Tool steel electrodes offer superior wear resistance and durability in EDM processes, while copper electrodes provide excellent electrical conductivity and faster machining speeds. Choosing between tool steel and copper depends on the specific requirements of precision, surface finish, and production volume.
Table of Comparison
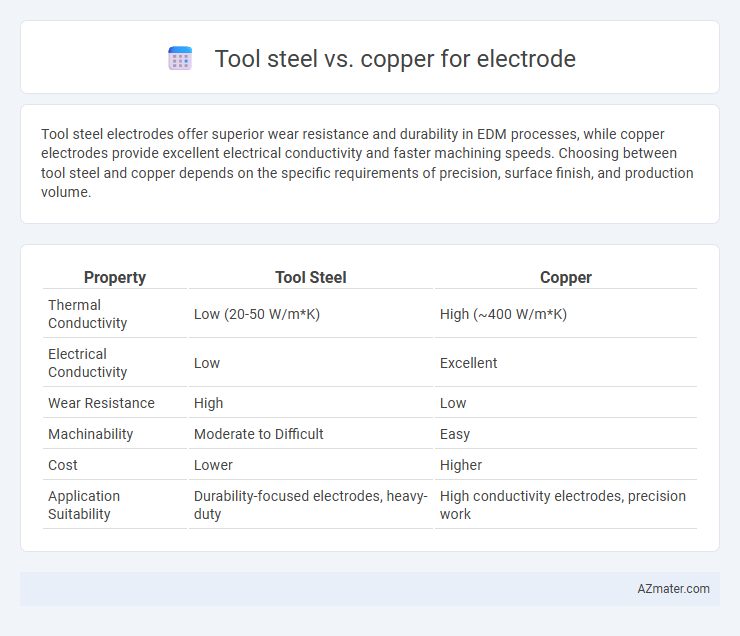
| Property | Tool Steel | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (20-50 W/m*K) | High (~400 W/m*K) |
| Electrical Conductivity | Low | Excellent |
| Wear Resistance | High | Low |
| Machinability | Moderate to Difficult | Easy |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Application Suitability | Durability-focused electrodes, heavy-duty | High conductivity electrodes, precision work |
Introduction to Electrode Materials
Tool steel electrodes offer high hardness and wear resistance, making them ideal for machining and EDM processes requiring precise shaping and durability. Copper electrodes provide excellent electrical conductivity and thermal efficiency, enhancing spark stability and reducing wear during electrical discharge machining. Selecting between tool steel and copper depends on the specific requirements for conductivity, wear resistance, and machining precision in electrode applications.
Overview of Tool Steel Electrodes
Tool steel electrodes offer superior hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability compared to copper electrodes, making them ideal for high-precision electrical discharge machining (EDM). These electrodes maintain dimensional accuracy under intense machining conditions and provide enhanced durability for complex shapes and fine finishes. The alloy composition in tool steel boosts its mechanical strength and corrosion resistance, ensuring consistent performance in demanding industrial applications.
Overview of Copper Electrodes
Copper electrodes offer superior electrical and thermal conductivity compared to tool steel, making them ideal for precision welding and EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) applications. Their high conductivity ensures efficient heat dissipation, reducing wear and extending electrode life during repetitive cycles. Copper's excellent machinability and resistance to arc erosion further enhance performance, especially in high-speed manufacturing environments.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Copper exhibits significantly higher electrical conductivity than tool steel, typically around 59.6 x 10^6 S/m compared to tool steel's approximate range of 1 to 10 x 10^6 S/m depending on alloy composition. This superior conductivity makes copper electrodes highly efficient for electrical applications by reducing energy losses and heat generation during operation. Tool steel's lower conductivity is compensated by its mechanical strength and wear resistance but results in decreased electrical efficiency in electrode performance.
Thermal Conductivity Differences
Tool steel electrodes exhibit significantly lower thermal conductivity, typically around 20-45 W/m*K, compared to copper electrodes, which offer high thermal conductivity values exceeding 300 W/m*K. This substantial difference affects heat dissipation during electrical discharge machining (EDM), with copper providing faster cooling and reduced thermal deformation of both the electrode and the workpiece. Consequently, copper electrodes enhance machining precision and electrode lifespan by minimizing thermal-related wear and distortion.
Wear Resistance and Durability
Tool steel electrodes exhibit superior wear resistance and durability compared to copper electrodes, making them ideal for high-stress machining and EDM applications. The hardness of tool steel enables it to withstand abrasive forces and maintain shape integrity under prolonged use, while copper electrodes, despite excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, tend to erode faster. Tool steel's enhanced lifespan reduces electrode replacement frequency, contributing to cost efficiency in manufacturing processes.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Tool steel electrodes offer lower initial material costs compared to copper, making them a budget-friendly choice for applications with moderate performance requirements. Copper electrodes, while more expensive, provide superior electrical conductivity and wear resistance, which can reduce long-term operational costs by minimizing replacement frequency. Availability of tool steel is generally higher and more consistent worldwide, whereas copper electrodes may face supply fluctuations due to metal market volatility and demand in electrical industries.
Applications in EDM and Welding
Tool steel electrodes offer superior durability and wear resistance in EDM due to their hardness, enabling precise machining of hard materials and prolonged tool life; copper electrodes excel in thermal conductivity, providing efficient heat dissipation and faster machining cycles. In welding, tool steel electrodes are preferred for high-strength joints requiring toughness and resistance to deformation, while copper electrodes are ideal for applications demanding excellent electrical conductivity and minimal contamination in spot welding. Selecting between tool steel and copper electrodes depends on the specific EDM or welding application requirements, balancing factors like thermal properties, electrical conductivity, and mechanical strength.
Maintenance and Lifespan
Tool steel electrodes offer superior wear resistance and longer lifespan compared to copper electrodes, reducing maintenance frequency in industrial applications. Copper electrodes, while providing excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, tend to wear faster and require more frequent surface reconditioning to maintain welding quality. Choosing tool steel enhances durability and lowers overall maintenance costs in high-stress machining and welding environments.
Choosing the Right Electrode Material
Selecting the right electrode material depends on factors like electrical conductivity, wear resistance, and thermal stability. Copper electrodes excel in electrical and thermal conductivity, making them ideal for applications requiring efficient heat dissipation and low resistance. Tool steel electrodes offer superior hardness and durability, preferred in high-wear environments where mechanical strength and longevity are critical.
Infographic: Tool steel vs Copper for Electrode
 azmater.com
azmater.com