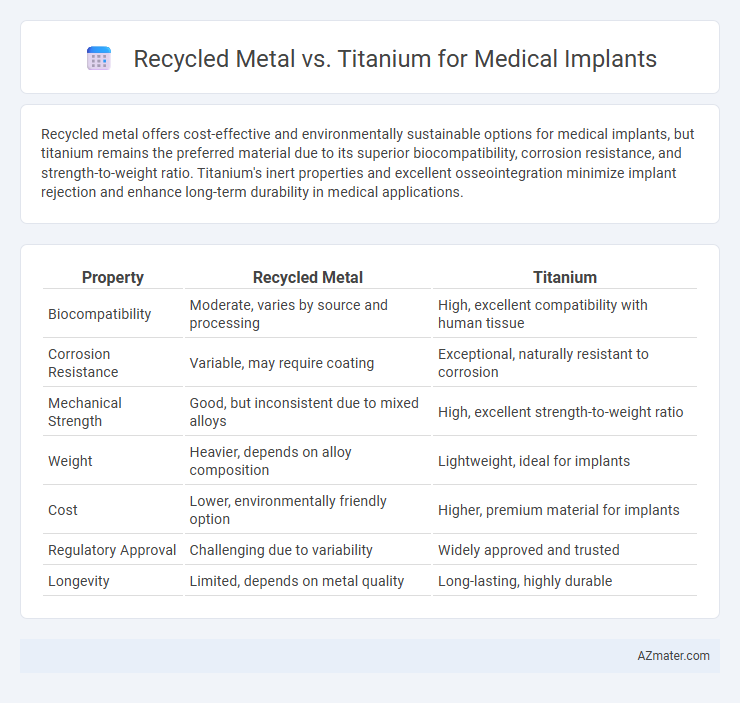
Recycled metal offers cost-effective and environmentally sustainable options for medical implants, but titanium remains the preferred material due to its superior biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and strength-to-weight ratio. Titanium's inert properties and excellent osseointegration minimize implant rejection and enhance long-term durability in medical applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Recycled Metal | Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Biocompatibility | Moderate, varies by source and processing | High, excellent compatibility with human tissue |
| Corrosion Resistance | Variable, may require coating | Exceptional, naturally resistant to corrosion |
| Mechanical Strength | Good, but inconsistent due to mixed alloys | High, excellent strength-to-weight ratio |
| Weight | Heavier, depends on alloy composition | Lightweight, ideal for implants |
| Cost | Lower, environmentally friendly option | Higher, premium material for implants |
| Regulatory Approval | Challenging due to variability | Widely approved and trusted |
| Longevity | Limited, depends on metal quality | Long-lasting, highly durable |
Introduction: The Importance of Material Choice in Medical Implants
Material selection in medical implants critically influences biocompatibility, durability, and patient outcomes, with recycled metals presenting cost-effective options but potential contamination risks. Titanium remains the gold standard for implants due to its superior corrosion resistance, strength-to-weight ratio, and exceptional osseointegration properties. Evaluating recycled metals against titanium requires thorough assessment of mechanical integrity, sterilization processes, and long-term biological response to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Overview of Recycled Metal in Medical Applications
Recycled metal in medical implants offers a sustainable alternative by repurposing scrap metals such as stainless steel and cobalt-chromium alloys, which retain essential mechanical properties and biocompatibility. Advances in purification and processing technologies ensure that recycled metals meet stringent medical-grade standards, reducing environmental impact while maintaining implant durability and corrosion resistance. This approach supports circular economy principles in healthcare, lowering costs without compromising safety or performance in orthopedic and dental applications.
Properties and Advantages of Titanium for Implants
Titanium exhibits exceptional biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and high strength-to-weight ratio, making it the preferred choice for medical implants over recycled metal, which may contain impurities affecting durability and safety. Its ability to osseointegrate with bone tissue enhances implant stability and longevity, crucial for patient recovery and function. Titanium's non-toxic and hypoallergenic nature minimizes adverse reactions, ensuring better clinical outcomes in orthopedic and dental applications.
Comparative Biocompatibility: Recycled Metal vs Titanium
Recycled metals used in medical implants often pose higher risks of biocompatibility issues due to variable alloy compositions and potential contaminants, which can trigger adverse immune responses or corrosion in the body. Titanium, renowned for its excellent biocompatibility, demonstrates superior corrosion resistance, low allergenic potential, and promotes osseointegration, making it the preferred choice for long-term implant success. Clinical studies consistently show titanium implants result in fewer complications and enhanced tissue integration compared to recycled metal counterparts.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Assessment
Titanium exhibits superior mechanical strength and durability compared to recycled metals, making it the preferred choice for medical implants requiring long-term reliability. Recycled metals often present inconsistent microstructures and potential impurities that reduce their fatigue resistance and corrosion resistance. Extensive assessments reveal titanium's ability to maintain structural integrity under cyclic loads and biological conditions, ensuring implant longevity and patient safety.
Corrosion Resistance in the Human Body
Titanium exhibits superior corrosion resistance in the human body due to its stable oxide layer, making it highly biocompatible and ideal for medical implants. Recycled metals, depending on their composition and processing, may contain impurities that compromise corrosion resistance, increasing the risk of implant failure or adverse tissue reactions. Medical-grade titanium's consistent quality and corrosion resistance ensure longevity and safety in implant applications compared to variable recycled metal alloys.
Cost Implications: Economic Analysis of Both Materials
Recycled metal offers significant cost advantages in medical implants due to lower raw material expenses and reduced manufacturing energy consumption, making it an economically viable option for budget-sensitive healthcare providers. Titanium, while more expensive upfront, provides superior biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and longevity, potentially lowering long-term costs associated with implant replacements and complications. A comprehensive economic analysis must weigh initial cost savings from recycled metals against the durability and performance benefits of titanium to determine the most cost-effective material choice in medical implant applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Recycled metal reduces environmental impact by minimizing mining waste and lowering energy consumption compared to primary metal extraction, offering a sustainable alternative in medical implant production. Titanium, prized for its biocompatibility and durability, is energy-intensive to extract and process, raising concerns about its sustainability despite superior performance in implants. Incorporating recycled metals into titanium alloy production could balance sustainability goals with the mechanical and biomedical advantages required for long-lasting medical implants.
Regulatory Approval and Safety Standards
Recycled metal used in medical implants must undergo stringent testing to meet regulatory approval standards set by bodies such as the FDA and EMA, ensuring biocompatibility and absence of contaminants. Titanium, favored for its corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, consistently meets global safety standards with fewer concerns about trace impurities. The regulatory pathway for titanium implants is typically more straightforward due to extensive clinical data supporting their long-term safety and efficacy in medical applications.
Future Trends and Innovations in Implant Material Science
Emerging advancements in implant material science emphasize the integration of recycled metals and titanium to enhance biocompatibility and sustainability in medical implants. Innovations such as additive manufacturing and surface modification techniques are enabling the development of customized titanium alloys with improved osseointegration and corrosion resistance, while recycled metals offer cost-effective and eco-friendly alternatives without compromising mechanical properties. Research trends prioritize combining recycled metal composites with titanium to achieve optimized strength-to-weight ratios and promote circular economy principles in medical device production.
Infographic: Recycled metal vs Titanium for Medical implant
 azmater.com
azmater.com