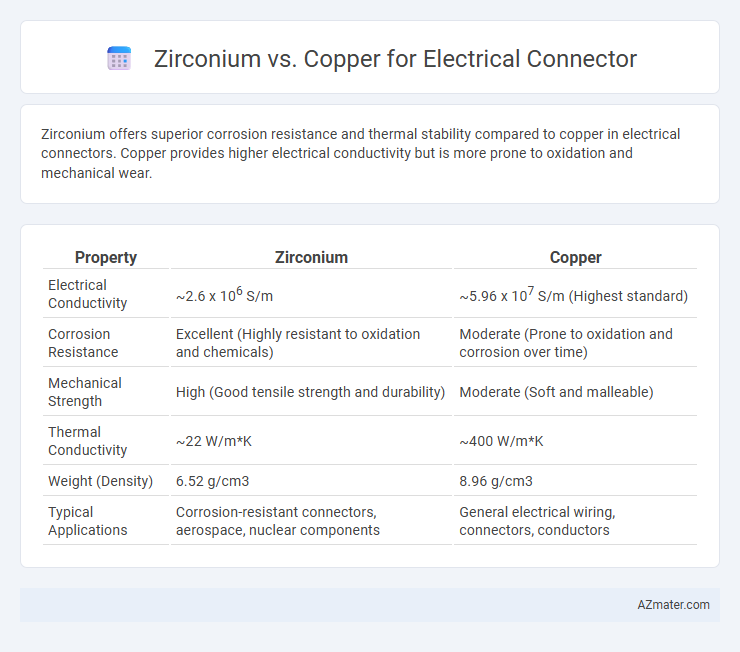
Zirconium offers superior corrosion resistance and thermal stability compared to copper in electrical connectors. Copper provides higher electrical conductivity but is more prone to oxidation and mechanical wear.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zirconium | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | ~2.6 x 106 S/m | ~5.96 x 107 S/m (Highest standard) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (Highly resistant to oxidation and chemicals) | Moderate (Prone to oxidation and corrosion over time) |
| Mechanical Strength | High (Good tensile strength and durability) | Moderate (Soft and malleable) |
| Thermal Conductivity | ~22 W/m*K | ~400 W/m*K |
| Weight (Density) | 6.52 g/cm3 | 8.96 g/cm3 |
| Typical Applications | Corrosion-resistant connectors, aerospace, nuclear components | General electrical wiring, connectors, conductors |
Overview: Zirconium vs Copper in Electrical Connectors
Zirconium and copper serve distinct roles in electrical connectors due to their different electrical and mechanical properties. Copper offers high electrical conductivity around 5.96 x 10^7 S/m, making it ideal for efficient current flow, while zirconium provides superior corrosion resistance and strength under extreme environments but with lower conductivity. Selecting between zirconium and copper hinges on specific application needs, balancing conductivity requirements with durability and environmental factors in connector performance.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Copper exhibits significantly higher electrical conductivity than zirconium, making it the preferred choice for electrical connectors where efficient current flow is critical. While copper's conductivity is approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m, zirconium offers much lower conductivity, around 2.7 x 10^6 S/m, which limits its effectiveness in high-performance electrical applications. This pronounced difference directly influences connector efficiency, signal integrity, and overall electrical resistance in conductive paths.
Thermal Conductivity Differences
Zirconium has a significantly lower thermal conductivity, approximately 22 W/m*K, compared to copper's high thermal conductivity of around 400 W/m*K, making copper far superior in heat dissipation for electrical connectors. The efficient thermal management of copper helps maintain connector stability and reduces the risk of overheating in high-current applications. Zirconium's lower thermal conductivity limits its use to niche applications where corrosion resistance is prioritized over heat transfer.
Corrosion Resistance: Which is Better?
Zirconium exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to copper, especially in aggressive environments containing chlorides, acids, or seawater, making it ideal for high-performance electrical connectors exposed to harsh conditions. Copper, while highly conductive, is prone to oxidation and tarnishing, which can impair connector longevity and performance in corrosive atmospheres. Choosing zirconium over copper enhances connector durability, reducing maintenance costs and ensuring reliable electrical conductivity in corrosive applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Zirconium offers superior mechanical strength compared to copper, providing enhanced resistance to deformation and wear in electrical connectors. Its durability under high-stress conditions and corrosion resistance extends connector lifespan, making it ideal for demanding environments. Copper, while highly conductive, tends to have lower mechanical strength and may degrade faster under mechanical stress and environmental exposure.
Cost Analysis: Zirconium vs Copper
Zirconium electrical connectors generally exhibit higher material costs compared to copper due to zirconium's rarity and complex extraction processes, impacting initial investment significantly. Copper remains the more cost-effective choice, benefiting from widespread availability and established supply chains that lower overall expenses in manufacturing and maintenance. Total cost analysis must also consider zirconium's superior corrosion resistance and durability, which can reduce long-term replacement and operational costs despite its premium price.
Weight and Density Considerations
Zirconium offers a lower density of approximately 6.52 g/cm3 compared to copper's higher density of 8.96 g/cm3, resulting in lighter electrical connectors when using zirconium. The reduced weight of zirconium connectors enhances applications requiring minimized mass without compromising structural integrity. Copper's greater density contributes to heavier connectors, which may affect the overall system weight but provides excellent electrical conductivity.
Applications in Different Industries
Zirconium offers superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability, making it ideal for electrical connectors in aerospace and marine industries where durability under extreme conditions is critical. Copper, known for its exceptional electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness, is predominantly used in telecommunications, automotive, and consumer electronics for efficient signal and power transmission. Industries requiring robust performance in harsh environments often favor zirconium, while copper remains the standard for general-purpose electrical connector applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Zirconium offers superior corrosion resistance and longer lifespan in electrical connectors, reducing waste and frequent replacements compared to copper. Copper mining and processing generate higher greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption, whereas zirconium extraction has a comparatively lower environmental footprint. Selecting zirconium over copper enhances sustainability by minimizing resource depletion and promoting durability in electrical infrastructure.
Choosing the Right Material for Electrical Connectors
Zirconium offers superior corrosion resistance and maintains conductivity under high-temperature conditions, making it ideal for electrical connectors in harsh environments. Copper, known for its excellent electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness, remains the preferred choice for standard electrical connectors in residential and commercial applications. Selecting the right material depends on balancing conductivity requirements, environmental factors, and budget constraints to ensure optimal connector performance and longevity.
Infographic: Zirconium vs Copper for Electrical Connector
 azmater.com
azmater.com