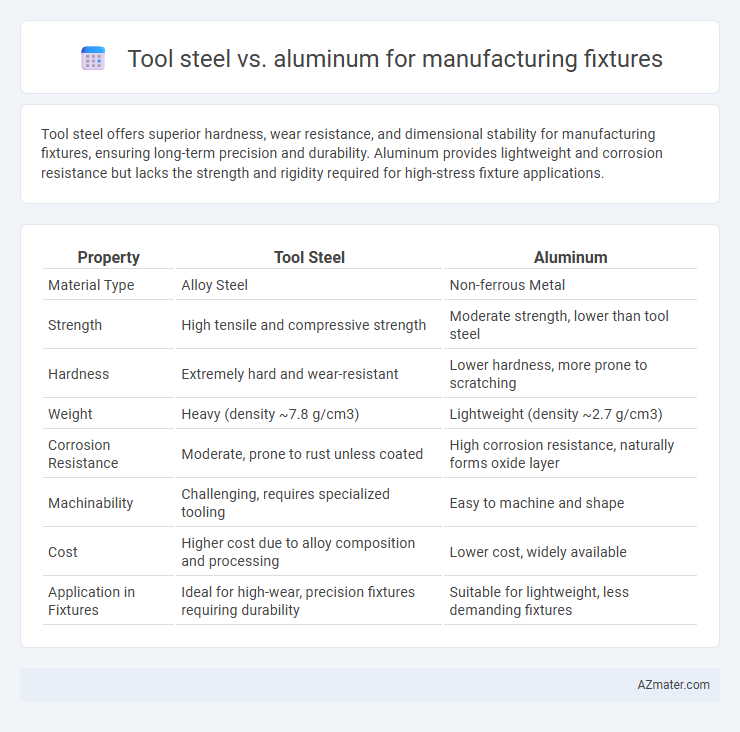
Tool steel offers superior hardness, wear resistance, and dimensional stability for manufacturing fixtures, ensuring long-term precision and durability. Aluminum provides lightweight and corrosion resistance but lacks the strength and rigidity required for high-stress fixture applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tool Steel | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Alloy Steel | Non-ferrous Metal |
| Strength | High tensile and compressive strength | Moderate strength, lower than tool steel |
| Hardness | Extremely hard and wear-resistant | Lower hardness, more prone to scratching |
| Weight | Heavy (density ~7.8 g/cm3) | Lightweight (density ~2.7 g/cm3) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate, prone to rust unless coated | High corrosion resistance, naturally forms oxide layer |
| Machinability | Challenging, requires specialized tooling | Easy to machine and shape |
| Cost | Higher cost due to alloy composition and processing | Lower cost, widely available |
| Application in Fixtures | Ideal for high-wear, precision fixtures requiring durability | Suitable for lightweight, less demanding fixtures |
Introduction: Tool Steel vs Aluminum in Manufacturing Fixtures
Tool steel offers superior hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for manufacturing fixtures subjected to high stress and repetitive use. Aluminum provides lightweight, corrosion resistance, and ease of machining, which benefits fixtures requiring frequent repositioning and reduced weight. Selecting between tool steel and aluminum depends on balancing durability requirements with weight and machining efficiency in fixture design.
Material Properties Comparison
Tool steel offers superior hardness, wear resistance, and dimensional stability compared to aluminum, making it ideal for manufacturing fixtures subjected to high stress and repetitive use. Aluminum provides lightweight advantages, excellent corrosion resistance, and better machinability but lacks the strength and toughness required for heavy-duty fixture applications. Choosing tool steel enhances fixture durability and longevity, while aluminum is preferred for less demanding setups requiring ease of handling and fast production.
Strength and Durability Considerations
Tool steel offers superior strength and durability compared to aluminum, making it ideal for manufacturing fixtures subjected to high stress and wear. Its hardness and resistance to deformation ensure long-lasting performance in demanding industrial environments. Aluminum, while lighter and easier to machine, lacks the tensile strength and abrasion resistance required for heavy-duty fixture applications.
Weight Differences and Handling
Tool steel is significantly heavier than aluminum, which impacts the overall weight of manufacturing fixtures and influences ease of handling. Aluminum's lighter weight facilitates quicker setup and reduces operator fatigue, making it ideal for fixtures requiring frequent repositioning. The weight difference of tool steel, often two to three times that of aluminum, requires consideration in ergonomics and transportation during manufacturing processes.
Machinability and Fabrication Ease
Tool steel offers superior strength and wear resistance compared to aluminum, making it ideal for heavy-duty manufacturing fixtures where durability is critical. Aluminum excels in machinability due to its lighter weight and softer nature, allowing faster cutting speeds and easier fabrication processes such as drilling and milling. The choice between tool steel and aluminum depends on the fixture's operational demands, with aluminum preferred for rapid prototyping and tool steel favored for long-term, high-stress applications.
Cost Analysis: Tool Steel vs Aluminum
Tool steel offers superior hardness and wear resistance for manufacturing fixtures, but its higher raw material and machining costs often lead to increased overall expenses compared to aluminum. Aluminum provides cost advantages due to lower material price, faster machining speeds, and reduced tooling wear, which can significantly decrease production cycle times. Evaluating the total cost of ownership includes factoring in fixture lifespan, maintenance frequency, and application requirements when choosing between tool steel and aluminum.
Corrosion Resistance and Maintenance
Tool steel offers high corrosion resistance essential for manufacturing fixtures exposed to harsh environments, reducing the frequency of maintenance and prolonging fixture lifespan. Aluminum, while lightweight and easier to machine, is more prone to oxidation and corrosion, often requiring protective coatings or treatments to maintain durability. Choosing tool steel minimizes downtime and maintenance costs, making it a preferred material for fixtures demanding long-term reliability.
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
Tool steel exhibits significantly lower thermal conductivity, approximately 15-30 W/m*K, compared to aluminum's high thermal conductivity of around 205 W/m*K, making aluminum more effective for heat dissipation in manufacturing fixtures. In terms of electrical conductivity, aluminum outperforms tool steel with a conductivity of about 37.7 MS/m versus tool steel's negligible levels, benefiting applications requiring efficient electrical pathways. The choice between tool steel and aluminum hinges on whether thermal management or structural durability is prioritized, with tool steel offering superior strength and wear resistance despite its limited conductivity.
Application Suitability and Industry Preferences
Tool steel offers superior hardness, wear resistance, and strength, making it ideal for fixtures requiring high durability in heavy-duty manufacturing processes such as metal stamping and machining. Aluminum, valued for its lightweight properties and corrosion resistance, suits applications needing easy handling and quick setup, common in electronics assembly or lightweight aerospace fixtures. Industries with high production volumes and abrasive conditions prefer tool steel, while those prioritizing weight reduction and corrosion resistance often opt for aluminum fixtures.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Fixture
Tool steel offers superior durability and wear resistance compared to aluminum, making it ideal for fixtures subjected to heavy loads and high stress. Aluminum provides lightweight properties and excellent corrosion resistance, suitable for fixtures requiring ease of handling and frequent repositioning. Selecting the right material depends on factors like load capacity, environmental conditions, machining ease, and cost efficiency to ensure fixture performance and longevity.
Infographic: Tool steel vs Aluminum for Manufacturing fixture
 azmater.com
azmater.com