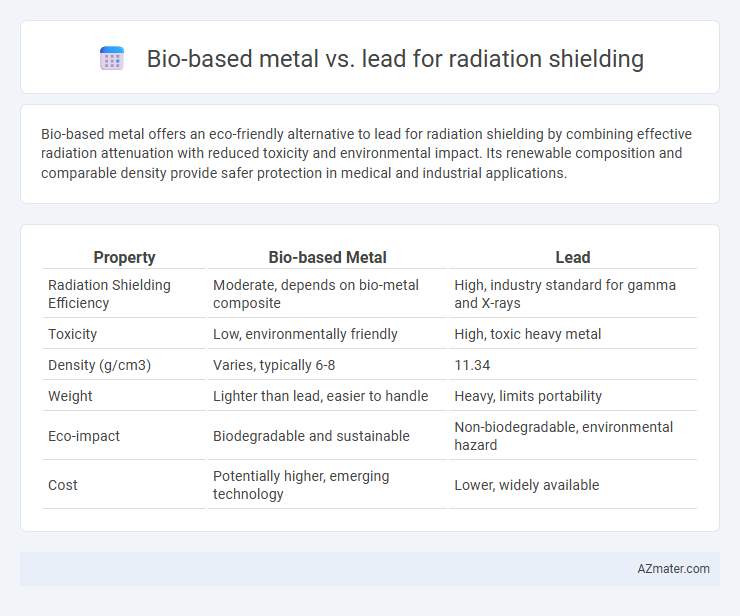
Bio-based metal offers an eco-friendly alternative to lead for radiation shielding by combining effective radiation attenuation with reduced toxicity and environmental impact. Its renewable composition and comparable density provide safer protection in medical and industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bio-based Metal | Lead |
|---|---|---|
| Radiation Shielding Efficiency | Moderate, depends on bio-metal composite | High, industry standard for gamma and X-rays |
| Toxicity | Low, environmentally friendly | High, toxic heavy metal |
| Density (g/cm3) | Varies, typically 6-8 | 11.34 |
| Weight | Lighter than lead, easier to handle | Heavy, limits portability |
| Eco-impact | Biodegradable and sustainable | Non-biodegradable, environmental hazard |
| Cost | Potentially higher, emerging technology | Lower, widely available |
Introduction to Radiation Shielding Materials
Bio-based metals for radiation shielding utilize sustainable, non-toxic materials that offer effective attenuation of ionizing radiation with minimal environmental impact. Lead, traditionally used for radiation shields, provides high density and excellent X-ray and gamma-ray attenuation but poses significant health and ecological hazards due to its toxicity and heavy metal contamination. Advances in bio-based composites combining metals with organic polymers demonstrate promising potential for safe, lightweight, and biodegradable radiation shielding alternatives in medical and industrial applications.
Overview of Bio-Based Metal Innovations
Bio-based metal innovations for radiation shielding leverage sustainable materials combined with metal matrices to enhance protection while reducing environmental impact compared to traditional lead shields. Researchers focus on integrating bio-derived polymers and fibers with metals like aluminum or magnesium to create lightweight, non-toxic, and efficient shields suitable for medical and nuclear applications. These advanced composites exhibit superior radiation attenuation, improved mechanical properties, and biodegradability, positioning them as viable alternatives to hazardous lead-based materials.
Traditional Use of Lead in Radiation Shields
Lead has been the traditional material of choice for radiation shields due to its high density and excellent attenuation properties against gamma rays and X-rays. Its widespread use spans medical imaging, nuclear power plants, and industrial radiography, providing reliable protection for both equipment and personnel. Despite lead's effectiveness, concerns about toxicity and environmental impact drive the exploration of bio-based metal alternatives that offer safer and more sustainable radiation shielding solutions.
Comparative Effectiveness: Bio-Based Metal vs Lead
Bio-based metals offer a sustainable alternative to lead in radiation shielding, providing comparable attenuation properties while significantly reducing environmental toxicity. Lead's high density and atomic number make it highly effective for radiation protection, but bio-based metals such as bismuth or tungsten composites show promising results with lower ecological and health risks. Comparative studies indicate that bio-based metals achieve efficient gamma and X-ray absorption, making them viable for applications demanding both performance and sustainability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bio-based metal composites used in radiation shields offer significant environmental advantages over traditional lead, as they are derived from renewable resources and exhibit lower toxicity during production and disposal. Lead-based shields pose substantial risks due to lead's high toxicity, potential for soil and water contamination, and challenges in recycling, which contribute to long-term environmental harm. Utilizing bio-based metals enhances sustainability by reducing hazardous waste and carbon footprint while maintaining effective radiation shielding properties.
Health and Safety Considerations
Bio-based metals used for radiation shielding offer significant health and safety advantages compared to traditional lead shields, primarily due to their non-toxic composition and reduced environmental hazards. Unlike lead, which poses risks of lead poisoning and requires careful handling and disposal, bio-based materials minimize exposure to heavy metal contaminants and are often biodegradable or more sustainable. Their lower toxicity enhances workplace safety during manufacturing, installation, and disposal, making them a preferable alternative in medical and industrial radiation applications.
Weight and Flexibility in Application
Bio-based metals used for radiation shielding offer significantly reduced weight compared to traditional lead, enhancing ease of handling and transportation in medical and industrial applications. These materials provide superior flexibility, allowing for customizable shapes and conformal coverage, which lead's rigidity cannot match. The combination of lightweight properties and adaptable form factors makes bio-based metals increasingly preferred for ergonomic and efficient radiation protection solutions.
Cost Analysis and Economic Feasibility
Bio-based metal composites for radiation shielding offer a competitive cost advantage compared to traditional lead shields, primarily due to lower raw material expenses and reduced environmental compliance costs. The lightweight nature of bio-based metals decreases transportation and installation costs, enhancing overall economic feasibility for large-scale applications. Long-term cost savings are achieved through improved recyclability and significantly lower health and environmental liabilities associated with bio-based alternatives.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Bio-based metal radiation shields offer a sustainable alternative to traditional lead shields while meeting stringent regulatory standards such as NRC (Nuclear Regulatory Commission) and FDA (Food and Drug Administration) requirements. These bio-based materials demonstrate compliance with environmental regulations like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals), minimizing toxic exposure risks associated with lead. Manufacturers adopting bio-based metals ensure adherence to radiation attenuation standards including ANSI N43.3 and ISO 4037, guaranteeing effective protection without compromising safety or environmental sustainability.
Future Trends and Industry Adoption
Bio-based metals for radiation shielding are emerging as sustainable alternatives to traditional lead, driven by increasing environmental regulations and health concerns associated with lead toxicity. Advances in material science enable bio-based composites to achieve comparable attenuation properties while reducing weight and environmental impact, attracting growing interest from medical, nuclear, and aerospace industries. Industry adoption is expected to accelerate as research improves durability and cost-effectiveness, aligning with global trends toward eco-friendly and health-conscious radiation protection solutions.
Infographic: Bio-based metal vs Lead for Radiation Shield
 azmater.com
azmater.com