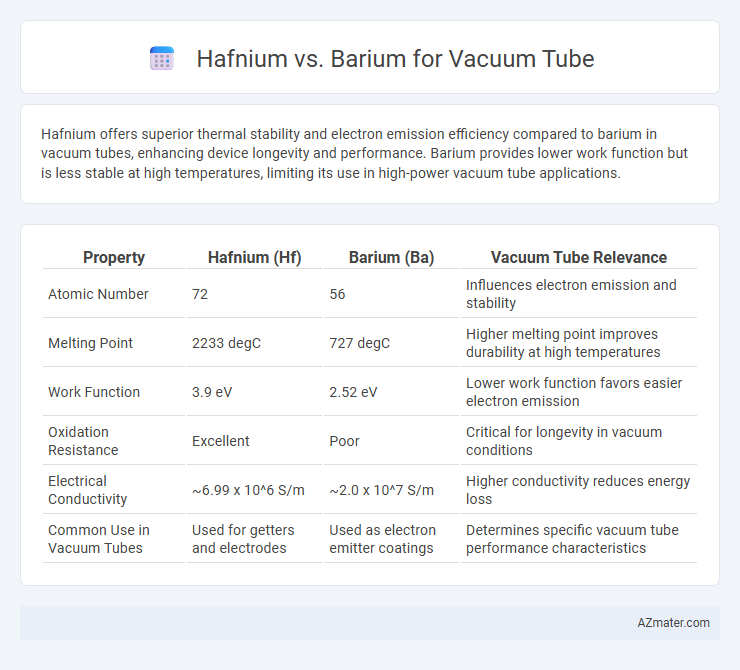
Hafnium offers superior thermal stability and electron emission efficiency compared to barium in vacuum tubes, enhancing device longevity and performance. Barium provides lower work function but is less stable at high temperatures, limiting its use in high-power vacuum tube applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hafnium (Hf) | Barium (Ba) | Vacuum Tube Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 72 | 56 | Influences electron emission and stability |
| Melting Point | 2233 degC | 727 degC | Higher melting point improves durability at high temperatures |
| Work Function | 3.9 eV | 2.52 eV | Lower work function favors easier electron emission |
| Oxidation Resistance | Excellent | Poor | Critical for longevity in vacuum conditions |
| Electrical Conductivity | ~6.99 x 10^6 S/m | ~2.0 x 10^7 S/m | Higher conductivity reduces energy loss |
| Common Use in Vacuum Tubes | Used for getters and electrodes | Used as electron emitter coatings | Determines specific vacuum tube performance characteristics |
Introduction to Hafnium and Barium in Vacuum Tubes
Hafnium and barium serve distinct roles in vacuum tubes, with hafnium primarily used as a filament or cathode material due to its high melting point and excellent electron emission properties, enhancing tube efficiency and longevity. Barium is commonly employed as a getter material or coating inside vacuum tubes, where it scavenges residual gases, maintaining the tube's vacuum quality for improved performance. Understanding the differences in their applications reveals why hafnium's robust thermal characteristics support high-temperature electron emission, while barium's chemical reactivity ensures sustained vacuum integrity.
Chemical Properties Relevant to Vacuum Tubes
Hafnium exhibits high melting points and exceptional resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for vacuum tube filaments subjected to intense heat and reactive environments. Barium is highly reactive and used as a getter material to maintain vacuum quality by absorbing residual gases, thus enhancing tube longevity and performance. The chemical stability of hafnium under high temperatures contrasts with barium's strong affinity for oxygen and nitrogen, dictating their complementary roles in vacuum tube technology.
Electron Emission Efficiency: Hafnium vs Barium
Hafnium exhibits superior electron emission efficiency compared to barium due to its higher melting point and stability under vacuum conditions, making it ideal for long-lasting vacuum tube cathodes. Barium offers strong electron emission at lower temperatures but tends to degrade faster, limiting its performance in high-temperature or high-stress vacuum environments. The choice between hafnium and barium significantly impacts the longevity and efficiency of electron emission in vacuum tube applications.
Thermionic Emission Characteristics
Hafnium exhibits superior thermionic emission characteristics compared to barium due to its higher melting point (2233degC) and lower work function, enabling more efficient electron emission at elevated temperatures. Barium, with a lower melting point (727degC) and slightly higher work function, tends to offer less stable emission and shorter filament life under high-temperature vacuum tube conditions. Consequently, hafnium-based cathodes provide enhanced durability and consistent electron flow, making them preferable in high-performance vacuum tube applications.
Role in Enhancing Tube Longevity
Hafnium significantly enhances vacuum tube longevity by improving cathode emission stability and resistance to degradation under high temperatures, ensuring prolonged operational lifespan. In contrast, barium primarily serves as a getter material, maintaining vacuum quality but offering less direct influence on cathode lifespan. The superior electron emission properties of hafnium make it a preferred choice for extending the durability and efficiency of vacuum tubes.
Vacuum Tube Performance: A Comparative Analysis
Hafnium and barium differ significantly in vacuum tube performance due to their work function and thermal stability, with hafnium offering superior electron emission efficiency and longer lifespan under high-temperature operation. Hafnium's higher melting point and lower vapor pressure reduce material degradation in vacuum environments, enhancing tube reliability and performance consistency. In contrast, barium, although effective as a getter material, tends to volatilize more rapidly, impacting the vacuum tube's overall stability and operational durability.
Stability Under High-Temperature Operations
Hafnium exhibits superior stability under high-temperature operations compared to barium, largely due to its higher melting point of 2233degC versus barium's 725degC, enabling longer lifespan in vacuum tube filaments. The refractory nature of hafnium reduces evaporation rates and maintains consistent electron emission, which is critical for reliable vacuum tube performance. In contrast, barium's lower thermal stability can lead to faster degradation and diminished vacuum tube efficiency under extended high-temperature conditions.
Impact on Signal Quality and Noise Reduction
Hafnium-coated electrodes in vacuum tubes significantly enhance signal quality due to their superior electron emission characteristics, resulting in a cleaner and more stable audio output compared to barium coatings. Hafnium's higher melting point and lower work function reduce noise and microphonic distortion, providing improved transient response and lower background hum. Barium coatings, while effective, tend to produce more noise and less consistent electron emission, leading to diminished clarity and increased signal degradation in high-fidelity applications.
Practical Applications and Industry Uses
Hafnium's high melting point and excellent electron emission properties make it ideal for vacuum tube cathodes in aerospace and military applications requiring durability under extreme temperatures. Barium, known for its effective secondary electron emission and ease of activation, is widely used in consumer electronics and audio amplification tubes to enhance signal clarity and longevity. Both materials contribute to vacuum tube performance, with hafnium preferred for high-stress environments and barium favored for cost-effective, standard operational devices.
Future Trends in Vacuum Tube Material Selection
Hafnium is gaining attention in vacuum tube manufacturing due to its superior high-temperature stability and enhanced electron emission compared to barium, which has traditionally been favored for its lower work function and reliable thermionic emission. Future trends indicate a shift towards hafnium-based cathodes aiming to improve tube longevity and performance in extreme environments, driven by increasing demands in advanced RF applications and aerospace technologies. Innovations in nanostructured hafnium coatings also promise to further optimize electron emission efficiency and reduce degradation rates, signaling a pivotal change in vacuum tube material selection.
Infographic: Hafnium vs Barium for Vacuum Tube
 azmater.com
azmater.com