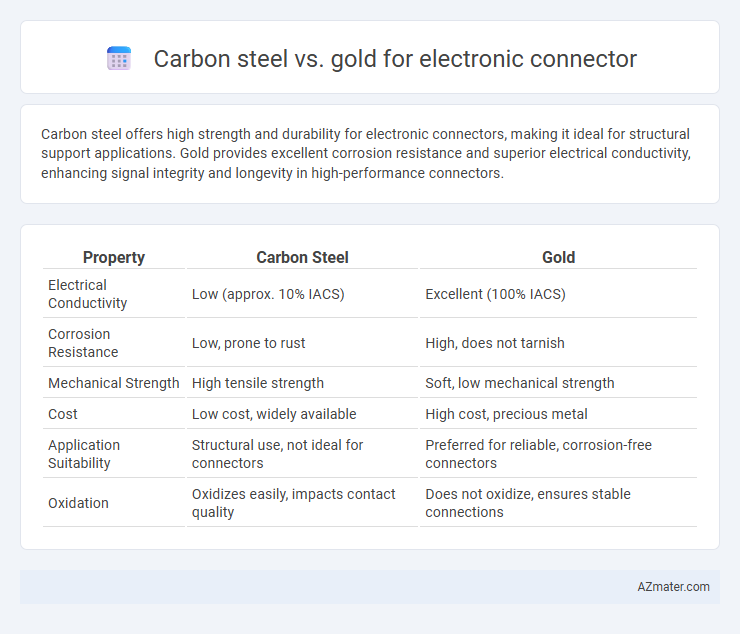
Carbon steel offers high strength and durability for electronic connectors, making it ideal for structural support applications. Gold provides excellent corrosion resistance and superior electrical conductivity, enhancing signal integrity and longevity in high-performance connectors.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Steel | Gold |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Low (approx. 10% IACS) | Excellent (100% IACS) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low, prone to rust | High, does not tarnish |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength | Soft, low mechanical strength |
| Cost | Low cost, widely available | High cost, precious metal |
| Application Suitability | Structural use, not ideal for connectors | Preferred for reliable, corrosion-free connectors |
| Oxidation | Oxidizes easily, impacts contact quality | Does not oxidize, ensures stable connections |
Introduction to Electronic Connector Materials
Carbon steel and gold are key materials used in electronic connectors due to their distinct properties. Carbon steel offers high mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for structural components, while gold provides excellent electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion, ensuring reliable signal transmission. The choice between carbon steel and gold depends on balancing durability, performance, and budget considerations in electronic connector design.
Overview of Carbon Steel in Electronics
Carbon steel offers a cost-effective and robust solution for electronic connectors, providing high tensile strength and excellent wear resistance essential for durable and reliable connections. Its magnetic properties and ease of machining make it suitable for various connector applications, though it requires protective coatings to prevent corrosion in electronic environments. The material's conductivity is lower than gold, but carbon steel's mechanical resilience and affordability make it a preferred choice in many industrial and consumer electronics applications.
Gold as a Material in Electronic Connectors
Gold is widely preferred in electronic connectors due to its excellent electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion, ensuring reliable signal transmission and long-term durability. Unlike carbon steel, gold does not oxidize, which prevents contact degradation and maintains low contact resistance, critical for high-performance electronic applications. Its malleability allows for precise plating on connector surfaces, enhancing both conductivity and mechanical stability in sensitive electronic devices.
Electrical Conductivity: Carbon Steel vs Gold
Gold exhibits significantly higher electrical conductivity than carbon steel, making it an ideal choice for electronic connectors requiring reliable signal transmission and minimal resistance. While carbon steel offers mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness, its lower conductivity can lead to signal loss and increased heat generation. The superior corrosion resistance of gold further preserves conductivity over time, ensuring consistent electrical performance in demanding applications.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Gold offers superior corrosion resistance compared to carbon steel, maintaining excellent conductivity and reliability even in harsh environmental conditions. Carbon steel is prone to oxidation and rust, which can degrade electrical performance over time without protective coatings. Choosing gold-plated connectors enhances durability and signal integrity, especially in high-humidity or corrosive industrial applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Carbon steel offers superior mechanical strength compared to gold, making it highly resistant to bending and deformation under stress in electronic connectors. Gold, while significantly softer, excels in corrosion resistance and provides stable conductivity over time, enhancing the durability of connectors in corrosive environments. The combination of carbon steel's robust structural integrity and gold's protective surface layer often results in connectors that balance strength with long-term reliability.
Cost Analysis: Carbon Steel vs Gold
Carbon steel offers a significantly lower cost compared to gold for electronic connectors, making it a budget-friendly choice for large-scale manufacturing. While gold provides superior corrosion resistance and conductivity, its high market price drastically increases overall production expenses. Cost analysis reveals carbon steel excels in affordability but may incur additional maintenance costs, whereas gold connectors justify their premium price through enhanced durability and performance.
Application Suitability in Electronics
Carbon steel offers excellent mechanical strength and cost efficiency, making it suitable for electronic connectors in applications where durability and structural integrity are priorities but high conductivity is less critical. Gold excels in electronic connectors requiring superior corrosion resistance and exceptional electrical conductivity, ideal for high-frequency and precision signal transmission in sensitive electronic devices. The choice between carbon steel and gold depends on balancing performance requirements with budget constraints, with gold typically reserved for high-reliability, low-resistance contacts.
Lifespan and Maintenance Considerations
Carbon steel connectors offer a robust lifespan but require regular maintenance to prevent rust and corrosion, impacting long-term reliability. Gold connectors provide excellent corrosion resistance and stable conductivity, resulting in a longer lifespan with minimal maintenance requirements. Choosing gold connectors significantly reduces signal degradation and maintenance costs in high-performance electronic applications.
Choosing the Right Material for Electronic Connectors
Selecting the right material for electronic connectors involves balancing conductivity, durability, and cost; gold offers excellent corrosion resistance and superior electrical conductivity, making it ideal for high-performance applications despite its higher price. Carbon steel provides strength and cost-effectiveness but requires surface treatment like plating to prevent oxidation and ensure reliable signal transmission. Considering environmental conditions and electrical requirements helps determine whether gold's premium properties or carbon steel's economic benefits best suit the connector application.
Infographic: Carbon steel vs Gold for Electronic connector
 azmater.com
azmater.com