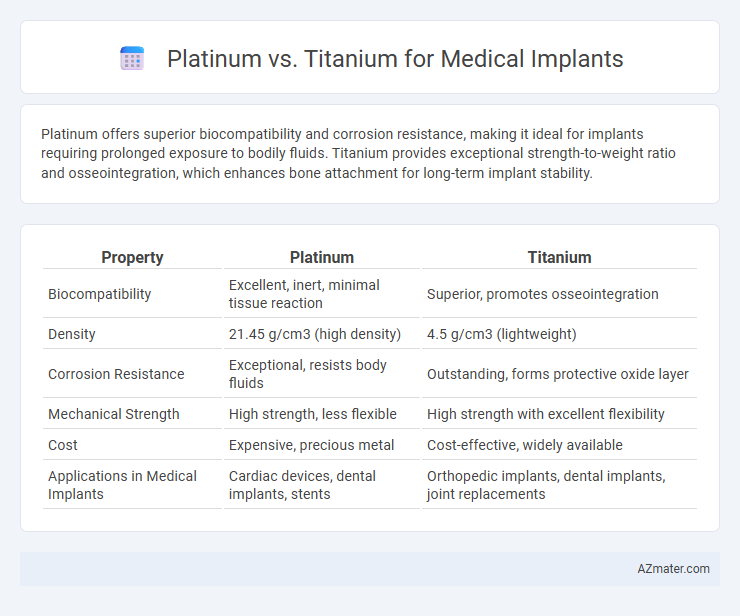
Platinum offers superior biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for implants requiring prolonged exposure to bodily fluids. Titanium provides exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and osseointegration, which enhances bone attachment for long-term implant stability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Platinum | Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Biocompatibility | Excellent, inert, minimal tissue reaction | Superior, promotes osseointegration |
| Density | 21.45 g/cm3 (high density) | 4.5 g/cm3 (lightweight) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Exceptional, resists body fluids | Outstanding, forms protective oxide layer |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength, less flexible | High strength with excellent flexibility |
| Cost | Expensive, precious metal | Cost-effective, widely available |
| Applications in Medical Implants | Cardiac devices, dental implants, stents | Orthopedic implants, dental implants, joint replacements |
Introduction to Medical Implant Materials
Medical implant materials must exhibit biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength to ensure long-term functionality within the human body. Platinum offers excellent corrosion resistance and biocompatibility but is relatively heavy and less mechanically robust compared to titanium. Titanium's superior strength-to-weight ratio, outstanding osseointegration properties, and resistance to bodily fluids make it a preferred choice for various medical implants.
Overview of Platinum and Titanium
Platinum is a dense, corrosion-resistant metal known for its excellent biocompatibility and inert properties, making it ideal for long-term medical implants such as pacemaker electrodes and vascular stents. Titanium features high strength-to-weight ratio, exceptional corrosion resistance due to its oxide layer, and superior osseointegration, commonly used in orthopedic implants and dental fixtures. Both metals offer distinct advantages: platinum excels in electrical conductivity and chemical stability, while titanium provides mechanical strength and bone integration.
Biocompatibility: Platinum vs Titanium
Titanium exhibits superior biocompatibility compared to platinum, with excellent corrosion resistance and the ability to osseointegrate, making it ideal for long-term medical implants. Platinum is inert and highly resistant to corrosion but lacks the bone integration properties that titanium offers. Titanium's biocompatibility reduces inflammatory responses and promotes stable, durable implant performance in orthopedic and dental applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Platinum and titanium exhibit distinct mechanical strengths and durability profiles crucial for medical implants, with titanium offering superior strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional corrosion resistance that enhances long-term implant stability. Titanium's elasticity closely matches human bone, reducing stress shielding and promoting osseointegration, whereas platinum's higher density and lower tensile strength limit its application in load-bearing implants. The durability of titanium alloys in biological environments outperforms platinum by maintaining structural integrity under cyclic loading conditions, making titanium the preferred choice for orthopedic and dental implants.
Corrosion Resistance in Biological Environments
Platinum exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance in biological environments due to its inert nature and resistance to oxidation, making it highly suitable for long-term medical implants. Titanium also offers excellent corrosion resistance, attributed to its stable oxide layer, which provides a protective barrier against bodily fluids and reduces ion release. However, titanium's oxide layer can be compromised under certain conditions, whereas platinum maintains superior stability, ensuring minimal degradation and enhanced biocompatibility in implant applications.
Longevity and Implant Lifespan
Platinum and titanium differ significantly in medical implant longevity, with titanium offering superior corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, leading to longer implant lifespan. Titanium's lightweight and strength properties reduce wear and mechanical failure risks, making it a preferred choice for long-term implants. Platinum, while highly biocompatible, is heavier and less durable under mechanical stress, which may limit its use in implants requiring extended durability.
Allergic Reactions and Patient Safety
Platinum shows excellent biocompatibility with a low incidence of allergic reactions due to its inert nature, making it safe for patients with metal sensitivities. Titanium is widely favored for medical implants because of its superior osseointegration and hypoallergenic properties, reducing the risk of adverse immune responses in patients. Both metals offer high corrosion resistance, but titanium's ability to promote bone growth enhances long-term implant stability and patient safety.
Cost and Availability for Medical Use
Platinum offers superior biocompatibility but comes with higher costs and limited availability, making it less common for widespread medical implant use. Titanium provides an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, lower cost, and abundant availability, which drives its preference in orthopedic and dental implants. The cost-effectiveness and supply stability of titanium support its dominant role in the medical implant market.
Common Clinical Applications
Platinum is primarily utilized in cardiovascular implants due to its excellent corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, making it ideal for pacemaker leads and stents. Titanium, favored for orthopedic implants such as joint replacements and dental implants, offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and osseointegration properties. Both metals exhibit high biocompatibility, but titanium's lighter weight and enhanced mechanical properties expand its use in load-bearing applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Implants
Platinum offers exceptional biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for implants requiring minimal allergic reactions and long-term stability. Titanium provides superior strength-to-weight ratio and promotes osseointegration, enhancing bone bonding and durability in load-bearing implants. Selecting the appropriate material depends on the implant's functional requirements and patient-specific factors, balancing biocompatibility, mechanical performance, and clinical outcomes.
Infographic: Platinum vs Titanium for Medical Implant
 azmater.com
azmater.com