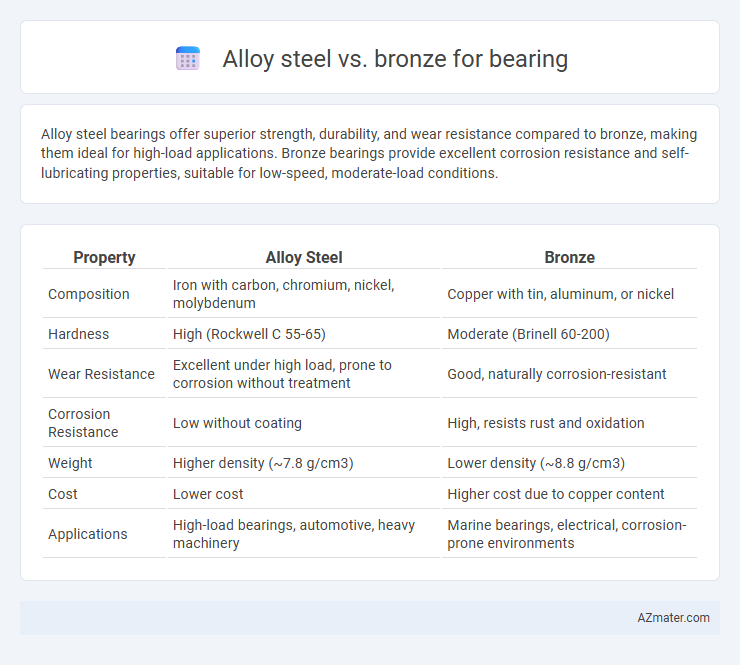
Alloy steel bearings offer superior strength, durability, and wear resistance compared to bronze, making them ideal for high-load applications. Bronze bearings provide excellent corrosion resistance and self-lubricating properties, suitable for low-speed, moderate-load conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Alloy Steel | Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Iron with carbon, chromium, nickel, molybdenum | Copper with tin, aluminum, or nickel |
| Hardness | High (Rockwell C 55-65) | Moderate (Brinell 60-200) |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent under high load, prone to corrosion without treatment | Good, naturally corrosion-resistant |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low without coating | High, resists rust and oxidation |
| Weight | Higher density (~7.8 g/cm3) | Lower density (~8.8 g/cm3) |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to copper content |
| Applications | High-load bearings, automotive, heavy machinery | Marine bearings, electrical, corrosion-prone environments |
Introduction to Bearing Materials
Alloy steel and bronze are widely used materials for bearing applications, each offering distinct advantages based on their mechanical properties and wear resistance. Alloy steel provides high strength, fatigue resistance, and hardness, making it suitable for heavy-load and high-speed bearings. Bronze, known for its excellent corrosion resistance, low friction coefficient, and good machinability, is often chosen for bearings in applications requiring reduced friction and quieter operation.
Overview of Alloy Steel for Bearings
Alloy steel for bearings is engineered with precise elemental compositions including chromium, nickel, and molybdenum to enhance hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue strength, making it ideal for high-load and high-speed applications. Its superior tensile strength and ability to maintain dimensional stability under thermal stress contribute to extended bearing life and reliability in demanding industrial environments. Alloy steel bearings exhibit excellent corrosion resistance and exceptional resistance to deformation, distinguishing them from bronze-based alternatives in heavy-duty machinery.
Overview of Bronze for Bearings
Bronze for bearings is prized for its excellent frictional properties, corrosion resistance, and ability to embed small particles, which helps prevent damage to the shaft. Common bronze alloys such as phosphor bronze and tin bronze offer high fatigue strength and wear resistance, making them suitable for heavy-load, low-speed applications. This material's self-lubricating attributes reduce maintenance needs and enhance bearing lifespan in harsh or wet environments.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability
Alloy steel exhibits superior tensile strength and fatigue resistance compared to bronze, making it ideal for high-load bearing applications. Bronze offers excellent wear resistance and corrosion resistance, extending durability in harsh environments but with lower overall strength. The choice between alloy steel and bronze bearings depends on the specific mechanical demands, balancing strength with resistance to environmental degradation.
Wear Resistance and Lifespan Comparison
Alloy steel bearings exhibit superior wear resistance due to their high hardness and ability to maintain strength under heavy loads, resulting in longer service life in demanding applications. Bronze bearings, while softer, offer excellent conformability and embedability, reducing wear in environments where debris is present but generally have shorter lifespan under heavy or high-speed conditions. The choice between alloy steel and bronze bearings depends on balancing wear resistance requirements with operational conditions to optimize lifespan.
Load Capacity and Performance
Alloy steel bearings offer superior load capacity due to their high tensile strength and hardness, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Bronze bearings provide excellent performance in terms of friction reduction and wear resistance, especially in low-speed or oscillating movements. The choice between alloy steel and bronze depends on the specific operating conditions, with alloy steel excelling in high-load, high-speed environments and bronze preferred for quieter, corrosion-resistant applications.
Corrosion Resistance: Alloy Steel vs Bronze
Bronze exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to alloy steel, especially in marine and highly humid environments where it forms a protective oxide layer that prevents further degradation. Alloy steel, while strong and wear-resistant, is more prone to rust and corrosion without specialized coatings or treatments, limiting its use in corrosive settings. Choosing bronze for bearings ensures longer life and reduced maintenance costs in applications exposed to moisture and corrosive substances.
Maintenance and Lubrication Requirements
Alloy steel bearings demand regular lubrication with high-quality oils or greases to prevent wear and corrosion, ensuring long-term performance under high-load conditions. Bronze bearings exhibit excellent self-lubricating properties, often requiring less frequent maintenance and enabling operation with minimal external lubrication. Both materials benefit from monitoring lubrication levels to extend lifespan, but bronze's inherent oil retention reduces the risk of lubrication failure in harsh environments.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Alloy steel bearings typically offer lower cost and higher load capacity compared to bronze bearings, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications with budget constraints. Bronze bearings, made from copper alloys, tend to be more expensive due to material costs but provide superior corrosion resistance and better performance in low-speed, high-friction environments. Availability of alloy steel bearings is generally higher worldwide, supported by mass production, while bronze bearings may require specialized suppliers or custom orders, influencing lead times and overall project costs.
Best Applications: Selecting the Right Bearing Material
Alloy steel bearings excel in high-load, high-speed applications such as automotive and heavy machinery due to their superior hardness and wear resistance. Bronze bearings are ideal for low-speed, heavy-duty environments like marine and agricultural equipment, offering excellent corrosion resistance and embedding properties. Choosing the right material depends on operating conditions, with alloy steel preferred for durability under stress and bronze favored for lubrication retention and friction reduction.
Infographic: Alloy steel vs Bronze for Bearing
 azmater.com
azmater.com