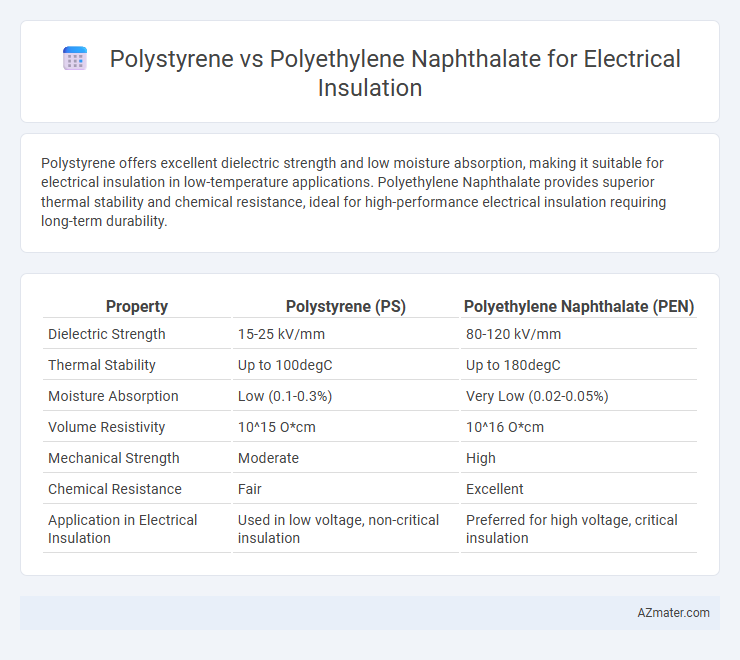
Polystyrene offers excellent dielectric strength and low moisture absorption, making it suitable for electrical insulation in low-temperature applications. Polyethylene Naphthalate provides superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, ideal for high-performance electrical insulation requiring long-term durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polystyrene (PS) | Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | 15-25 kV/mm | 80-120 kV/mm |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 100degC | Up to 180degC |
| Moisture Absorption | Low (0.1-0.3%) | Very Low (0.02-0.05%) |
| Volume Resistivity | 10^15 O*cm | 10^16 O*cm |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Fair | Excellent |
| Application in Electrical Insulation | Used in low voltage, non-critical insulation | Preferred for high voltage, critical insulation |
Introduction to Electrical Insulation Materials
Polystyrene and Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) are prominent polymers used in electrical insulation due to their unique dielectric properties. Polystyrene offers excellent electrical resistivity and low dielectric loss, making it suitable for capacitors and insulating films, while PEN provides superior thermal stability and mechanical strength, enhancing performance in high-temperature electrical applications. Selecting between these materials depends on factors like operating temperature, dielectric constant, and environmental durability requirements in electrical insulation design.
Overview of Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene (PS) is a thermoplastic polymer widely used for electrical insulation due to its excellent dielectric properties and high resistivity, which prevent electrical current leakage. Its rigid structure provides good mechanical strength and dimensional stability, making it suitable for components like capacitors and insulating housings. Polystyrene also offers high insulation resistance and low moisture absorption, enhancing its reliability in various electrical applications compared to materials like polyethylene naphthalate (PEN).
Overview of Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN)
Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) is a high-performance polyester known for its excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and superior mechanical strength, making it ideal for advanced electrical insulation applications. PEN exhibits higher dielectric strength and lower moisture absorption compared to Polystyrene, enhancing its reliability and longevity in electrical components. Its inherent dimensional stability and resistance to thermal degradation surpass many common polymers, positioning PEN as a preferred material in high-temperature, demanding insulation environments.
Key Properties Comparison: Polystyrene vs Polyethylene Naphthalate
Polystyrene offers excellent electrical insulation with high dielectric strength and low moisture absorption, making it suitable for low-frequency applications. Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) exhibits superior thermal stability, dimensional stability, and chemical resistance, which enhances its performance in high-frequency and high-temperature electrical insulation environments. PEN's better mechanical strength and reduced dielectric loss angle make it more reliable for advanced electrical insulation compared to polystyrene.
Dielectric Strength: PS vs PEN
Polystyrene (PS) exhibits a dielectric strength typically around 20-30 kV/mm, offering reliable electrical insulation but with limitations under high-voltage conditions. Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) surpasses PS with dielectric strength values approximately 100-140 kV/mm, providing superior insulation performance and enhanced thermal stability in demanding electrical applications. The higher dielectric strength of PEN makes it a preferred choice for advanced insulating materials in electronics and electrical engineering.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) exhibits superior thermal stability and heat resistance compared to Polystyrene, making it more suitable for electrical insulation in high-temperature environments. PEN maintains mechanical integrity and dielectric properties at temperatures exceeding 200degC, whereas Polystyrene typically degrades above 100degC, limiting its use in demanding thermal conditions. The enhanced aromatic structure of PEN contributes to its higher melting point and reduced thermal expansion, ensuring reliable insulation performance in electronic applications.
Mechanical Durability and Flexibility
Polystyrene offers high rigidity and dimensional stability but lacks flexibility, making it prone to cracking under mechanical stress compared to Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN). PEN exhibits superior mechanical durability with enhanced impact resistance and excellent flexibility, allowing it to withstand repeated bending and deformation without failure. These properties make PEN a preferred choice for electrical insulation applications requiring long-term mechanical resilience and adaptability to dynamic environments.
Moisture Absorption and Chemical Resistance
Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) demonstrates significantly lower moisture absorption compared to Polystyrene (PS), making it more suitable for electrical insulation in humid environments. PEN's superior chemical resistance, especially against oils and solvents, enhances its durability and performance in aggressive conditions where PS tends to degrade or swell. These properties position PEN as a preferred material for high-reliability electrical insulation applications requiring long-term stability and resistance to environmental factors.
Applications in Electrical and Electronic Industries
Polystyrene offers excellent dielectric properties and high insulation resistance, making it suitable for capacitors and speaker cones in electrical and electronic applications. Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) provides superior thermal stability, moisture resistance, and dimensional stability, ideal for flexible printed circuit boards and insulating films in advanced electronics. PEN's enhanced mechanical strength and conductivity stability under thermal stress make it preferable for high-performance insulation in demanding electrical environments.
Environmental Impact and Recycling Considerations
Polystyrene and Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) differ significantly in environmental impact and recycling potential for electrical insulation applications; polystyrene is derived from petroleum and is less biodegradable, often contributing to landfill waste and microplastic pollution due to limited recycling options. PEN offers greater environmental benefits with higher thermal stability and better mechanical properties, enabling longer service life in electrical components and improved recyclability through chemical recycling processes that recover monomers effectively. Choosing PEN over polystyrene enhances sustainability in electrical insulation by reducing ecological footprint and supporting circular economy practices.
Infographic: Polystyrene vs Polyethylene Naphthalate for Electrical Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com