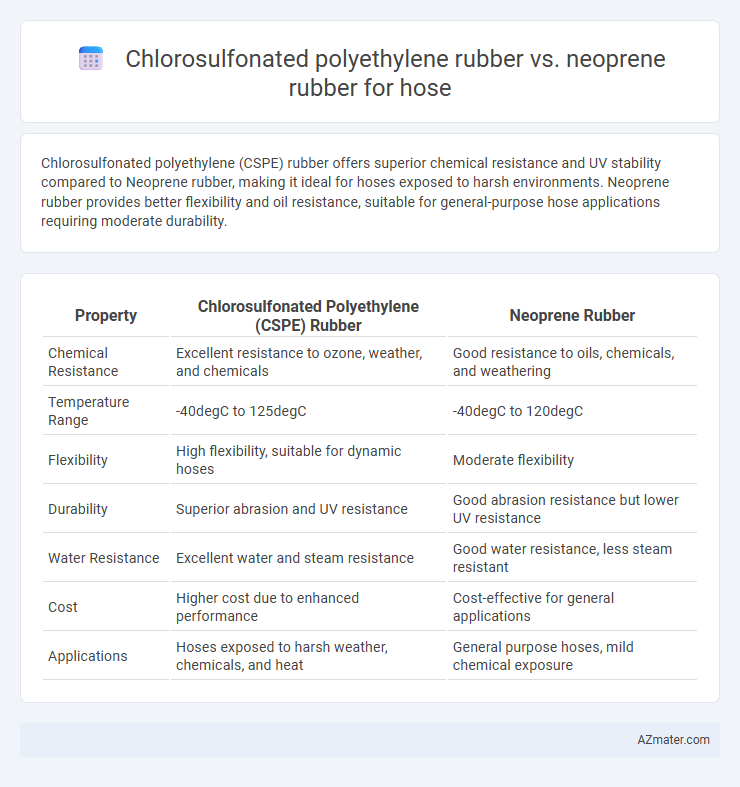
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber offers superior chemical resistance and UV stability compared to Neoprene rubber, making it ideal for hoses exposed to harsh environments. Neoprene rubber provides better flexibility and oil resistance, suitable for general-purpose hose applications requiring moderate durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSPE) Rubber | Neoprene Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to ozone, weather, and chemicals | Good resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 125degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, suitable for dynamic hoses | Moderate flexibility |
| Durability | Superior abrasion and UV resistance | Good abrasion resistance but lower UV resistance |
| Water Resistance | Excellent water and steam resistance | Good water resistance, less steam resistant |
| Cost | Higher cost due to enhanced performance | Cost-effective for general applications |
| Applications | Hoses exposed to harsh weather, chemicals, and heat | General purpose hoses, mild chemical exposure |
Introduction to Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSM) and Neoprene Rubber
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) is a synthetic rubber known for its excellent resistance to chemicals, weathering, and ozone, making it ideal for durable hose applications exposed to harsh environments. Neoprene rubber offers good mechanical properties and moderate resistance to oils, heat, and weather, commonly used in industrial hoses requiring flexibility and durability. Compared to neoprene, CSM provides superior chemical and abrasion resistance, enhancing hose longevity in demanding conditions.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber features a polyethylene backbone with chlorosulfonyl functional groups, providing excellent chemical resistance, ozone resistance, and durability in harsh environments. Neoprene rubber, composed of polychloroprene chains, exhibits balanced chemical stability, elasticity, and resistance to oils, heat, and weathering. The sulfonyl chloride groups in CSM contribute to superior resistance against hydrocarbons and solvents compared to Neoprene's chlorine atoms, making CSM more suitable for aggressive chemical hose applications.
Physical and Mechanical Properties of CSM vs Neoprene
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and chemical degradation compared to Neoprene, making it ideal for hoses exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Neoprene rubber provides enhanced flexibility and better tensile strength, contributing to improved durability under dynamic stress and mechanical fatigue. CSM exhibits higher hardness and compression set resistance, ensuring dimensional stability, while Neoprene excels in oil and solvent resistance, influencing hose performance based on specific application requirements.
Weather and Ozone Resistance in Hose Applications
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber exhibits superior weather and ozone resistance compared to neoprene rubber, making it highly suitable for hose applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. CSPE maintains its flexibility and durability under UV radiation, ozone, and extreme temperatures, preventing cracks and degradation over prolonged outdoor use. Neoprene, while resistant to oils and chemicals, generally shows less resilience against ozone and weather aging, resulting in more frequent replacements in exposed hose systems.
Performance Under Extreme Temperatures
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber exhibits superior resistance to extreme temperatures, maintaining flexibility and integrity between -40degC and 130degC, making it highly suitable for hoses used in harsh environmental conditions. Neoprene rubber performs well within a narrower temperature range of approximately -30degC to 100degC but can become brittle under prolonged exposure to low temperatures and degrade faster at high temperatures compared to CSPE. The enhanced thermal stability of CSPE hoses ensures longer service life and reliability in applications requiring consistent performance under thermal stress.
Chemical and Oil Resistance for Industrial Hoses
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior chemical and oil resistance compared to neoprene rubber, making it highly suitable for industrial hoses exposed to aggressive chemicals and hydrocarbons. CSM resists oxidation, ozone, acids, alkalis, and various solvents, maintaining integrity under prolonged exposure to oils and fuels, whereas neoprene offers moderate resistance but degrades faster in harsh chemical environments. Industrial hoses made from CSM provide enhanced durability and longer service life in chemical processing, petroleum handling, and oil transfer applications due to its robust molecular structure and resistance to swelling.
Flexibility, Durability, and Aging Characteristics
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber offers superior resistance to ozone, chemicals, and weathering compared to neoprene, enhancing durability for hose applications exposed to harsh environments. CSPE hoses maintain flexibility over a broader temperature range, ensuring better performance in both low and high temperatures, whereas neoprene tends to become stiffer in cold conditions. Aging characteristics favor CSPE as it exhibits less degradation under prolonged UV exposure and oxidative stress, leading to longer service life in outdoor or industrial hose applications.
Cost and Availability in the Hose Market
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber often has a higher cost than neoprene rubber due to its specialized chemical resistance and durability properties, impacting overall hose pricing. Neoprene rubber enjoys wider availability and more established supply chains in the hose market, making it a cost-effective choice for various industrial and commercial applications. Market demand trends and regional supply factors further influence the price and accessibility of both CSPE and neoprene hose materials.
Typical Applications and Industry Usage Scenarios
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber excels in chemical resistance and weatherability, making it ideal for hoses used in harsh environments such as chemical processing, mining, and oil refineries. Neoprene rubber offers superior flexibility and resistance to oils, ozone, and moderate chemicals, commonly used in automotive, refrigeration, and general industrial hose applications. Both materials provide durability, but CSM is preferred for extreme outdoor conditions while Neoprene suits environments requiring moderate chemical exposure and enhanced flexibility.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Rubber for Hose Requirements
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers superior chemical resistance, weatherability, and ozone resistance, making it ideal for hoses exposed to harsh environmental conditions or aggressive chemicals. Neoprene rubber provides excellent oil resistance, moderate chemical resistance, and flexibility, suited for general-purpose hoses requiring durability and resistance to oils and fuels. Selecting the right rubber depends on the specific hose application, prioritizing CSM for outdoor or chemical-intensive use, while neoprene fits better where oil exposure and flexibility are critical.
Infographic: Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber vs Neoprene rubber for Hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com