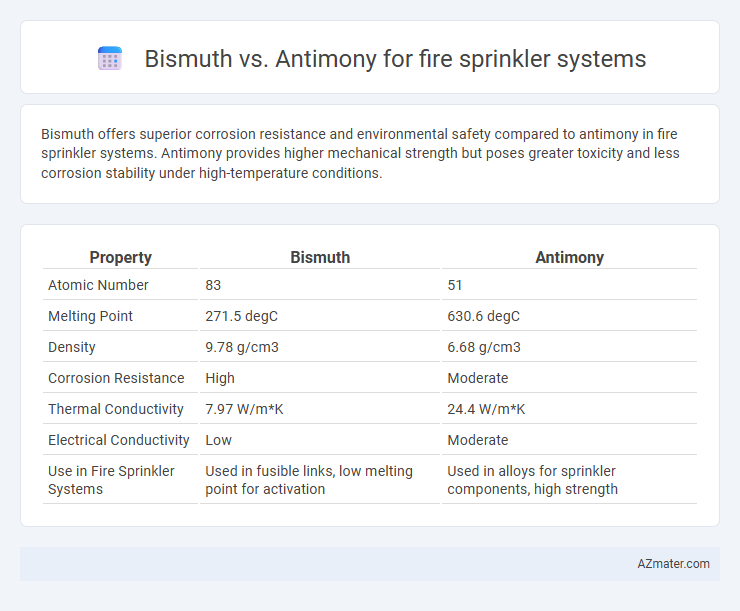
Bismuth offers superior corrosion resistance and environmental safety compared to antimony in fire sprinkler systems. Antimony provides higher mechanical strength but poses greater toxicity and less corrosion stability under high-temperature conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bismuth | Antimony |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 83 | 51 |
| Melting Point | 271.5 degC | 630.6 degC |
| Density | 9.78 g/cm3 | 6.68 g/cm3 |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Thermal Conductivity | 7.97 W/m*K | 24.4 W/m*K |
| Electrical Conductivity | Low | Moderate |
| Use in Fire Sprinkler Systems | Used in fusible links, low melting point for activation | Used in alloys for sprinkler components, high strength |
Introduction to Fire Sprinkler Alloys
Bismuth and antimony are critical elements used in fire sprinkler alloys due to their thermal and mechanical properties. Antimony enhances the strength and hardness of sprinkler components, improving their durability under high heat conditions, while bismuth offers excellent thermal expansion control and corrosion resistance. The selection between bismuth and antimony alloys affects the reliability and longevity of fire sprinkler systems in industrial and commercial applications.
Overview of Bismuth and Antimony in Sprinkler Systems
Bismuth and antimony are both metalloid additives used in fire sprinkler systems to enhance the properties of the sprinkler head components, particularly in fusible links. Bismuth alloys offer low melting points and excellent corrosion resistance, which improve the reliability and longevity of the sprinkler activation mechanism. Antimony is valued for its flame retardant properties and mechanical strength, helping maintain system integrity under high-temperature conditions essential for effective fire response.
Chemical Properties: Bismuth vs Antimony
Bismuth and Antimony are both metalloid elements used in fire sprinkler systems, but their chemical properties differ significantly. Bismuth exhibits low toxicity, excellent thermal conductivity, and a melting point of 271.5degC, making it suitable for fusible links in sprinklers that require precise heat activation. In contrast, Antimony has a higher melting point of 630.6degC and is more brittle with greater chemical reactivity, often used as an alloying agent to enhance the hardness and corrosion resistance of sprinkler components.
Melting Point Comparison: Relevance for Sprinklers
Bismuth, with a melting point of approximately 271degC (520degF), offers a lower activation temperature compared to antimony, which melts at around 631degC (1168degF). This significant difference makes bismuth alloys more suitable for fire sprinkler systems that require quick response and activation at precise temperatures. Antimony's higher melting point limits its use in sprinkler fusible links where timely activation during a fire is critical for safety.
Environmental Impact and Toxicity
Bismuth exhibits a lower environmental impact and reduced toxicity compared to antimony, making it a safer alternative for fire sprinkler systems. Antimony compounds are known to be toxic and bioaccumulative, posing risks to aquatic life and human health during manufacturing and disposal processes. Bismuth, being less toxic and more environmentally benign, offers an effective and eco-friendly solution in fire protection applications.
Corrosion Resistance in Wet and Dry Systems
Bismuth offers superior corrosion resistance compared to antimony in fire sprinkler systems, especially in wet environments where moisture accelerates metal degradation. Antimony tends to form more corrosive compounds under fluctuating wet and dry conditions, leading to potential system failures. Using bismuth-enhanced alloys improves longevity and reliability by reducing corrosion-induced blockages and leaks in both wet and dry fire sprinkler setups.
Performance and Reliability in Fire Suppression
Bismuth offers superior corrosion resistance and non-toxicity in fire sprinkler systems, enhancing long-term reliability and performance under extreme heat conditions. Antimony's higher melting point contributes to stronger alloys used in sprinkler components, but it may be more susceptible to oxidation, potentially impacting system longevity. Fire suppression efficiency favors bismuth for its stability and resistance to thermal degradation, ensuring consistent activation and dependable firefighting response.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Bismuth is generally more expensive and less abundant than antimony, impacting the overall cost of fire sprinkler systems incorporating these elements. Antimony's widespread availability and lower market price make it a more cost-effective choice for manufacturers seeking to balance performance and budget. The decision between bismuth and antimony hinges on cost-efficiency and supply stability within fire protection material sourcing.
Regulatory Guidelines and Industry Standards
Bismuth and antimony differ in their compliance with fire sprinkler system regulations and industry standards, with antimony being more commonly recognized due to its established fire-resistance properties and inclusion in standards such as NFPA 13. Regulatory guidelines prioritize materials that ensure corrosion resistance, mechanical integrity, and non-toxicity during activation, where antimony alloys meet these criteria more consistently than bismuth alloys. Industry standards emphasize antimony's proven performance in temperature-sensitive sprinkler components, making it the preferred choice for meeting UL and FM approval requirements in fire protection systems.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Alloy for Fire Sprinklers
Bismuth alloys offer superior corrosion resistance and lower melting points, enhancing fire sprinkler system reliability and ease of activation, while antimony alloys provide higher mechanical strength and thermal stability, ensuring durability under extreme conditions. Selecting the right alloy depends on the specific fire protection requirements, balancing activation temperature, mechanical robustness, and environmental factors. Optimizing alloy choice improves system performance, safety, and longevity in fire sprinkler applications.
Infographic: Bismuth vs Antimony for Fire sprinkler system
 azmater.com
azmater.com