Indium roofing sheets offer superior corrosion resistance and enhanced thermal conductivity compared to zinc, making them ideal for harsh environmental conditions. Zinc roofing sheets provide excellent durability and natural patina formation, ensuring long-lasting protection with lower upfront costs.
Table of Comparison
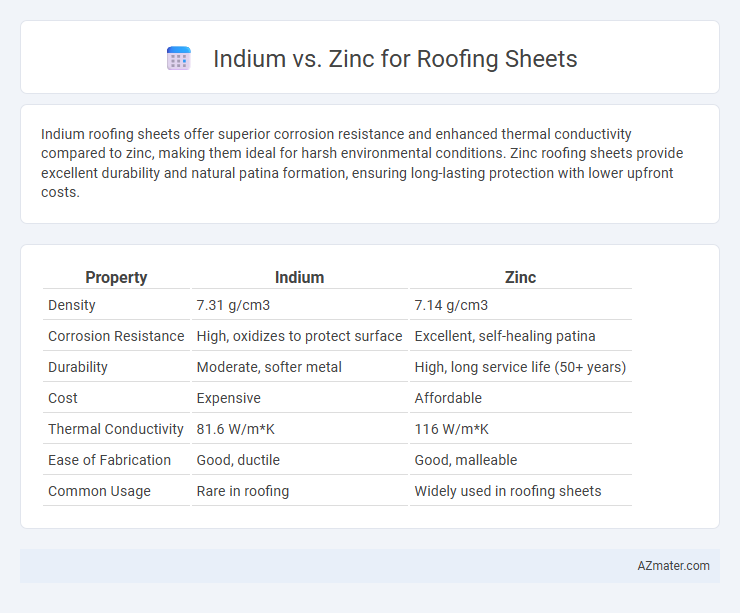
| Property | Indium | Zinc |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 7.31 g/cm3 | 7.14 g/cm3 |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, oxidizes to protect surface | Excellent, self-healing patina |
| Durability | Moderate, softer metal | High, long service life (50+ years) |
| Cost | Expensive | Affordable |
| Thermal Conductivity | 81.6 W/m*K | 116 W/m*K |
| Ease of Fabrication | Good, ductile | Good, malleable |
| Common Usage | Rare in roofing | Widely used in roofing sheets |
Introduction to Indium and Zinc Roofing Sheets
Indium roofing sheets offer exceptional corrosion resistance, enhanced durability, and superior malleability, making them ideal for complex architectural designs and long-lasting roof protection. Zinc roofing sheets provide natural self-healing properties, environmental sustainability, and impressive longevity, often lasting over 50 years with minimal maintenance. Both materials excel in lightweight construction and aesthetic versatility, supporting sustainable building practices with distinct advantages for different roofing needs.
Chemical Properties: Indium vs Zinc
Indium exhibits excellent corrosion resistance due to its stable oxide layer, maintaining durability in various environmental conditions, whereas zinc forms a protective but more reactive zinc oxide layer that can alter over time. Indium's melting point of 156.6degC is significantly lower than zinc's 419.5degC, affecting thermal stability in roofing applications. The chemical inertness of indium offers superior resistance to oxidation compared to zinc, which can undergo gradual degradation through galvanic corrosion in moist or acidic environments.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Indium roofing sheets offer exceptional corrosion resistance and a lifespan exceeding 50 years, making them highly durable in harsh environmental conditions. Zinc roofing sheets provide natural self-healing properties and can last between 40 to 60 years with minimal maintenance. Both metals excel in longevity, but Indium's superior resistance to oxidation gives it an edge in extended durability for roofing applications.
Corrosion Resistance in Roofing Applications
Indium roofing sheets offer superior corrosion resistance compared to zinc, making them ideal for harsh environments with high humidity or saline exposure. Indium forms a stable oxide layer that effectively prevents rust and deterioration over time, whereas zinc can corrode more quickly in acidic or polluted atmospheres. This enhanced durability of indium roofing significantly extends the lifespan and reduces maintenance costs in roofing applications.
Cost Analysis: Indium vs Zinc Roofing
Indium roofing sheets are significantly more expensive than zinc due to the rarity and high extraction costs of indium, typically costing several times more per square foot. Zinc roofing offers a more budget-friendly solution with moderate durability and maintenance costs, making it a popular choice for large-scale projects. Considering long-term investment, zinc roofing balances affordability and lifespan, whereas indium roofing is suited for specialized applications where its unique properties justify the higher initial expenditure.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Indium roofing sheets offer high recyclability and low toxicity, reducing environmental harm compared to traditional metals, while zinc roofing sheets are renowned for their natural corrosion resistance and longevity, which minimizes waste and frequent replacements. Zinc production requires less energy and generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions than indium, making zinc roofing sheets more sustainable for large-scale applications. Both metals contribute to sustainable roofing solutions, but zinc's abundance and eco-friendly lifecycle make it a preferred choice for environmentally conscious construction projects.
Installation Processes and Techniques
Indium roofing sheets require specialized handling due to their softness and malleability, necessitating careful fastening techniques to avoid surface damage and ensure weather-tight seams. Zinc roofing sheets benefit from well-established installation methods like standing seam and interlocking panels, allowing for faster assembly and robust durability. Both materials demand precise thermal expansion accommodation in installation to maintain structural integrity over time.
Aesthetic Differences and Finishing Options
Indium roofing sheets offer a unique metallic luster and a smooth, polished finish that enhances modern architectural aesthetics, while zinc roofing sheets provide a naturally matte surface with a subtle patina that evolves over time, adding character and rustic charm. Indium's ability to achieve vibrant, high-reflective coatings allows for a broader range of color customization and sleek, contemporary finishes compared to zinc's traditional bluish-gray tones and textured appearance. Both metals are compatible with various finishing techniques such as anodizing or powder coating, but indium's superior malleability allows for finer detailing and complex shapes in roofing applications.
Maintenance Requirements Over Time
Indium roofing sheets require minimal maintenance due to their excellent corrosion resistance and self-healing oxide layer that prevents long-term degradation. Zinc roofing sheets, while also corrosion-resistant, may develop a patina over time that protects the metal but can demand occasional cleaning and inspection to manage potential buildup or damage. Both materials offer durable options, but indium's superior resistance reduces maintenance frequency and associated costs over the lifespan of the roofing system.
Which Roofing Material is Best for Your Project?
Indium offers excellent corrosion resistance and superior durability, making it a premium choice for roofing sheets in harsh environments, while zinc provides affordable cost, natural self-healing properties, and a longer lifespan due to its passive oxide layer. For projects prioritizing longevity and environmental sustainability, zinc roofing sheets are often preferred due to their recyclability and proven performance. Indium roofing materials may be better suited for specialized applications requiring exceptional resistance to chemical and atmospheric exposure despite higher costs.
Infographic: Indium vs Zinc for Roofing Sheet
 azmater.com
azmater.com