Titanium offers superior corrosion resistance and strength-to-weight ratio compared to brass, making it ideal for high-performance valve applications in harsh environments. Brass valves provide excellent machinability and cost-effectiveness, suitable for standard water and air flow control systems.
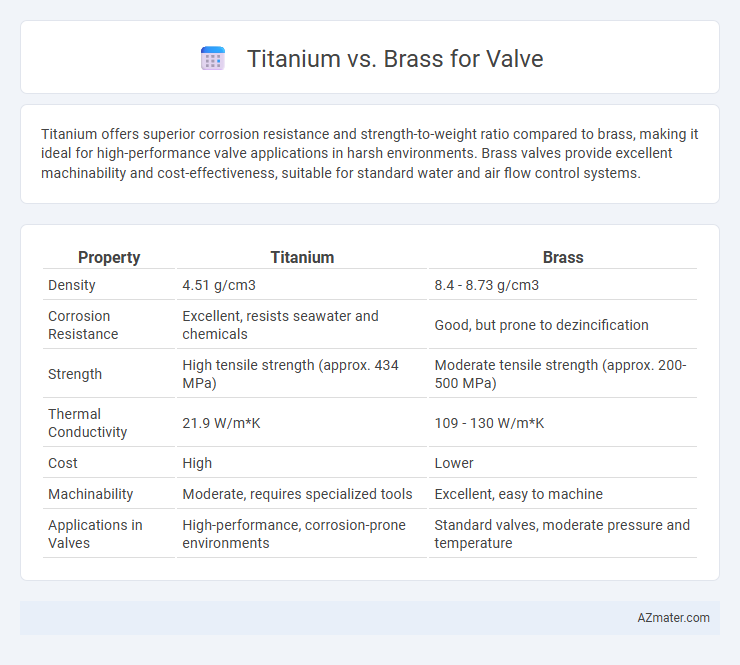
Table of Comparison
| Property | Titanium | Brass |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 4.51 g/cm3 | 8.4 - 8.73 g/cm3 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, resists seawater and chemicals | Good, but prone to dezincification |
| Strength | High tensile strength (approx. 434 MPa) | Moderate tensile strength (approx. 200-500 MPa) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 21.9 W/m*K | 109 - 130 W/m*K |
| Cost | High | Lower |
| Machinability | Moderate, requires specialized tools | Excellent, easy to machine |
| Applications in Valves | High-performance, corrosion-prone environments | Standard valves, moderate pressure and temperature |
Introduction to Titanium and Brass Valves
Titanium valves offer exceptional corrosion resistance, lightweight properties, and high strength, making them ideal for harsh environments and applications requiring durability. Brass valves, composed primarily of copper and zinc, provide excellent machinability, cost-effectiveness, and good resistance to water corrosion, commonly used in residential plumbing and HVAC systems. The choice between titanium and brass valves depends on specific requirements such as pressure, temperature, and environmental conditions.
Material Composition and Properties
Titanium valves boast a high strength-to-weight ratio, exceptional corrosion resistance, and excellent biocompatibility due to their alloy primarily consisting of titanium and small amounts of aluminum and vanadium. Brass valves, composed mainly of copper and zinc, provide good machinability, moderate corrosion resistance, and antimicrobial properties but are heavier and less durable under extreme conditions. The choice between titanium and brass valves hinges on application requirements, balancing titanium's superior durability and lightness against brass's cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacture.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Titanium valves exhibit superior durability and strength compared to brass, as titanium offers a high strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional corrosion resistance, especially in harsh or high-pressure environments. Brass valves, while more cost-effective and easier to machine, have lower tensile strength and are more prone to dezincification and wear over time. For applications requiring long-term reliability and resistance to mechanical stress, titanium valves provide enhanced performance and longevity.
Corrosion Resistance: Titanium vs Brass
Titanium exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to brass, especially in aggressive environments such as seawater, acidic solutions, and chloride-rich conditions, where titanium's passive oxide layer prevents degradation. Brass, an alloy primarily composed of copper and zinc, is more susceptible to dezincification and corrosion in acidic or high-chloride environments, leading to reduced durability and potential valve failure. For valves requiring longevity and reliability in harsh chemical or marine settings, titanium is often the preferred material due to its exceptional resistance to corrosion and minimal maintenance needs.
Weight and Design Implications
Titanium valves offer significantly lower weight compared to brass, reducing overall system mass by up to 40%, which enhances efficiency in aerospace and automotive applications. The high strength-to-weight ratio of titanium allows for more compact and streamlined valve designs without sacrificing durability or performance. In contrast, brass valves, though heavier, provide excellent corrosion resistance and machinability but impose design constraints due to their density and weight.
Cost Analysis: Titanium vs Brass Valves
Titanium valves typically exhibit higher upfront costs due to the metal's superior corrosion resistance, lightweight properties, and durability, making them ideal for demanding industrial applications. Brass valves are more cost-effective initially, favored in residential or low-pressure environments where budget constraints outweigh the need for extreme performance. Over time, titanium valves may offer lower total cost of ownership through reduced maintenance and longer lifespan, offsetting the initial price differential compared to brass.
Typical Applications in Industry
Titanium valves dominate aerospace, chemical processing, and marine industries due to their superior corrosion resistance and high strength-to-weight ratio, especially under extreme temperatures and aggressive environments. Brass valves are widely favored in plumbing, HVAC, and water supply systems for their excellent machinability, cost-effectiveness, and reliable performance in low-pressure, non-corrosive applications. Industrial sectors prioritize titanium for critical applications requiring durability and resistance to harsh chemicals, while brass remains preferred for routine fluid control where cost and ease of installation are key factors.
Maintenance and Longevity Factors
Titanium valves offer superior corrosion resistance and require minimal maintenance compared to brass, ensuring longer service life in harsh environments. Brass valves, while cost-effective and easier to machine, are more prone to dezincification and wear, leading to increased maintenance efforts over time. The inherent durability and resistance to scaling make titanium the optimal choice for applications demanding longevity and reduced upkeep.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Titanium valves offer superior environmental benefits due to their corrosion resistance and longer service life, reducing the frequency of replacements and waste generation. Brass valves, while widely used, often contain lead and are prone to dezincification, which can lead to environmental contamination and higher maintenance demands. Titanium's recyclability and lower ecological footprint make it a more sustainable choice for valve manufacturing in industrial and marine applications.
Choosing the Right Valve Material: Key Considerations
Titanium offers superior corrosion resistance and strength, making it ideal for valves in harsh environments such as seawater or chemical processing. Brass provides excellent machinability and cost-effectiveness while maintaining good corrosion resistance for domestic plumbing and low-pressure applications. Selecting the right valve material depends on factors like operating pressure, temperature, fluid compatibility, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Titanium vs Brass for Valve
 azmater.com
azmater.com