Carbon steel pipes offer higher tensile strength and flexibility, making them ideal for high-pressure applications. Cast iron pipes provide excellent corrosion resistance and durability but are more brittle and prone to cracking under impact.
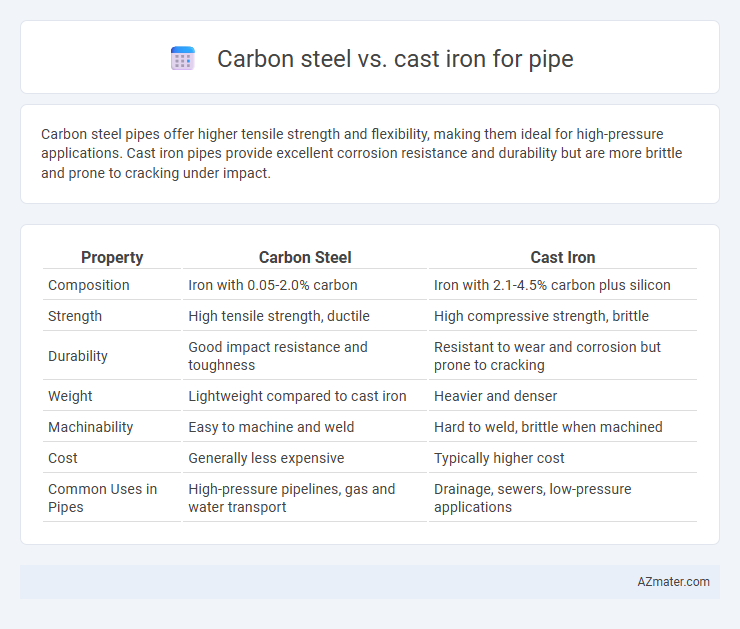
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Steel | Cast Iron |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Iron with 0.05-2.0% carbon | Iron with 2.1-4.5% carbon plus silicon |
| Strength | High tensile strength, ductile | High compressive strength, brittle |
| Durability | Good impact resistance and toughness | Resistant to wear and corrosion but prone to cracking |
| Weight | Lightweight compared to cast iron | Heavier and denser |
| Machinability | Easy to machine and weld | Hard to weld, brittle when machined |
| Cost | Generally less expensive | Typically higher cost |
| Common Uses in Pipes | High-pressure pipelines, gas and water transport | Drainage, sewers, low-pressure applications |
Introduction to Carbon Steel and Cast Iron Pipes
Carbon steel pipes, made from an alloy of iron and carbon, offer high tensile strength and excellent durability, making them suitable for high-pressure applications such as oil and gas transportation. Cast iron pipes, composed primarily of iron with a higher carbon content, are known for their corrosion resistance and rigidity, commonly used in water and sewage systems. Both materials serve distinct industrial needs based on their mechanical properties and cost-efficiency.
Chemical Composition and Structure Differences
Carbon steel pipes primarily consist of iron with a varying carbon content typically between 0.05% and 0.25%, resulting in a finer grain structure and higher tensile strength compared to cast iron. Cast iron contains 2-4% carbon along with 1-3% silicon, which leads to a brittle, graphite-flake microstructure that reduces ductility but enhances compressive strength and corrosion resistance. The lower carbon content and more uniform ferrite-pearlite matrix in carbon steel allow for better weldability and impact resistance, making it more suitable for high-pressure piping applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Carbon steel pipes exhibit higher tensile strength and better ductility compared to cast iron, making them more suitable for high-pressure applications. Cast iron pipes have superior compressive strength and excellent resistance to corrosion and wear, but they are more brittle and prone to cracking under stress. The choice between carbon steel and cast iron pipes depends on the required balance between toughness, flexibility, and durability in specific mechanical environments.
Corrosion Resistance: Carbon Steel vs Cast Iron
Carbon steel pipes exhibit moderate corrosion resistance but are prone to rust when exposed to moisture and corrosive environments without proper protective coatings. Cast iron pipes offer better natural corrosion resistance due to their higher carbon content and the formation of a protective oxide layer, which helps reduce rust over time. However, cast iron can still corrode in acidic or highly chlorinated environments, making protective linings essential for long-term durability.
Durability and Longevity in Piping Systems
Carbon steel pipes offer superior durability with high tensile strength and resistance to impact, making them ideal for high-pressure applications in piping systems. Cast iron pipes exhibit excellent corrosion resistance and longevity in low-pressure, non-corrosive environments but are more brittle and prone to cracking under stress. The longevity of carbon steel pipes often exceeds that of cast iron in industrial settings due to better flexibility and easier maintenance.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Carbon steel pipes generally offer a lower initial cost compared to cast iron, making them more economical for large-scale projects where budget constraints are critical. The durability and corrosion resistance of carbon steel reduce maintenance expenses over time, providing better cost efficiency in the long term. Cast iron pipes, while more expensive upfront, may incur higher repair and replacement costs due to their brittleness and susceptibility to rust, impacting overall economic feasibility.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Carbon steel pipes offer easier installation due to their lighter weight and higher flexibility compared to cast iron, which is more brittle and requires specialized handling to avoid cracking. Maintenance of carbon steel pipes demands regular inspection for corrosion, especially in environments with moisture or chemicals, while cast iron pipes are more resistant to corrosion but prone to cracking and chipping over time. Both materials require specific joining techniques--welding or threading for carbon steel and gasketed joints or lead joints for cast iron--to ensure leak-proof systems.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Carbon steel pipes are extensively used in high-pressure applications such as oil and gas transportation, power plants, and structural frameworks due to their strength, durability, and flexibility. Cast iron pipes are preferred in water and sewage systems, plumbing, and drainage infrastructure for their corrosion resistance and longevity in low-pressure environments. Both materials serve critical roles in construction, industrial piping, and municipal utilities, with carbon steel favored for heavy-duty industrial use and cast iron for underground and waste-handling applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon steel pipes demonstrate lower environmental impact due to higher recyclability and reduced energy consumption in manufacturing compared to cast iron. Cast iron production generates more carbon emissions and involves mining processes that lead to greater habitat disruption. Choosing carbon steel supports sustainability goals by minimizing resource extraction and enhancing lifecycle recyclability.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Piping Needs
Carbon steel pipes offer high tensile strength and excellent weldability, making them ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications in industrial settings. Cast iron pipes provide superior corrosion resistance and noise-dampening qualities, suited for water distribution and drainage systems where longevity and quiet operation are priorities. Selecting between carbon steel and cast iron depends on factors like pressure requirements, environmental exposure, and maintenance expectations to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Infographic: Carbon steel vs Cast iron for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com