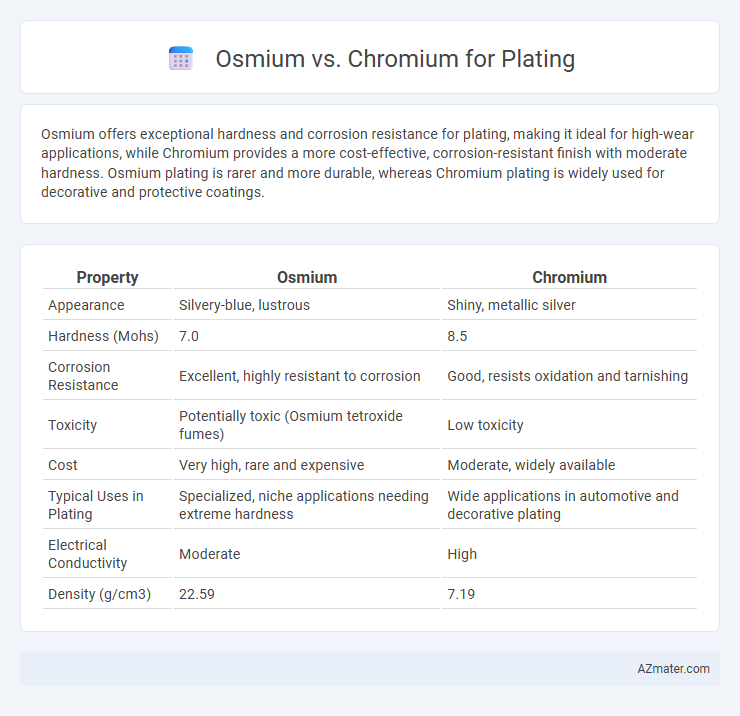
Osmium offers exceptional hardness and corrosion resistance for plating, making it ideal for high-wear applications, while Chromium provides a more cost-effective, corrosion-resistant finish with moderate hardness. Osmium plating is rarer and more durable, whereas Chromium plating is widely used for decorative and protective coatings.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Osmium | Chromium |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Silvery-blue, lustrous | Shiny, metallic silver |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 7.0 | 8.5 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, highly resistant to corrosion | Good, resists oxidation and tarnishing |
| Toxicity | Potentially toxic (Osmium tetroxide fumes) | Low toxicity |
| Cost | Very high, rare and expensive | Moderate, widely available |
| Typical Uses in Plating | Specialized, niche applications needing extreme hardness | Wide applications in automotive and decorative plating |
| Electrical Conductivity | Moderate | High |
| Density (g/cm3) | 22.59 | 7.19 |
Introduction to Osmium and Chromium Plating
Osmium and chromium are two distinct metals commonly used in plating for their hardness and corrosion resistance. Osmium plating offers exceptional durability and a unique blue-gray sheen, making it ideal for high-wear applications and fine electronics. Chromium plating is widely favored for its bright, reflective finish and excellent scratch resistance, commonly applied in automotive, tools, and decorative industries.
Chemical Properties Comparison
Osmium exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance and is one of the densest elements, making it highly durable for plating applications where wear resistance is critical. Chromium offers excellent hardness and forms a stable, protective oxide layer that prevents tarnishing and enhances corrosion resistance. While both metals provide protective coatings, osmium's superior chemical inertness contrasts with chromium's versatility and widespread use in decorative and industrial plating.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Osmium plating offers superior durability and exceptional wear resistance due to its extremely high hardness and chemical inertness, making it ideal for applications requiring long-lasting protection. Chromium plating is also durable and resistant to corrosion but tends to wear down faster under heavy abrasion compared to osmium. The dense atomic structure of osmium gives it a significant edge in maintaining surface integrity over extended periods, especially in harsh environments.
Corrosion Resistance
Osmium plating offers superior corrosion resistance compared to chromium, making it ideal for applications requiring extreme durability in harsh environments. Osmium's dense atomic structure creates an exceptionally hard, chemically inert surface that resists oxidation and wear better than chromium. Chromium plating, while effective against rust and corrosion, tends to degrade faster under acidic or high-moisture conditions relative to osmium.
Aesthetic Appeal and Finish
Osmium plating offers a unique deep-blue to bluish-silver finish with exceptional hardness and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for high-end decorative applications where durability and a rare metallic sheen are desired. Chromium plating provides a bright, mirror-like silver finish highly valued for its reflective quality and resistance to tarnishing, commonly used in automotive and hardware industries for a sleek, modern aesthetic. While chromium delivers a classic shiny appeal, osmium's distinct coloration and superior wear resistance create a luxury finish well-suited for premium accessories and fine jewelry.
Industrial Applications
Osmium offers exceptional hardness and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for high-wear industrial applications such as electrical contacts and wear-resistant coatings. Chromium provides excellent adhesion and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in automotive and aerospace industries for decorative and anti-corrosive plating. While osmium plating ensures superior durability in extreme environments, chromium remains the standard for large-scale industrial use due to its availability and versatility.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Osmium plating commands a significantly higher cost due to its extreme rarity and complex extraction process, making it less accessible for widespread industrial use. Chromium, sourced abundantly as a by-product of mining chromite ore, offers a cost-effective and readily available alternative for plating applications. The price disparity and better supply chain infrastructure favor chromium as the preferred choice for durable, corrosion-resistant coatings in commercial and manufacturing sectors.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Osmium plating offers exceptional corrosion resistance with lower toxicity risks compared to hexavalent chromium, which is highly carcinogenic and environmentally hazardous due to its solubility and persistence in water systems. Chromium plating processes often release toxic hexavalent chromium compounds, posing significant occupational health risks and requiring stringent environmental regulations to minimize soil and water contamination. Osmium's rarity and potential toxicity in powdered form necessitate careful handling, but its plating process generates fewer harmful emissions, making it a more sustainable choice for specialized applications where environmental impact and worker safety are critical.
Maintenance and Longevity
Osmium plating offers exceptional corrosion resistance and hardness, significantly reducing maintenance frequency compared to chromium plating, which can tarnish and corrode over time. Osmium's dense atomic structure provides superior durability, extending the lifespan of plated items under harsh environmental conditions. Chromium plating, although more common and cost-effective, often requires regular polishing and reapplication to maintain its appearance and protective qualities.
Choosing the Right Metal for Plating
Selecting the right metal for plating depends on desired durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic finish; osmium offers exceptional hardness and a brilliant, long-lasting shine but is rare and costly, while chromium provides excellent corrosion resistance, affordability, and a sleek, reflective surface ideal for automotive and industrial applications. Osmium plating excels in wear resistance and conductivity, making it suitable for specialized electronics, whereas chromium plating is widely used for decorative purposes and protection against tarnish. Evaluating factors such as environmental exposure, budget constraints, and intended use helps determine whether osmium or chromium plating is the optimal choice.
Infographic: Osmium vs Chromium for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com