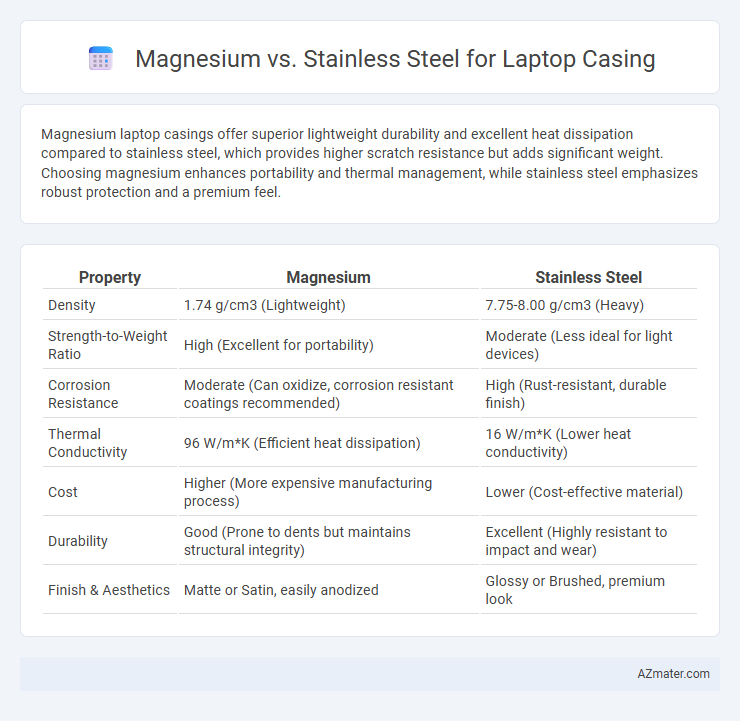
Magnesium laptop casings offer superior lightweight durability and excellent heat dissipation compared to stainless steel, which provides higher scratch resistance but adds significant weight. Choosing magnesium enhances portability and thermal management, while stainless steel emphasizes robust protection and a premium feel.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Magnesium | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.74 g/cm3 (Lightweight) | 7.75-8.00 g/cm3 (Heavy) |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | High (Excellent for portability) | Moderate (Less ideal for light devices) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate (Can oxidize, corrosion resistant coatings recommended) | High (Rust-resistant, durable finish) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 96 W/m*K (Efficient heat dissipation) | 16 W/m*K (Lower heat conductivity) |
| Cost | Higher (More expensive manufacturing process) | Lower (Cost-effective material) |
| Durability | Good (Prone to dents but maintains structural integrity) | Excellent (Highly resistant to impact and wear) |
| Finish & Aesthetics | Matte or Satin, easily anodized | Glossy or Brushed, premium look |
Introduction: Importance of Laptop Casing Materials
Laptop casing materials significantly impact durability, heat dissipation, and overall device weight. Magnesium offers lightweight strength and excellent thermal conductivity, enhancing portability and cooling performance. Stainless steel delivers superior rigidity and scratch resistance but adds considerable weight, affecting comfort during extended use.
Overview of Magnesium and Stainless Steel
Magnesium laptop casings offer a lightweight and durable solution due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and excellent thermal conductivity, making them ideal for portable devices. Stainless steel casings provide superior toughness and scratch resistance with higher density, contributing to increased device weight but enhanced structural integrity and premium feel. Both materials balance durability and aesthetics but cater to different priorities in laptop design, emphasizing portability for magnesium and robustness for stainless steel.
Weight Comparison: Magnesium vs Stainless Steel
Magnesium laptop casings weigh approximately 33-50% less than stainless steel, making magnesium an ideal choice for ultra-lightweight and portable devices. Stainless steel, while offering superior strength and durability, typically adds significant weight, often making laptops heavier by 200-400 grams compared to magnesium equivalents. The reduced weight of magnesium enhances mobility and user comfort without compromising structural integrity, favoring it for premium and travel-focused laptops.
Durability and Strength Factors
Magnesium laptop casings offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, providing durable protection while remaining lightweight and resistant to impacts. Stainless steel casings excel in hardness and corrosion resistance, delivering robust structural integrity but adding significant weight and slightly reduced portability. When prioritizing durability, magnesium balances lightweight resilience, whereas stainless steel ensures superior toughness under heavy mechanical stress.
Thermal Conductivity and Heat Dissipation
Magnesium laptop casings offer superior thermal conductivity, typically around 156 W/mK, enabling efficient heat dissipation and maintaining lower internal temperatures during intensive tasks. Stainless steel, with a much lower thermal conductivity of approximately 16 W/mK, tends to retain heat, potentially leading to thermal throttling and reduced performance. Choosing magnesium improves overall cooling, enhancing device longevity and user comfort during extended use.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Magnesium laptop casings offer a sleek, lightweight finish with excellent design flexibility due to their malleability, allowing for intricate shapes and slim profiles that enhance aesthetic appeal. Stainless steel provides a premium, polished look with superior durability and resistance to scratches, but its rigidity limits complex design options. Choosing between magnesium and stainless steel hinges on whether a laptop prioritizes lightweight elegance or robust, high-end visual durability.
Cost Analysis: Production and Material Expenses
Magnesium laptop casings generally involve higher production costs due to complex casting processes and specialized alloy treatments, while stainless steel offers a cost-effective alternative with lower material expenses but increased machining time. Magnesium alloys provide a favorable strength-to-weight ratio, reducing shipping and handling costs, whereas stainless steel's durability can lower repair and replacement expenses over time. Choosing between magnesium and stainless steel impacts total manufacturing budgets significantly, with magnesium commanding higher upfront investments balanced by potential long-term savings in weight and performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Magnesium laptop casings offer a lighter weight and higher recyclability compared to stainless steel, reducing overall environmental impact by requiring less energy to transport and recycle. Stainless steel, while highly durable and corrosion-resistant, has a higher carbon footprint due to intensive mining and smelting processes that consume significant energy and produce greenhouse gas emissions. Choosing magnesium over stainless steel for laptop casings contributes to sustainability by promoting resource efficiency and minimizing ecological disruption throughout the product lifecycle.
User Experience: Feel and Ergonomics
Magnesium laptop casings offer a lightweight and sturdy feel, enhancing portability without compromising durability, making them ideal for extended use and travel. Stainless steel casings provide a solid, premium heft that delivers a robust and lasting impression but may increase overall weight and reduce comfort during prolonged handling. Ergonomically, magnesium's lighter profile supports better grip and reduces strain, while stainless steel's cooler surface temperature can benefit users in warmer environments.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Best Casing Material
Magnesium laptop casings offer superior lightweight durability and excellent heat dissipation, making them ideal for portable, high-performance devices. Stainless steel casings provide exceptional strength and resistance to corrosion but tend to add significant weight and reduce thermal efficiency. Choosing the best casing material depends on prioritizing either lightweight portability and heat management with magnesium or maximum structural durability with stainless steel.
Infographic: Magnesium vs Stainless Steel for Laptop Casing
 azmater.com
azmater.com