially in humid or harsh environments. Gold, while more expensive, provides superior corrosion resistance and maintains reliable conductivity due to its inertness, making it ideal for long-lasting electrical connectors. The enhanced longevity of gold-plated connectors reduces maintenance and replacement costs in critical applications.
Cost Comparison: Copper and Gold Connectors
Copper connectors offer a cost-effective solution with significantly lower material expenses compared to gold connectors, making them ideal for budget-sensitive applications. Gold connectors, while substantially more expensive due to gold's market price and superior corrosion resistance, provide enhanced conductivity and long-term reliability in demanding environments. The cost difference often influences the choice, with copper favored for general use and gold reserved for high-performance, critical connections where durability and signal integrity are paramount.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Copper offers excellent mechanical strength and high tensile durability, making it ideal for electrical connectors that require robust structural integrity under stress. Gold, while softer and more malleable, provides superior corrosion resistance and long-term contact reliability due to its inertness against oxidation. The choice between copper and gold depends on whether mechanical robustness or enhanced durability against environmental degradation is prioritized in connector performance.
Performance in High-Frequency Applications
Copper excels in electrical connectors for high-frequency applications due to its superior electrical conductivity (5.96 x 10^7 S/m) and low skin effect losses, enabling efficient signal transmission with minimal attenuation. Gold offers excellent corrosion resistance and stable contact resistance over time, which ensures reliability and consistent performance in harsh environments despite its lower conductivity (4.10 x 10^7 S/m). In high-frequency scenarios, copper's lower resistive loss often results in better signal integrity, while gold plating is typically used to enhance durability and prevent oxidation on copper connectors.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Copper offers superior electrical conductivity and recyclability, making it a sustainable choice for electrical connectors with a lower environmental footprint. Gold's corrosion resistance ensures long-term reliability but involves intensive mining processes that result in higher ecological impact and energy consumption. Choosing copper typically supports greater sustainability due to its widespread recyclability and reduced environmental degradation compared to gold extraction.
Industry Standards and Common Applications
Copper is the primary material for electrical connectors due to its excellent electrical conductivity, as defined by industry standards such as UL 486 and IEC 60439. Gold plating is often used on copper connectors in applications requiring corrosion resistance and reliable low-level signal transmission, following MIL-DTL-45204 specifications. Common applications include power distribution systems for copper connectors and high-frequency or sensitive electronic devices for gold-plated connectors.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Connector
Copper offers excellent electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness, making it a common choice for electrical connectors in general applications. Gold plating enhances corrosion resistance and ensures reliable signal transmission, especially in low-voltage or sensitive electronic devices where durability and contact integrity are critical. Selecting the right material depends on factors such as environmental conditions, current load, and budget constraints, with copper suited for high current and cost-sensitive uses, while gold is preferred for precision and longevity in harsh environments.
Infographic: Copper vs Gold for Electrical Connector
 azmater.com
azmater.com