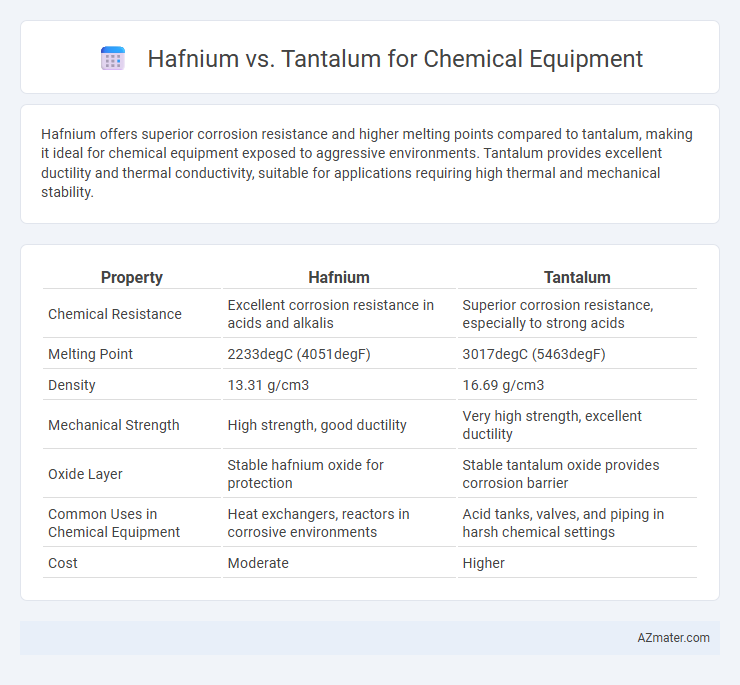
Hafnium offers superior corrosion resistance and higher melting points compared to tantalum, making it ideal for chemical equipment exposed to aggressive environments. Tantalum provides excellent ductility and thermal conductivity, suitable for applications requiring high thermal and mechanical stability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hafnium | Tantalum |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent corrosion resistance in acids and alkalis | Superior corrosion resistance, especially to strong acids |
| Melting Point | 2233degC (4051degF) | 3017degC (5463degF) |
| Density | 13.31 g/cm3 | 16.69 g/cm3 |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength, good ductility | Very high strength, excellent ductility |
| Oxide Layer | Stable hafnium oxide for protection | Stable tantalum oxide provides corrosion barrier |
| Common Uses in Chemical Equipment | Heat exchangers, reactors in corrosive environments | Acid tanks, valves, and piping in harsh chemical settings |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Introduction to Hafnium and Tantalum in Chemical Equipment
Hafnium and tantalum are critical materials in chemical equipment due to their exceptional corrosion resistance and high melting points, making them ideal for harsh chemical environments. Hafnium's strong resistance to acids and ability to maintain structural integrity at elevated temperatures make it suitable for reactor components and heat exchangers. Tantalum is favored for its superb chemical inertness, particularly against strong acids like hydrochloric and sulfuric acid, which is essential for tanks, piping, and valves in chemical processing.
Key Material Properties: Hafnium vs Tantalum
Hafnium exhibits excellent corrosion resistance and high melting point, making it ideal for chemical equipment exposed to aggressive environments and extreme temperatures. Tantalum's superior ductility and exceptional resistance to acids enhance its performance in highly corrosive chemical processes. Both materials offer outstanding chemical stability, but hafnium's higher thermal stability and tantalum's enhanced mechanical flexibility dictate their specific suitability for different chemical equipment applications.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison for Chemical Applications
Hafnium exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to tantalum in aggressive chemical environments due to its stable oxide layer that protects against acids and alkalis. Tantalum also offers excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in sulfuric and hydrochloric acids, but hafnium's resistance extends more effectively to oxidizing agents and high-temperature corrosion scenarios. For chemical equipment exposed to harsh oxidizing chemicals and elevated temperatures, hafnium provides enhanced durability and longevity over tantalum.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Hafnium exhibits superior corrosion resistance and mechanical strength compared to tantalum, making it ideal for chemical equipment exposed to aggressive environments. Tantalum's high ductility and excellent resistance to acids provide durability, but hafnium's higher melting point and robust hardness enhance its longevity under extreme mechanical stress. The combination of hafnium's toughness and tantalum's chemical stability ensures optimized performance in demanding industrial applications.
Chemical Compatibility and Reactivity
Hafnium exhibits excellent chemical resistance in highly acidic and oxidative environments, making it suitable for corrosive chemical equipment. Tantalum offers superior stability against strong acids like hydrochloric and sulfuric acid, ensuring minimal reactivity and extended durability in chemical processing. Both metals demonstrate low reactivity, but tantalum's exceptional corrosion resistance often makes it the preferred choice for chemical compatibility in aggressive industrial applications.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Hafnium and tantalum exhibit distinct cost profiles impacting chemical equipment selection, with hafnium generally commanding higher prices due to its limited availability and complex extraction processes. Tantalum offers a more cost-effective option while maintaining excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, crucial for chemical reactors and heat exchangers. Economic considerations also weigh the lifecycle costs, where hafnium's superior performance in extreme chemical environments may justify its premium price through reduced maintenance and longer service life.
Availability and Supply Chain Factors
Hafnium is less abundant and primarily obtained as a byproduct of zirconium processing, leading to a more limited and complex supply chain compared to tantalum. Tantalum is found in more concentrated deposits in countries like the Democratic Republic of Congo, Australia, and Brazil, facilitating a more established and reliable supply chain. Supply risk for hafnium is higher due to its dependency on zirconium refining, while tantalum benefits from broader global mining operations and diversified sourcing options.
Common Industrial Uses for Hafnium and Tantalum
Hafnium is commonly used in chemical equipment for its exceptional resistance to corrosion and high-temperature stability, making it ideal for reactor control rods and heat exchangers in nuclear and chemical industries. Tantalum is prized for its excellent corrosion resistance and bio-compatibility, frequently utilized in chemical reactors, condenser tubes, and surgical implants. Both metals are critical in industrial applications requiring durability in harsh chemical environments, with hafnium preferred for nuclear-related processes and tantalum favored for highly corrosive chemical processing.
Maintenance, Fabrication, and Longevity Concerns
Hafnium offers superior corrosion resistance compared to tantalum, making it ideal for chemical equipment exposed to aggressive acids and high temperatures, thereby reducing maintenance frequency and costs. Tantalum, while easier to fabricate due to its ductility and weldability, may require more frequent inspections and replacements under extreme conditions because of its susceptibility to stress corrosion cracking. Choosing hafnium ensures longer equipment longevity and lower downtime, although its higher fabrication complexity demands skilled processing techniques.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Hafnium and Tantalum
Choosing between hafnium and tantalum for chemical equipment depends on the application's specific needs: hafnium offers superior corrosion resistance in high-temperature acidic environments, while tantalum excels in highly corrosive media due to its exceptional chemical inertness. Tantalum's lower cost and availability make it a preferred choice for broader industrial use, whereas hafnium's strength and stability at extreme temperatures are critical in specialized processes. Evaluating factors like operating conditions, corrosion resistance, thermal stability, and budget ensures the optimal material selection for durable, efficient chemical equipment.
Infographic: Hafnium vs Tantalum for Chemical Equipment
 azmater.com
azmater.com