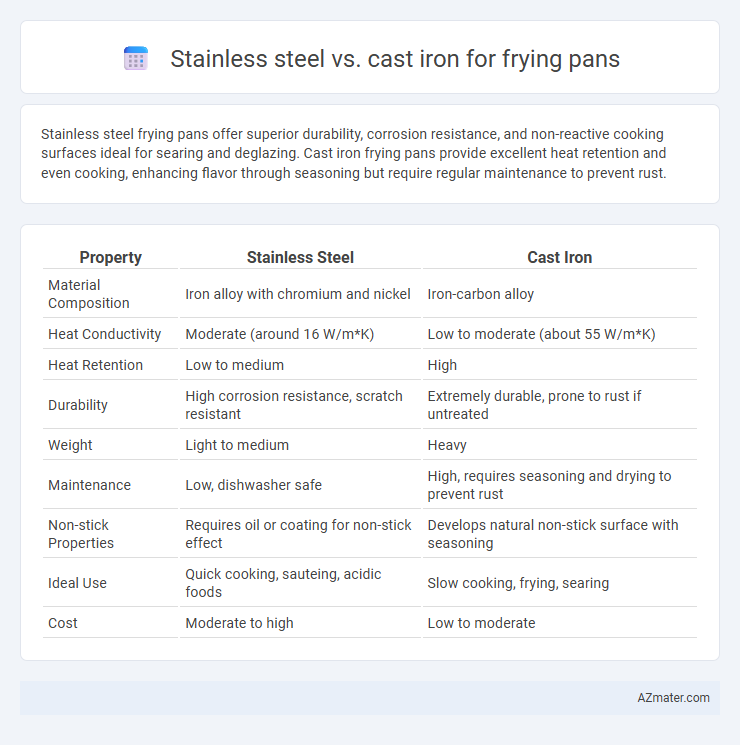
Stainless steel frying pans offer superior durability, corrosion resistance, and non-reactive cooking surfaces ideal for searing and deglazing. Cast iron frying pans provide excellent heat retention and even cooking, enhancing flavor through seasoning but require regular maintenance to prevent rust.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Stainless Steel | Cast Iron |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Iron alloy with chromium and nickel | Iron-carbon alloy |
| Heat Conductivity | Moderate (around 16 W/m*K) | Low to moderate (about 55 W/m*K) |
| Heat Retention | Low to medium | High |
| Durability | High corrosion resistance, scratch resistant | Extremely durable, prone to rust if untreated |
| Weight | Light to medium | Heavy |
| Maintenance | Low, dishwasher safe | High, requires seasoning and drying to prevent rust |
| Non-stick Properties | Requires oil or coating for non-stick effect | Develops natural non-stick surface with seasoning |
| Ideal Use | Quick cooking, sauteing, acidic foods | Slow cooking, frying, searing |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
Introduction: Stainless Steel vs Cast Iron Frying Pans
Stainless steel frying pans offer excellent durability, non-reactive cooking surfaces, and easy maintenance, making them ideal for searing and deglazing. Cast iron frying pans provide superior heat retention and even distribution, perfect for high-heat cooking and developing natural non-stick seasoning over time. Choosing between stainless steel and cast iron depends on cooking style, desired heat performance, and care preferences.
Material Composition and Construction
Stainless steel frying pans consist primarily of iron alloyed with chromium and nickel, offering superior corrosion resistance and a smooth, non-reactive cooking surface. Cast iron pans are made from molten iron poured into molds, providing exceptional heat retention and a naturally non-stick seasoning layer developed through polymerized oils. The multi-ply construction of stainless steel pans often incorporates aluminum or copper cores for improved heat distribution, whereas cast iron pans rely on their mass and thickness for even heating.
Heat Conductivity and Retention
Stainless steel frying pans offer moderate heat conductivity, ensuring even cooking but require thicker bases or aluminum cores to enhance performance. Cast iron excels in heat retention, maintaining consistent temperatures ideal for searing and frying, though it heats more slowly than stainless steel. Choosing between them depends on cooking style: stainless steel pans provide responsive temperature control, while cast iron pans deliver superior heat retention for prolonged cooking.
Cooking Performance and Results
Stainless steel frying pans provide even heat distribution and excellent browning capabilities, making them ideal for searing and deglazing. Cast iron pans excel in heat retention, offering superior heat consistency and enhancing flavor through seasoning, especially for slow-cooked and high-heat dishes. Both materials deliver distinct cooking performance, with stainless steel favored for precision and versatility, while cast iron is prized for its durability and ability to maintain steady temperatures.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Stainless steel frying pans require less maintenance due to their resistance to rust and corrosion, making them easy to clean with regular dish soap and water; they are dishwasher safe and do not need seasoning. Cast iron pans demand more intensive upkeep, including seasoning to maintain a non-stick surface and prevent rust, and must be dried thoroughly after washing to avoid oxidation. While cast iron may require hand washing and occasional re-seasoning, stainless steel offers a more convenient maintenance routine ideal for busy kitchens.
Durability and Longevity
Stainless steel frying pans exhibit superior durability due to their resistance to rust, corrosion, and warping, making them ideal for long-term use in both home and professional kitchens. Cast iron pans, while prone to rust if not properly maintained, offer extreme longevity through their robust material that can withstand high heat and heavy use for decades. Proper seasoning and care significantly extend the lifespan of cast iron pans, whereas stainless steel requires less maintenance to sustain its durability and reliable performance over time.
Weight and Handling Comfort
Stainless steel frying pans are generally lighter, enhancing handling comfort and making them easier to maneuver during cooking. Cast iron pans, while heavier and requiring more effort to lift and handle, offer superior heat retention and even cooking. For those prioritizing ease of use and reduced wrist strain, stainless steel is preferable, whereas cast iron suits users valuing heat distribution over weight.
Price Point and Value for Money
Stainless steel frying pans typically cost more upfront, ranging from $30 to $150 depending on brand and thickness, but offer exceptional durability and low maintenance that enhance long-term value. Cast iron pans are generally more affordable, priced between $15 and $60, providing excellent heat retention and versatility but require seasoning and careful care to prevent rust. Evaluating price point against durability and cooking performance, stainless steel offers superior value for frequent use, while cast iron delivers cost-effective functionality for budget-conscious buyers.
Suitability for Different Cooking Methods
Stainless steel frying pans excel in high-heat searing, sauteing, and deglazing due to their non-reactive surface and even heat distribution, making them ideal for techniques requiring precise temperature control. Cast iron pans retain heat exceptionally well, providing superior performance for frying, slow cooking, and oven use, especially in recipes that benefit from consistent, radiant heat and seasoning buildup. Choosing between stainless steel and cast iron depends on desired cooking methods, with stainless steel favored for quick, high-heat tasks and cast iron preferred for heat retention and versatility in both stovetop and oven applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Frying Pan for Your Kitchen
Stainless steel frying pans offer superior durability, non-reactive cooking surfaces, and excellent heat distribution, making them ideal for versatile, everyday use. Cast iron pans provide exceptional heat retention and natural non-stick properties when properly seasoned, perfect for high-heat searing and slow cooking. Selecting the right frying pan depends on your cooking style, maintenance preference, and heat control needs, with stainless steel favored for ease of use and cast iron preferred for robust heat performance.
Infographic: Stainless steel vs Cast iron for Frying pan
 azmater.com
azmater.com