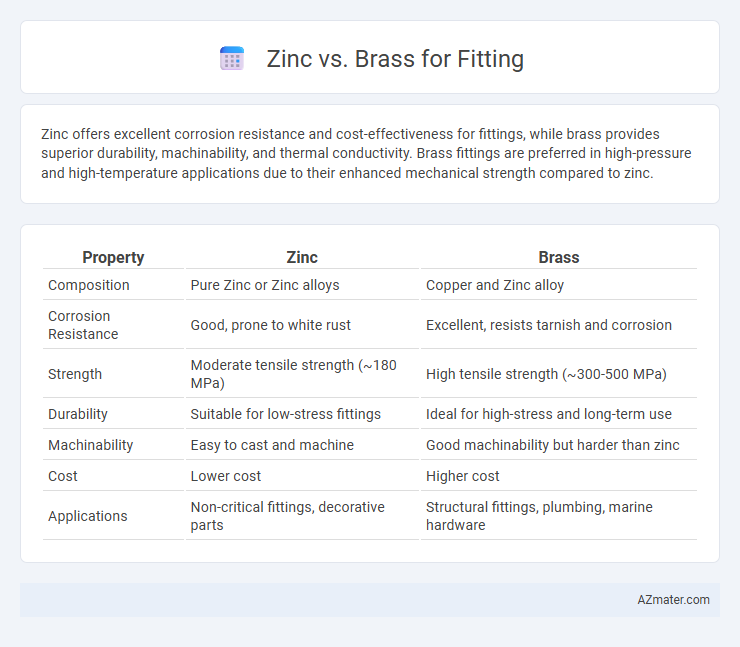
Zinc offers excellent corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness for fittings, while brass provides superior durability, machinability, and thermal conductivity. Brass fittings are preferred in high-pressure and high-temperature applications due to their enhanced mechanical strength compared to zinc.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zinc | Brass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure Zinc or Zinc alloys | Copper and Zinc alloy |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good, prone to white rust | Excellent, resists tarnish and corrosion |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength (~180 MPa) | High tensile strength (~300-500 MPa) |
| Durability | Suitable for low-stress fittings | Ideal for high-stress and long-term use |
| Machinability | Easy to cast and machine | Good machinability but harder than zinc |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Applications | Non-critical fittings, decorative parts | Structural fittings, plumbing, marine hardware |
Introduction to Zinc and Brass Fittings
Zinc fittings are valued for their corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness in plumbing and industrial applications. Brass fittings, composed primarily of copper and zinc, offer superior strength, durability, and resistance to high temperatures and pressure. Both materials serve essential roles in fluid control systems, but brass fittings typically provide enhanced longevity and reliability compared to zinc.
Chemical Composition and Material Properties
Zinc fittings primarily consist of zinc alloy, which includes aluminum, copper, and magnesium, offering good corrosion resistance and moderate strength for plumbing applications. Brass fittings are composed mainly of copper and zinc, with varying copper content that enhances durability, machinability, and resistance to dezincification compared to zinc alloys. The higher copper percentage in brass provides superior mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for high-pressure and marine environments.
Corrosion Resistance: Zinc vs Brass
Brass fittings exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to zinc, especially in environments exposed to moisture and chemicals, due to their copper content which forms a protective oxide layer. Zinc fittings are prone to zinc pest and can corrode more quickly when exposed to acidic or alkaline conditions, limiting their durability in harsh settings. Choosing brass over zinc enhances longevity and reliability in plumbing, industrial, and marine applications where corrosion resistance is critical.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Zinc fittings offer moderate strength and corrosion resistance suitable for light-duty plumbing and low-pressure applications, but they tend to wear faster under constant stress. Brass fittings provide superior strength and durability due to their higher tensile strength and excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for heavy-duty plumbing, industrial, and high-pressure environments. Brass's ability to withstand higher temperatures and mechanical stress ensures longer service life compared to zinc in demanding conditions.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Zinc fittings generally offer a lower upfront cost compared to brass, making them more suitable for budget-conscious projects or large-scale applications where cost efficiency is critical. Brass fittings, while more expensive, provide superior durability and corrosion resistance, potentially reducing maintenance costs and replacement frequency over time. Evaluating total lifecycle expenses alongside initial budget constraints ensures optimal material selection for fitting applications.
Common Applications in Plumbing and Industry
Zinc fittings are commonly used in plumbing for their corrosion resistance and affordability, making them suitable for low-pressure water systems and drainage applications. Brass fittings, favored in both plumbing and industrial sectors, offer superior durability, corrosion resistance, and machinability, making them ideal for high-pressure water supply lines, gas distribution, and HVAC systems. Brass's antimicrobial properties and ability to withstand extreme temperatures also make it a preferred choice in medical and food processing industries.
Installation and Maintenance Differences
Zinc fittings provide easier installation due to their lightweight nature and corrosion-resistant surface, which reduces the need for frequent adjustments or replacements. Brass fittings offer superior durability and are less prone to cracking under high pressure or extreme temperatures, though they require periodic polishing to maintain appearance and prevent tarnishing. Maintenance for zinc fittings is generally lower, but brass fittings offer longer service life, especially in plumbing systems exposed to aggressive water conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Zinc fittings offer superior corrosion resistance and are often recycled efficiently, reducing environmental impact compared to brass, which contains copper and zinc and requires more intensive mining processes. Brass production has a higher carbon footprint due to the extraction and processing of copper, whereas zinc's recyclability supports sustainable manufacturing with lower energy consumption. Choosing zinc fittings can contribute to greater sustainability in plumbing and industrial applications by minimizing resource depletion and supporting circular economy practices.
Compatibility with Other Materials
Zinc fittings offer excellent corrosion resistance and are highly compatible with a variety of plumbing materials, including copper and PVC, making them suitable for diverse piping systems. Brass fittings, composed mainly of copper and zinc, provide superior compatibility with both copper and steel pipes due to their mechanical strength and corrosion resistance. While brass fittings maintain reliable connections in mixed-metal installations, zinc fittings may face galvanic corrosion issues when paired with certain metals, limiting their use in some composite systems.
Choosing the Right Fitting: Key Takeaways
Zinc fittings offer excellent corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for indoor plumbing and low-pressure applications. Brass fittings provide superior strength, durability, and resistance to high temperatures, ideal for potable water systems and high-pressure environments. Choosing the right fitting depends on assessing application requirements such as pressure, temperature, and exposure to corrosive elements.
Infographic: Zinc vs Brass for Fitting
 azmater.com
azmater.com