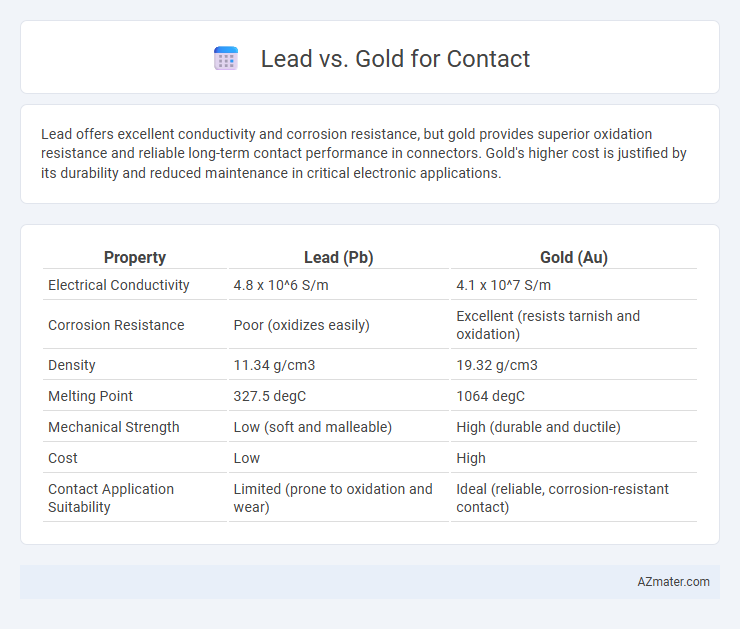
Lead offers excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance, but gold provides superior oxidation resistance and reliable long-term contact performance in connectors. Gold's higher cost is justified by its durability and reduced maintenance in critical electronic applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lead (Pb) | Gold (Au) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 4.8 x 10^6 S/m | 4.1 x 10^7 S/m |
| Corrosion Resistance | Poor (oxidizes easily) | Excellent (resists tarnish and oxidation) |
| Density | 11.34 g/cm3 | 19.32 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 327.5 degC | 1064 degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Low (soft and malleable) | High (durable and ductile) |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Contact Application Suitability | Limited (prone to oxidation and wear) | Ideal (reliable, corrosion-resistant contact) |
Introduction to Contact Materials: Lead vs Gold
Lead and gold are common materials used in electrical contacts, each offering distinct advantages for conductivity and durability. Gold provides excellent corrosion resistance and stable low contact resistance, making it ideal for sensitive electronic applications. Lead, while less conductive and prone to oxidation, is valued for its cost-effectiveness and mechanical compliance in specific contact mechanisms.
Electrical Conductivity: Lead vs Gold
Gold exhibits significantly higher electrical conductivity than lead, with gold's conductivity around 45.2 million Siemens per meter (MS/m), compared to lead's much lower value of approximately 4.8 MS/m. This substantial difference makes gold a preferred choice for electrical contacts where efficient current flow and minimized energy loss are critical. Despite gold's superior conductivity, lead is less commonly used in contacts due to its inferior electrical performance and higher resistance.
Corrosion Resistance in Lead and Gold Contacts
Lead contacts exhibit moderate corrosion resistance due to the formation of a protective oxide layer, but they are prone to degradation in acidic or oxidizing environments, impacting electrical conductivity over time. Gold contacts offer superior corrosion resistance, maintaining excellent conductivity by resisting oxidation and tarnish even in harsh conditions. This makes gold the preferred choice for critical applications requiring long-lasting, reliable electrical connections.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Gold offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for long-term contact durability and stable performance in harsh environments. Lead, while softer and more malleable, exhibits lower mechanical strength and higher susceptibility to wear and deformation under repetitive contact stress. The higher hardness and fatigue resistance of gold contacts ensure prolonged service life and reliable functionality in precision electronic applications.
Cost Comparison: Lead vs Gold Contacts
Lead contacts typically incur lower costs compared to gold contacts due to the use of more economical materials and simpler manufacturing processes. Gold contacts, favored for their superior conductivity and corrosion resistance, demand higher expenses from the price of gold and specialized production techniques. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals lead contacts as budget-friendly options for basic applications, while gold contacts justify their premium cost in high-reliability electronic environments.
Health and Environmental Considerations
Lead exposure in contact materials poses significant health risks due to its toxicity, causing neurological damage and developmental issues. Gold, being inert and biocompatible, presents minimal health hazards and resists corrosion, reducing environmental contamination. Choosing gold for contacts ensures safer human interaction and lowers ecological impact compared to lead-based alternatives.
Industrial Applications of Lead and Gold Contacts
Lead contacts are widely used in industrial applications for their excellent corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for heavy-duty electrical connectors and switchgear in harsh environments. Gold contacts, preferred in high-precision and low-resistance applications, provide superior conductivity and oxidation resistance, crucial for reliable performance in aerospace, telecommunications, and medical equipment. The choice between lead and gold contacts depends on factors such as electrical conductivity requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints within industrial systems.
Suitability for High-Frequency and High-Current Uses
Lead contacts excel in high-current applications due to their excellent conductivity and resistance to electrical arcing, making them suitable for heavy-duty switches and relays. Gold contacts, while offering superior corrosion resistance and reliable low-level signal transmission, are better suited for high-frequency signals where minimal signal loss and stable contact resistance are critical. For high-frequency and high-current uses, lead is preferred for handling large currents, whereas gold is optimized for high-frequency signal integrity and durability in low-current scenarios.
Performance in Extreme Conditions
Lead contacts exhibit superior performance in extreme conditions due to their excellent resistance to corrosion and lower electrical resistance at high temperatures, which ensures reliable conductivity and durability. Gold contacts maintain stable electrical performance by resisting oxidation and tarnishing even under high humidity and aggressive environments, making them ideal for low voltage and signal applications. Both metals excel in specific scenarios: lead is preferred for heavy-duty, high-current circuits in harsh environments, while gold is favored for precision and reliability in sensitive electronic components exposed to varying extremes.
Summary: Choosing Between Lead and Gold for Contacts
Selecting between Lead and Gold for contacts depends on targeting priorities and campaign goals, with Lead suited for acquiring potential clients showing interest, and Gold tailored for nurturing high-value, loyal customers. Lead contacts provide opportunities for conversion through initial engagement metrics, while Gold contacts emphasize long-term relationship management and retention strategies. Optimal contact segmentation leverages Lead data to expand reach, whereas Gold data supports maximizing lifetime customer value and personalized marketing.
Infographic: Lead vs Gold for Contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com