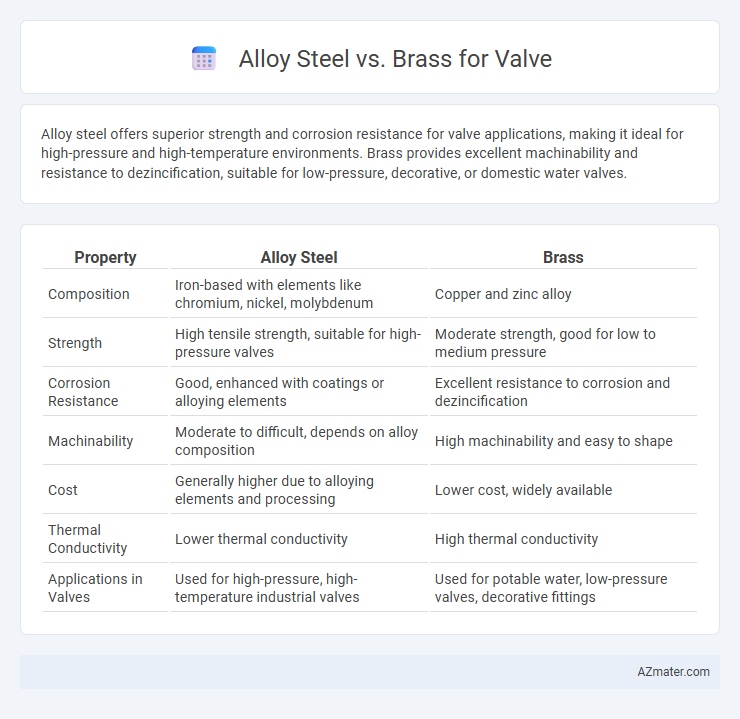
Alloy steel offers superior strength and corrosion resistance for valve applications, making it ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature environments. Brass provides excellent machinability and resistance to dezincification, suitable for low-pressure, decorative, or domestic water valves.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Alloy Steel | Brass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Iron-based with elements like chromium, nickel, molybdenum | Copper and zinc alloy |
| Strength | High tensile strength, suitable for high-pressure valves | Moderate strength, good for low to medium pressure |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good, enhanced with coatings or alloying elements | Excellent resistance to corrosion and dezincification |
| Machinability | Moderate to difficult, depends on alloy composition | High machinability and easy to shape |
| Cost | Generally higher due to alloying elements and processing | Lower cost, widely available |
| Thermal Conductivity | Lower thermal conductivity | High thermal conductivity |
| Applications in Valves | Used for high-pressure, high-temperature industrial valves | Used for potable water, low-pressure valves, decorative fittings |
Introduction to Alloy Steel and Brass Valves
Alloy steel valves offer superior strength, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature durability, making them ideal for demanding industrial applications such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation. Brass valves provide excellent machinability, corrosion resistance in water systems, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in plumbing, HVAC, and low-pressure fluid control. Selecting between alloy steel and brass valves depends on operational requirements, including pressure ratings, temperature tolerance, and media compatibility.
Material Composition: Alloy Steel vs Brass
Alloy steel valves are primarily composed of iron combined with elements such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, enhancing strength, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature performance. Brass valves consist mainly of copper and zinc, offering excellent machinability and moderate corrosion resistance suitable for low-pressure applications. The distinct material compositions determine their suitability: alloy steel excels in industrial, high-stress environments, while brass is preferred for residential plumbing and decorative uses.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Alloy steel valves exhibit significantly higher mechanical strength compared to brass, with tensile strength values typically ranging from 700 to 1200 MPa, while brass generally falls between 300 and 600 MPa. The superior hardness and toughness of alloy steel make it ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature valve applications. Brass valves offer corrosion resistance and machinability but lack the mechanical robustness required for heavy-duty industrial use.
Corrosion Resistance in Different Environments
Alloy steel valves exhibit superior corrosion resistance in harsh industrial environments due to their enhanced chromium and molybdenum content, making them ideal for acidic or high-temperature applications. Brass valves offer excellent corrosion resistance in water and mild environments but tend to corrode in highly acidic or saline conditions, limiting their usage in aggressive media. Selecting alloy steel over brass ensures longer valve lifespan and reliability in chemical plants, marine settings, and oil and gas industries where exposure to corrosive substances is common.
Temperature Tolerance and Performance
Alloy steel valves exhibit superior temperature tolerance, effectively withstanding extreme heat up to 1100degF (593degC), making them ideal for high-temperature industrial applications. Brass valves, with a maximum temperature limit around 400degF (204degC), perform well in moderate temperature environments but can deform or fail under excessive heat. Performance-wise, alloy steel offers enhanced strength, corrosion resistance, and durability for demanding conditions, whereas brass provides good machinability and moderate corrosion resistance suited for low to medium temperature systems.
Cost Effectiveness and Economic Considerations
Alloy steel valves offer superior strength and durability, making them cost-effective for high-pressure and high-temperature applications despite a higher initial price. Brass valves provide excellent corrosion resistance and machinability at a lower upfront cost, ideal for low-pressure, non-corrosive environments, reducing maintenance expenses. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including lifespan and operating conditions, is crucial for economically selecting between alloy steel and brass valves.
Applications and Industry Usage
Alloy steel valves are widely used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation due to their exceptional strength and corrosion resistance. Brass valves are preferred in plumbing, HVAC, and water supply industries for their excellent machinability, corrosion resistance in water, and cost-effectiveness. The choice between alloy steel and brass valves depends on the specific industry requirements, with alloy steel favored for demanding environments and brass for general-purpose fluid control.
Maintenance and Longevity
Alloy steel valves exhibit superior durability and corrosion resistance, reducing maintenance frequency and extending service life compared to brass valves. Brass valves, while easier to machine and more cost-effective initially, are prone to dezincification and wear in high-pressure or high-temperature applications, leading to increased maintenance needs. Choosing alloy steel ensures better performance and longer valve longevity in demanding industrial environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Alloy steel valves generally have a lower environmental footprint due to their durability and recyclability, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste. Brass valves, while corrosion-resistant and easy to machine, often involve higher energy consumption and environmental impact during extraction and processing of copper and zinc. Sustainable valve choices prioritize materials like alloy steel that support longer service life and efficient recycling, aligning with green manufacturing and circular economy principles.
Choosing the Right Valve Material: Key Factors
Selecting between alloy steel and brass for valve construction depends heavily on factors like corrosion resistance, pressure tolerance, and temperature range. Alloy steel offers superior strength and is ideal for high-pressure, high-temperature applications but may require protective coatings to prevent corrosion. Brass provides excellent corrosion resistance and machinability, making it suitable for low to medium pressure systems, particularly in water and plumbing applications.
Infographic: Alloy steel vs Brass for Valve
 azmater.com
azmater.com