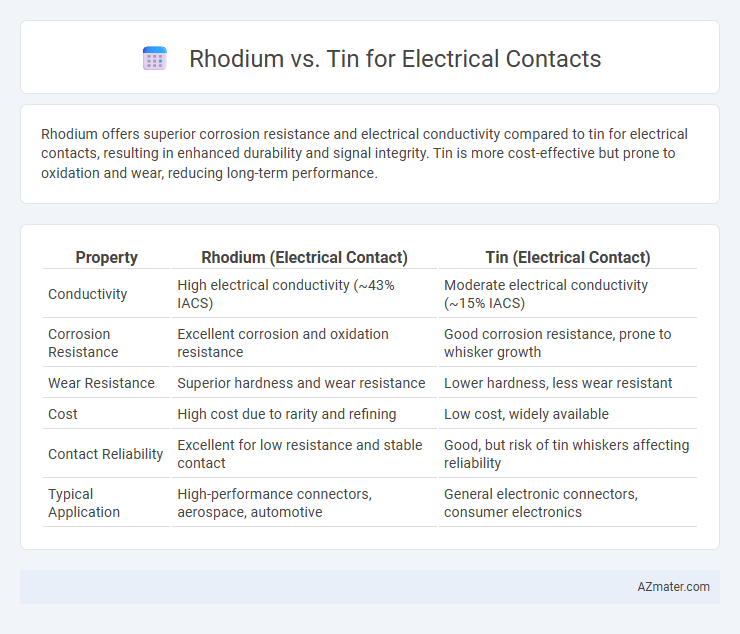
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity compared to tin for electrical contacts, resulting in enhanced durability and signal integrity. Tin is more cost-effective but prone to oxidation and wear, reducing long-term performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Rhodium (Electrical Contact) | Tin (Electrical Contact) |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | High electrical conductivity (~43% IACS) | Moderate electrical conductivity (~15% IACS) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent corrosion and oxidation resistance | Good corrosion resistance, prone to whisker growth |
| Wear Resistance | Superior hardness and wear resistance | Lower hardness, less wear resistant |
| Cost | High cost due to rarity and refining | Low cost, widely available |
| Contact Reliability | Excellent for low resistance and stable contact | Good, but risk of tin whiskers affecting reliability |
| Typical Application | High-performance connectors, aerospace, automotive | General electronic connectors, consumer electronics |
Introduction to Rhodium and Tin in Electrical Contacts
Rhodium is a precious metal known for its exceptional corrosion resistance, high hardness, and excellent conductivity, making it ideal for electrical contacts that require durability and low electrical resistance. Tin, a more abundant and cost-effective metal, provides good solderability and moderate corrosion protection but tends to wear faster and may suffer from oxidation over time. The choice between rhodium and tin coatings depends on the application's demand for longevity, conductivity stability, and cost-efficiency in electrical contact manufacturing.
Material Properties: Rhodium vs Tin
Rhodium exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance and high hardness, making it ideal for durable electrical contacts that require long-term stability and minimal signal loss. Tin, while offering excellent solderability and cost efficiency, tends to suffer from whisker growth and lower wear resistance under electrical stress. The superior conductivity and oxidation resistance of rhodium often outweigh tin's advantages in high-performance, mission-critical electrical applications.
Conductivity Comparison
Rhodium exhibits superior electrical conductivity compared to tin, making it a preferred choice for high-performance electrical contacts. Its low electrical resistance and excellent corrosion resistance ensure efficient current flow and long-term reliability in demanding applications. Although tin is more cost-effective, its higher resistivity and susceptibility to oxidation limit its effectiveness in critical electrical contact environments.
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Rhodium exhibits superior corrosion and oxidation resistance compared to tin, making it highly suitable for electrical contacts exposed to harsh environments. Its inertness prevents surface degradation, ensuring stable conductivity and long-term reliability under high-temperature conditions. Tin, while cost-effective, is prone to oxidation and corrosion, which can lead to increased contact resistance and potential failure in critical electrical applications.
Durability and Lifespan
Rhodium offers superior durability and extended lifespan in electrical contacts due to its high resistance to corrosion, oxidation, and wear under harsh conditions. Tin, while more cost-effective, tends to degrade faster when exposed to moisture and mechanical stress, leading to increased contact resistance over time. The exceptional hardness and chemical stability of rhodium make it the preferred choice for applications demanding long-term reliability and minimal maintenance.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and conductivity for electrical contacts but comes at a significantly higher cost, often exceeding $10,000 per ounce, making it less economical for large-scale applications. Tin, in contrast, is much more affordable, priced around $20 per pound, providing a cost-effective solution with adequate conductivity for many consumer electronics. Economic considerations favor tin when budget constraints and mass production are priorities, while rhodium is reserved for high-reliability environments despite its expense.
Application Suitability and Industry Usage
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent conductivity, making it ideal for high-reliability electrical contacts in aerospace and medical devices where durability and signal clarity are critical. Tin, valued for its cost-effectiveness and good solderability, is widely used in consumer electronics and automotive connectors requiring moderate conductivity and corrosion protection. Industrial applications demanding long-term performance and resistance to harsh environments typically prefer rhodium plating despite its higher cost, whereas tin remains the standard for mass-produced, cost-sensitive components.
Maintenance and Reliability
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it highly reliable for electrical contacts with minimal maintenance requirements. Tin, while more cost-effective, is prone to oxidation and wear, leading to increased maintenance needs and potential contact failures over time. The durability and low contact resistance of rhodium significantly enhance long-term reliability in high-performance electrical applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, but its mining involves significant environmental challenges, including habitat disruption and high energy consumption. Tin, while less conductive and durable, is more abundant and recyclable, resulting in lower environmental impact and greater sustainability for electrical contacts. Choosing tin over rhodium supports reduced ecological footprint and aligns better with circular economy principles in electronics manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Material for Electrical Contacts
Rhodium offers superior conductivity, corrosion resistance, and wear durability, making it ideal for high-performance electrical contacts requiring long-lasting reliability. Tin provides cost-effective conductivity and excellent solderability but tends to oxidize and wear faster under heavy electrical loads. Choosing the right material depends on application demands, balancing rhodium's premium performance with tin's affordability for efficient and durable electrical contacts.
Infographic: Rhodium vs Tin for Electrical Contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com