Iridium offers superior corrosion resistance and durability compared to lead, making it ideal for high-pressure and corrosive pipe applications. Lead pipes are prone to corrosion and pose health risks due to lead leaching, limiting their use in potable water systems.
Table of Comparison
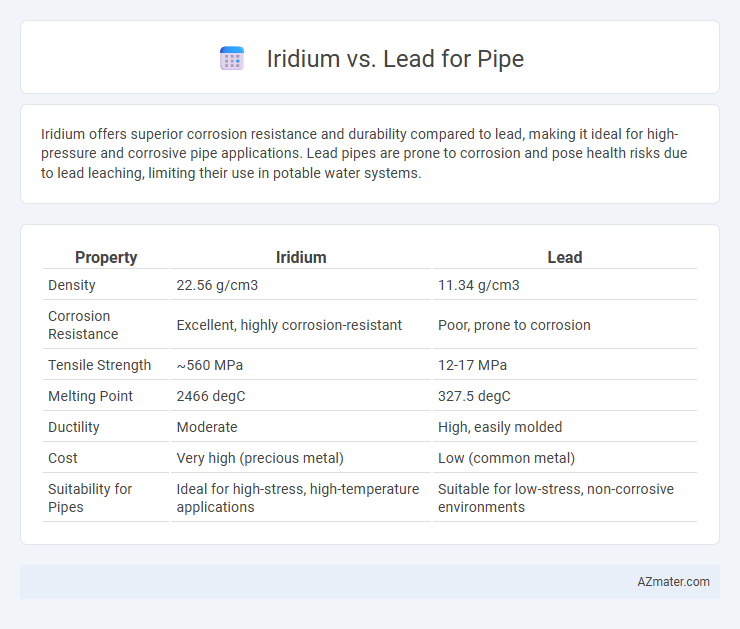
| Property | Iridium | Lead |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 22.56 g/cm3 | 11.34 g/cm3 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, highly corrosion-resistant | Poor, prone to corrosion |
| Tensile Strength | ~560 MPa | 12-17 MPa |
| Melting Point | 2466 degC | 327.5 degC |
| Ductility | Moderate | High, easily molded |
| Cost | Very high (precious metal) | Low (common metal) |
| Suitability for Pipes | Ideal for high-stress, high-temperature applications | Suitable for low-stress, non-corrosive environments |
Introduction to Iridium and Lead Pipes
Iridium pipes offer exceptional corrosion resistance and superior strength compared to traditional lead pipes, making them ideal for high-performance and specialized industrial applications. Lead pipes, historically used for water distribution, are now largely phased out due to health risks associated with lead contamination and their susceptibility to corrosion over time. Advances in iridium pipe manufacturing provide enhanced durability and safety, positioning iridium as a cutting-edge alternative in environments demanding longevity and chemical inertness.
Chemical Properties: Iridium vs Lead
Iridium exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance and inertness due to its high density (22.56 g/cm3) and stable oxidation states, making it highly suitable for pipes exposed to harsh chemical environments. Lead, with a density of 11.34 g/cm3, is more prone to oxidation and corrosion, especially in acidic or alkaline conditions, which limits its durability in piping applications. The chemical inertness of iridium ensures minimal reaction with transported substances, unlike lead, which can leach into fluids and pose health risks.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Iridium pipes exhibit exceptional durability due to their high resistance to corrosion, heat, and wear, significantly surpassing lead in longevity. Lead pipes, while historically common, tend to degrade faster, becoming brittle and prone to leaching harmful substances into water systems. Engineering assessments highlight iridium's superior lifespan, often lasting decades longer than lead, making it a more sustainable and safe choice for long-term piping applications.
Safety and Health Considerations
Iridium pipes offer superior safety and health benefits compared to lead, as iridium is highly resistant to corrosion and bio-inert, preventing toxic metal leaching into water systems. Lead pipes pose significant health risks due to lead's neurotoxicity, which can cause severe developmental and neurological damage upon exposure. Regulatory agencies worldwide have phased out lead pipes to minimize contamination, making iridium a safer alternative for plumbing applications.
Environmental Impact of Iridium and Lead
Iridium pipes exhibit minimal environmental impact due to their inert nature, resisting corrosion and leaching, which prevents soil and water contamination. In contrast, lead pipes pose significant environmental hazards as lead can leach into groundwater and ecosystems, causing toxic contamination harmful to both wildlife and human health. The durability and chemical stability of iridium make it a more sustainable choice compared to the ecological risks associated with lead pipe corrosion and pollution.
Cost Analysis: Iridium Pipes vs Lead Pipes
Iridium pipes, known for their exceptional corrosion resistance and longevity, come with a significantly higher upfront cost compared to lead pipes, which are much cheaper but pose health risks due to lead toxicity. The initial investment in iridium pipes can be justified by lower maintenance expenses and enhanced durability, leading to reduced replacement frequency over time. Lead pipes may offer cost savings initially but often incur higher long-term costs related to health remediation, regulatory compliance, and replacement programs.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Iridium pipes require specialized equipment and skilled technicians for installation due to their high corrosion resistance and unique alloy composition, resulting in longer setup times compared to lead pipes. Lead pipes offer easier installation with simpler tools but demand frequent maintenance and monitoring because of their susceptibility to corrosion and health hazards. Maintenance of iridium pipes is minimal and cost-effective over time, while lead pipes incur higher long-term costs due to regular repairs and potential replacement to ensure safe usage.
Applications in Plumbing and Industry
Iridium offers superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability compared to lead, making it ideal for specialized plumbing applications in aggressive chemical environments and industrial processes requiring durability under extreme conditions. Lead, while historically prevalent in plumbing, is largely restricted due to toxicity concerns but remains in use for certain industrial applications like radiation shielding and soundproofing where its density is advantageous. Choosing iridium over lead enhances safety and longevity in critical plumbing systems within chemical plants, while lead's industrial utility persists despite environmental limitations.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Iridium pipes are rarely used in standard plumbing due to high material costs and limited regulatory approval, whereas lead pipes face stringent restrictions and are banned in many countries under regulations such as the U.S. Safe Drinking Water Act and the EU Drinking Water Directive. Compliance with regulatory standards prioritizes materials like copper, PVC, and PEX, which meet health and safety criteria, contrasting with lead's toxic properties and the scarcity of data supporting iridium's suitability in plumbing. Regulatory bodies emphasize lead-free alternatives to prevent lead contamination, making lead pipes non-compliant while iridium remains largely unregulated but impractical for widespread use.
Future Trends in Pipe Materials
Iridium's exceptional corrosion resistance and strength position it as a potential future material for high-performance pipes in extreme environments, although its high cost limits widespread adoption compared to traditional lead pipes. Lead pipes, widely used historically, face declining usage due to toxicity concerns and regulatory restrictions, driving innovation toward safer alternatives like iridium alloys or composite materials. Emerging trends emphasize sustainability, durability, and health safety, with iridium offering promising advancements in longevity and environmental impact for specialized industrial applications.
Infographic: Iridium vs Lead for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com