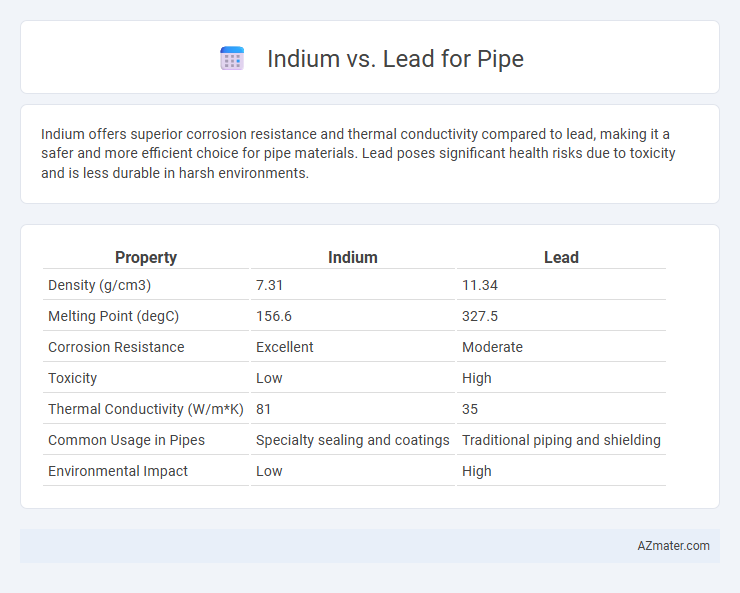
Indium offers superior corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity compared to lead, making it a safer and more efficient choice for pipe materials. Lead poses significant health risks due to toxicity and is less durable in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Indium | Lead |
|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm3) | 7.31 | 11.34 |
| Melting Point (degC) | 156.6 | 327.5 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Toxicity | Low | High |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m*K) | 81 | 35 |
| Common Usage in Pipes | Specialty sealing and coatings | Traditional piping and shielding |
| Environmental Impact | Low | High |
Overview: Indium vs Lead in Pipe Applications
Indium and lead differ significantly in pipe applications due to their material properties; indium offers superior corrosion resistance and non-toxicity, making it ideal for specialized industrial uses such as cryogenics and electronics cooling systems. Lead, while historically widespread in plumbing, poses health risks due to toxicity and is increasingly restricted in potable water systems, though it remains effective in radiation shielding and certain industrial pipe fittings. The choice between indium and lead hinges on balancing safety regulations, thermal conductivity requirements, and environmental impact in pipe material selection.
Physical Properties: Indium and Lead Compared
Indium has a melting point of 156.6degC, significantly higher than lead's melting point of 327.5degC, making lead more suitable for low-temperature applications but indium preferable for moderate heat resistance and flexibility. Indium's density is approximately 7.31 g/cm3, lighter than lead's 11.34 g/cm3, which affects the overall weight of piping systems and ease of installation. Indium exhibits higher ductility and softness, enabling better sealing and deformation without cracking compared to the more brittle and harder lead used in traditional piping.
Corrosion Resistance: Indium vs Lead Pipes
Indium pipes exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to lead pipes due to indium's ability to form a stable oxide layer that protects against oxidizing environments and chemical degradation. Lead pipes, while historically used, are more prone to corrosion and leaching, which can compromise water quality and safety. The enhanced corrosion resistance of indium makes it a preferable choice for applications requiring longevity and environmental safety.
Environmental Impact and Safety Concerns
Indium pipes present significantly lower toxicity risks compared to lead pipes, as lead exposure is linked to severe health problems including neurological damage and developmental delays. From an environmental perspective, indium is less harmful since it does not leach into soil and groundwater, unlike lead which contaminates ecosystems and poses long-term ecological hazards. The use of indium in piping reduces the risk of bioaccumulation and pollution, aligning with stricter environmental safety regulations and promoting safer water supply systems.
Cost Analysis: Indium Pipes vs Lead Pipes
Indium pipes typically cost significantly more than lead pipes due to the scarcity and higher production expenses of indium, with prices often exceeding lead by several times per kilogram. Lead pipes remain economically advantageous for large-scale applications given their lower material cost and widespread availability, despite environmental and health concerns. The cost analysis must also factor in long-term expenses such as maintenance and regulatory compliance, where lead pipes may incur additional liabilities and remediation costs.
Installation and Maintenance Differences
Indium exhibits excellent corrosion resistance and malleability, making it easier to install in complex pipe fittings compared to lead, which is heavier and more brittle. Indium's non-toxic properties reduce health risks during installation and ongoing maintenance, whereas lead pipes require strict handling precautions due to lead contamination concerns. Maintenance of indium pipes often demands less frequent inspection and replacement, as lead pipes tend to degrade faster and pose environmental hazards.
Longevity and Durability in Piping Systems
Indium exhibits superior corrosion resistance and lower toxicity compared to lead, making it a longer-lasting and safer option for piping systems. Lead pipes are prone to corrosion and degradation over time, which can lead to contamination and structural failures. The durability of indium alloys enhances the lifespan of pipes, reducing maintenance and replacement costs in long-term applications.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Indium pipes face fewer regulatory restrictions than lead pipes, which are heavily regulated due to lead's toxicity and health risks, especially in potable water systems under standards like the Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA). Indium offers compliance advantages, aligning with RoHS and REACH directives by avoiding hazardous substance classification, making it preferable in environments with strict environmental and safety standards. Lead pipes require extensive testing, certification, and often replacement mandates, increasing compliance costs in municipal and industrial applications.
Industry Uses: Indium vs Lead Piping
Indium piping is favored in high-tech industries such as electronics and aerospace for its excellent corrosion resistance and low melting point, enabling precise welding and reliable performance in specialized applications. Lead pipes, historically used in plumbing and construction, face declining use due to toxicity concerns and stricter environmental regulations limiting their application in potable water systems. Modern industry trends prioritize indium alloys for safe, durable, and environmentally friendly piping solutions in advanced manufacturing and niche sectors.
Future Trends and Alternative Materials
Indium's rising prominence as a safer alternative to lead in pipe applications is driven by increasing regulatory restrictions on lead due to its toxicity and environmental hazards. Future trends favor the integration of indium alloys and other non-toxic metals such as stainless steel, PEX, and copper, which offer enhanced durability and corrosion resistance. Innovations in nanotechnology and sustainable materials research continue to propel the development of lead-free piping solutions for safer infrastructure and public health.
Infographic: Indium vs Lead for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com