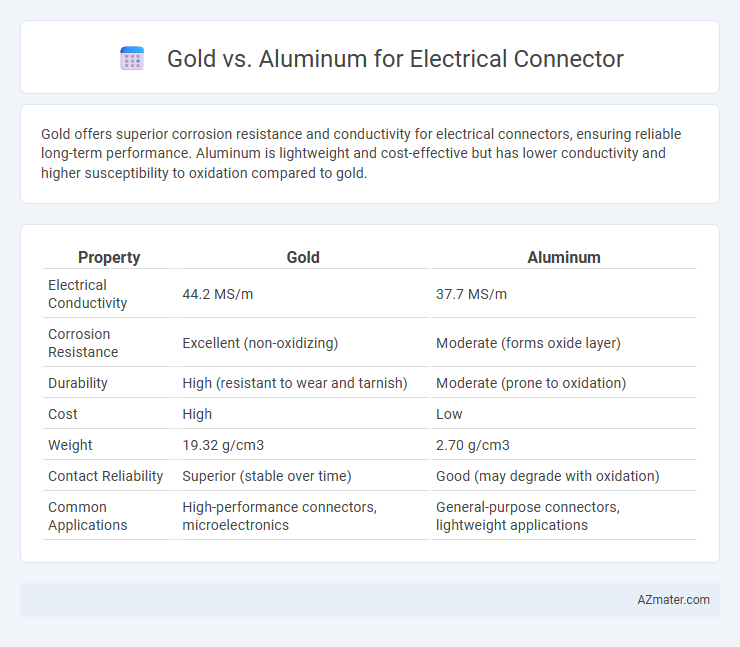
Gold offers superior corrosion resistance and conductivity for electrical connectors, ensuring reliable long-term performance. Aluminum is lightweight and cost-effective but has lower conductivity and higher susceptibility to oxidation compared to gold.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Gold | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 44.2 MS/m | 37.7 MS/m |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (non-oxidizing) | Moderate (forms oxide layer) |
| Durability | High (resistant to wear and tarnish) | Moderate (prone to oxidation) |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Weight | 19.32 g/cm3 | 2.70 g/cm3 |
| Contact Reliability | Superior (stable over time) | Good (may degrade with oxidation) |
| Common Applications | High-performance connectors, microelectronics | General-purpose connectors, lightweight applications |
Introduction: Gold vs Aluminum in Electrical Connectors
Gold offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for reliable electrical connectors in demanding environments. Aluminum, while more cost-effective and lightweight, presents higher electrical resistance and is prone to oxidation, which can compromise connector performance over time. Choosing between gold and aluminum in electrical connectors hinges on balancing performance requirements with budget considerations.
Material Properties Comparison
Gold offers superior electrical conductivity and exceptional corrosion resistance, making it ideal for reliable, long-term electrical connectors in high-performance applications. Aluminum, while lighter and more cost-effective, has lower conductivity and is prone to oxidation, which can impair connector performance over time. The choice between gold and aluminum depends on the balance between durability, conductivity requirements, and budget constraints in electrical connector design.
Conductivity and Electrical Performance
Gold exhibits superior conductivity with a resistivity of approximately 2.44 uO*cm, ensuring minimal signal loss and stable electrical performance in connectors. Aluminum, with higher resistivity around 2.82 uO*cm, tends to have greater voltage drops and potential oxidation issues, which can degrade connector reliability over time. The excellent corrosion resistance and consistent conductivity of gold make it the preferred choice for high-performance and low-resistance electrical connectors.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Gold offers superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminum, as it does not oxidize or tarnish over time, ensuring stable electrical conductivity in connectors. Aluminum connectors are prone to oxidation, forming an insulating oxide layer that degrades performance and reduces longevity. Consequently, gold-plated connectors provide enhanced durability and reliable long-term electrical connections in harsh environments.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Gold offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent conductivity in electrical connectors, but aluminum provides higher mechanical strength and better resistance to wear and deformation under mechanical stress. Aluminum connectors withstand more flexing and vibration cycles without fracturing, making them ideal for applications requiring durability and robust mechanical performance. The choice depends on balancing gold's conductivity and corrosion resistance with aluminum's enhanced mechanical resilience and cost-effectiveness.
Cost Analysis: Gold vs Aluminum
Gold connectors offer superior conductivity and corrosion resistance but come with significantly higher material costs compared to aluminum. Aluminum connectors provide a cost-effective alternative due to lower raw material prices and lighter weight, although they may require protective coatings to enhance durability and conductivity. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and lifecycle performance, is crucial when comparing gold and aluminum for electrical connector applications.
Applications in Modern Electronics
Gold offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for high-performance connectors in modern electronics such as smartphones, aerospace systems, and medical devices. Aluminum, while lighter and more cost-effective, is commonly used in large-scale or less critical applications like power distribution and consumer electronics where weight savings are prioritized. The choice between gold and aluminum connectors depends on balancing conductivity requirements, environmental exposure, and cost constraints in contemporary electronic design.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gold offers exceptional corrosion resistance and conductivity, reducing maintenance needs and extending connector lifespan, which supports sustainability despite the environmental costs of gold mining such as habitat disruption and high energy consumption. Aluminum is abundant, lightweight, and requires less energy to mine and process, lowering its carbon footprint, but it suffers from higher oxidation rates and lower conductivity, potentially increasing waste due to more frequent replacement. Choosing between gold and aluminum for electrical connectors involves balancing the durable performance and recyclability of gold with the environmentally lighter production impact of aluminum.
Industry Standards and Compliance
Gold electrical connectors offer superior corrosion resistance and excellent conductivity, meeting stringent industry standards such as UL and IEC for high-reliability applications. Aluminum connectors, while lightweight and cost-effective, require surface treatments to comply with ASTM standards for corrosion protection and electrical performance. Compliance with RoHS and REACH regulations is critical for both materials to ensure environmental and safety standards are met in global manufacturing and assembly processes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material
Gold offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for critical and high-reliability connectors. Aluminum provides a lightweight and cost-effective alternative, suitable for applications where weight and budget constraints are paramount but may require protective coatings to prevent oxidation. Selecting between gold and aluminum connectors depends on balancing performance requirements, environmental conditions, and overall system cost.
Infographic: Gold vs Aluminum for Electrical Connector
 azmater.com
azmater.com