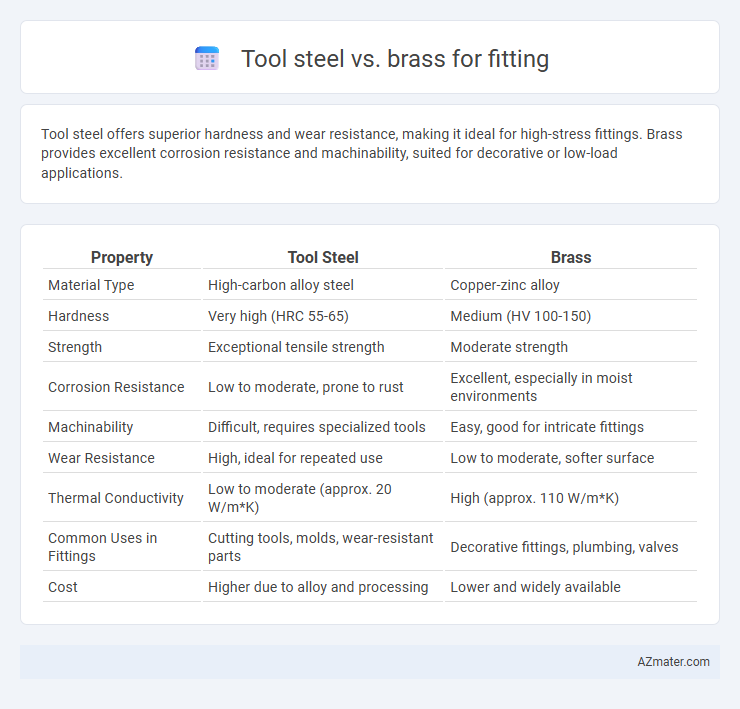
Tool steel offers superior hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for high-stress fittings. Brass provides excellent corrosion resistance and machinability, suited for decorative or low-load applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tool Steel | Brass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-carbon alloy steel | Copper-zinc alloy |
| Hardness | Very high (HRC 55-65) | Medium (HV 100-150) |
| Strength | Exceptional tensile strength | Moderate strength |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low to moderate, prone to rust | Excellent, especially in moist environments |
| Machinability | Difficult, requires specialized tools | Easy, good for intricate fittings |
| Wear Resistance | High, ideal for repeated use | Low to moderate, softer surface |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low to moderate (approx. 20 W/m*K) | High (approx. 110 W/m*K) |
| Common Uses in Fittings | Cutting tools, molds, wear-resistant parts | Decorative fittings, plumbing, valves |
| Cost | Higher due to alloy and processing | Lower and widely available |
Introduction to Tool Steel and Brass for Fittings
Tool steel, known for its hardness, wear resistance, and high tensile strength, is often used in fittings requiring durability and precision under heavy mechanical stress. Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, offers excellent corrosion resistance, malleability, and thermal conductivity, making it ideal for fittings in plumbing and decorative applications. Choosing between tool steel and brass depends on the specific performance requirements, including strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability for the fitting's intended environment.
Key Material Properties of Tool Steel
Tool steel is prized for its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and ability to maintain a sharp edge under high stress, making it ideal for precision fittings requiring durability in demanding environments. Its high tensile strength and heat resistance surpass those of brass, which, while easier to machine and corrosion-resistant, lacks the structural toughness needed for heavy-duty applications. The superior fatigue strength and impact resistance of tool steel ensure longevity and reliability in fittings subjected to repetitive mechanical stress.
Key Material Properties of Brass
Brass offers excellent corrosion resistance and superior machinability, making it ideal for fittings exposed to moisture and various chemicals. Its low friction coefficient and moderate tensile strength ensure reliable performance in sealing and joining applications. Compared to tool steel, brass provides better conductivity and aesthetic appeal, which are critical for decorative and electronic fittings.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Tool steel offers superior strength and durability compared to brass, making it ideal for high-stress fitting applications requiring resistance to wear and deformation. Brass, while easier to machine and corrosion-resistant, lacks the hardness and tensile strength of tool steel, leading to faster wear under heavy loads. For fittings exposed to mechanical strain and impact, tool steel ensures longer service life and enhanced performance.
Corrosion Resistance: Tool Steel vs Brass
Brass offers superior corrosion resistance compared to tool steel, especially in moist or marine environments, due to its copper and zinc composition that naturally forms a protective oxide layer. Tool steel, while extremely durable and wear-resistant, is prone to rust and corrosion unless specially treated or coated, limiting its use in corrosive settings. Choosing brass for fittings ensures longer lifespan and reliability where resistance to oxidation and tarnishing is critical.
Machinability and Fabrication Considerations
Tool steel offers superior hardness and wear resistance but presents challenges in machinability due to its toughness, often requiring slower cutting speeds and specialized tooling. Brass excels in machinability with excellent chip formation and minimal tool wear, facilitating faster fabrication and precision fittings. The choice between tool steel and brass hinges on balancing the need for durability against ease of machining in fitting applications.
Cost Analysis: Tool Steel vs Brass Fittings
Tool steel fittings generally exhibit higher initial costs compared to brass due to their superior hardness and wear resistance, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Brass fittings offer cost advantages in lower price per pound and better machinability, resulting in reduced manufacturing expenses. Lifetime costs may favor tool steel when factoring in durability and replacement frequency, especially in high-stress environments.
Common Applications in Fittings
Tool steel is commonly used in fittings requiring high strength, wear resistance, and precise dimensions, such as hydraulic valve components and machine tooling parts. Brass fittings are preferred in plumbing, electrical connectors, and decorative applications due to their excellent corrosion resistance, machinability, and thermal conductivity. The choice between tool steel and brass depends on application-specific demands for durability, corrosion resistance, and mechanical performance.
Maintenance and Longevity
Tool steel offers superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to brass, making it ideal for fittings exposed to high stress and abrasive environments. Brass fittings require regular maintenance to prevent tarnishing and corrosion, especially in humid or corrosive conditions. The inherent hardness and wear resistance of tool steel significantly extend the longevity of fittings, reducing replacement frequency and maintenance costs over time.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Fittings
Tool steel offers exceptional strength and wear resistance, making it ideal for fittings exposed to high stress and impact. Brass provides excellent corrosion resistance and machinability, suitable for fittings requiring durability in moist or chemically aggressive environments. Selecting the right material depends on the application's mechanical demands and environmental conditions to ensure longevity and performance.
Infographic: Tool steel vs Brass for Fitting
 azmater.com
azmater.com