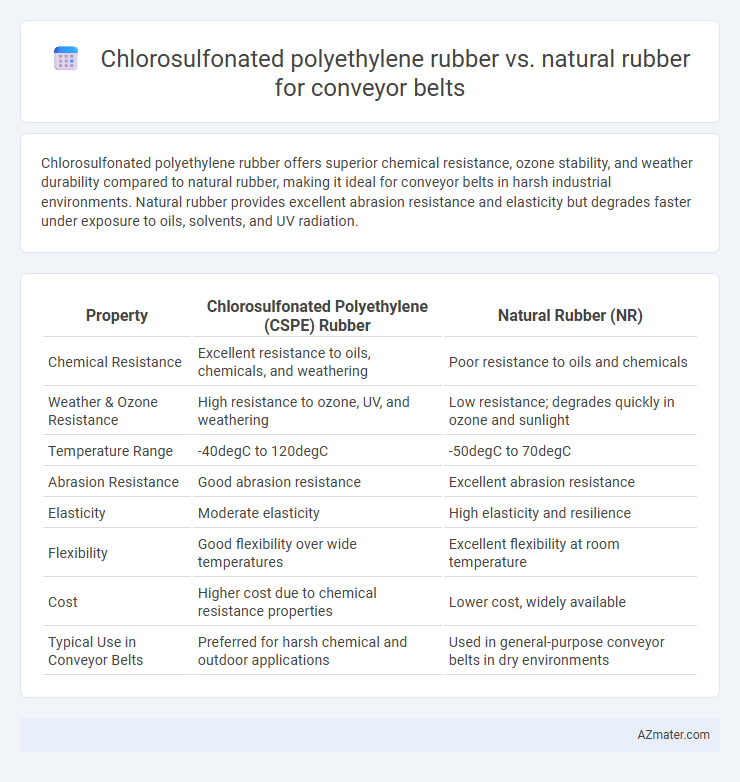
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber offers superior chemical resistance, ozone stability, and weather durability compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for conveyor belts in harsh industrial environments. Natural rubber provides excellent abrasion resistance and elasticity but degrades faster under exposure to oils, solvents, and UV radiation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSPE) Rubber | Natural Rubber (NR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering | Poor resistance to oils and chemicals |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | High resistance to ozone, UV, and weathering | Low resistance; degrades quickly in ozone and sunlight |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -50degC to 70degC |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good abrasion resistance | Excellent abrasion resistance |
| Elasticity | Moderate elasticity | High elasticity and resilience |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility over wide temperatures | Excellent flexibility at room temperature |
| Cost | Higher cost due to chemical resistance properties | Lower cost, widely available |
| Typical Use in Conveyor Belts | Preferred for harsh chemical and outdoor applications | Used in general-purpose conveyor belts in dry environments |
Overview of Conveyor Belt Materials
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers exceptional chemical resistance, weather durability, and flame retardancy, making it ideal for conveyor belts operating in harsh industrial environments. Natural rubber provides superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength, ensuring reliable performance under heavy loads and impact conditions. Selecting between CSM and natural rubber depends on specific operational demands such as chemical exposure, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical stress in conveyor belt applications.
Introduction to Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers exceptional chemical resistance, ozone tolerance, and weather durability, making it ideal for conveyor belts exposed to harsh environments. Unlike natural rubber, CSM provides superior resistance to hydrocarbons, acids, and alkalis, enhancing belt longevity and performance in industrial applications. Its strong tensile strength and abrasion resistance ensure reliable operation in demanding material handling processes.
Properties of Natural Rubber
Natural rubber exhibits excellent tensile strength, high abrasion resistance, and superior elasticity, making it well-suited for conveyor belt applications involving heavy loads and dynamic stress. Its inherent resilience allows for efficient energy absorption and resistance to fatigue, ensuring longer service life in demanding industrial environments. Natural rubber also provides strong adhesion to fabric reinforcements, enhancing the overall durability and flexibility of conveyor belts.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to natural rubber in conveyor belt applications, offering enhanced tensile strength and abrasion resistance. CSPE's chemical composition provides excellent durability against environmental factors, resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance costs. Natural rubber, while flexible and cost-effective, tends to have lower tensile strength and inferior resistance to oil and chemicals, limiting its performance in demanding conveyor belt environments.
Chemical and Weather Resistance
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance against acids, alkalis, and solvents, making it highly suitable for conveyor belts exposed to harsh industrial environments. Its excellent weather resistance includes strong UV stability, ozone resistance, and minimal degradation under extreme temperatures, outperforming natural rubber in outdoor applications. In contrast, natural rubber offers good elasticity and abrasion resistance but is prone to degradation from oils, chemicals, and ultraviolet exposure, limiting its durability in chemically aggressive or high-UV environments.
Abrasion and Wear Performance
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior abrasion resistance and enhanced wear performance compared to natural rubber in conveyor belt applications, making it ideal for handling abrasive materials. The molecular structure of CSM provides excellent resistance to chemicals, ozone, and weathering, further extending the conveyor belt's operational life in harsh environments. Natural rubber, while offering good tensile strength and elasticity, tends to wear faster under abrasive conditions, reducing its effectiveness in heavy-duty conveyor belt systems.
Temperature Resistance Differences
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior temperature resistance compared to natural rubber, maintaining performance in continuous use up to 120degC and short-term peaks around 150degC. Natural rubber typically withstands temperatures only up to 70degC before degrading, making it less suitable for high-temperature conveyor belt applications. The enhanced thermal stability of CSM results from its chlorine and sulfonyl functional groups, which provide improved heat and ozone resistance essential for industrial conveyor belts exposed to elevated temperatures.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber generally incurs higher initial costs compared to natural rubber due to its synthetic composition and specialized manufacturing process, but offers superior chemical and weather resistance that can reduce long-term maintenance expenses. Natural rubber remains more cost-effective and widely available, benefiting from large-scale global production and renewable sourcing, which supports lower upfront investment for conveyor belts. Availability of natural rubber is subject to agricultural variables and climate conditions, while CSPE's synthetic nature ensures consistent supply and quality, crucial for industries requiring reliability and durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber offers enhanced resistance to ozone, weathering, and chemicals, reducing maintenance and extending conveyor belt lifespan, thus lowering overall environmental impact compared to natural rubber. Natural rubber, sourced from Hevea brasiliensis trees, is renewable and biodegradable but involves deforestation risks and higher water consumption during cultivation. Choosing CSPE balances durability and chemical resistance with synthetic production impacts, while natural rubber supports sustainability through renewability yet requires responsible sourcing to minimize ecological harm.
Best Applications for Each Rubber Type
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber excels in conveyor belts exposed to harsh chemicals, oils, and extreme weather due to its superior chemical resistance and UV stability. Natural rubber is ideal for conveyor belts requiring excellent abrasion resistance, high tensile strength, and flexibility, especially in heavy-load and high-impact applications such as mining and quarrying. Selecting between CSM and natural rubber depends on the conveyor environment, with CSM suited for aggressive conditions and natural rubber preferred for durability under mechanical stress.
Infographic: Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber vs Natural rubber for Conveyor belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com