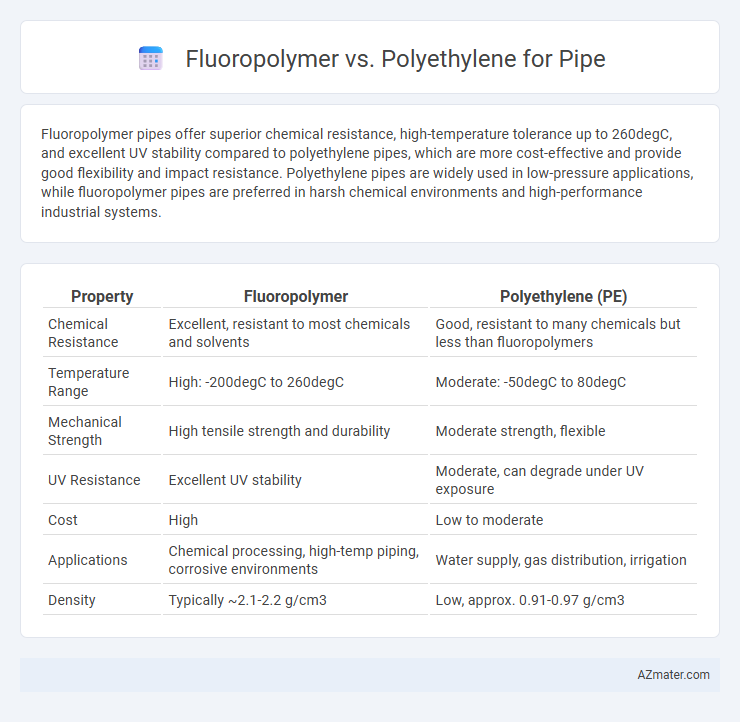
Fluoropolymer pipes offer superior chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance up to 260degC, and excellent UV stability compared to polyethylene pipes, which are more cost-effective and provide good flexibility and impact resistance. Polyethylene pipes are widely used in low-pressure applications, while fluoropolymer pipes are preferred in harsh chemical environments and high-performance industrial systems.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluoropolymer | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resistant to most chemicals and solvents | Good, resistant to many chemicals but less than fluoropolymers |
| Temperature Range | High: -200degC to 260degC | Moderate: -50degC to 80degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and durability | Moderate strength, flexible |
| UV Resistance | Excellent UV stability | Moderate, can degrade under UV exposure |
| Cost | High | Low to moderate |
| Applications | Chemical processing, high-temp piping, corrosive environments | Water supply, gas distribution, irrigation |
| Density | Typically ~2.1-2.2 g/cm3 | Low, approx. 0.91-0.97 g/cm3 |
Introduction to Fluoropolymer and Polyethylene Pipes
Fluoropolymer pipes are made from high-performance fluorinated polymers known for exceptional chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and non-stick surface properties, making them ideal for aggressive chemical transport and demanding industrial applications. Polyethylene pipes, composed of thermoplastic polymers, offer durability, flexibility, and excellent resistance to corrosion and low temperatures, commonly used in water, gas, and sewage systems. Comparing these materials reveals fluoropolymers excel in specialized, high-stress environments, while polyethylene provides cost-effective, versatile solutions for general piping infrastructure.
Material Composition and Structure
Fluoropolymer pipes consist of carbon-fluorine bonds, providing exceptional chemical resistance and high-temperature stability due to their strong molecular structure, while polyethylene pipes are composed of long chains of ethylene molecules, resulting in flexibility and impact resistance but lower temperature tolerance. The tightly-packed crystalline structure of polyethylene offers durability and ease of installation but lacks the superior inertness of fluoropolymer materials. Fluoropolymers, such as PTFE and FEP, have a non-stick, low-friction surface ideal for corrosive environments, whereas polyethylene is often favored for cost-effective, general-purpose piping with moderate chemical exposure.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Fluoropolymer pipes exhibit superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance compared to polyethylene, making them ideal for high-stress and corrosive environments. Polyethylene pipes offer excellent flexibility and impact resistance but may degrade under extreme temperatures and UV exposure. Durability of fluoropolymer materials surpasses polyethylene, ensuring longer service life in demanding industrial applications.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Fluoropolymer pipes exhibit superior chemical resistance compared to polyethylene, withstanding aggressive acids, bases, and solvents without degradation, making them ideal for highly corrosive environments. Polyethylene pipes, while resistant to many chemicals, can swell or degrade when exposed to strong oxidizers or hydrocarbons over time. The molecular structure of fluoropolymers, featuring strong carbon-fluorine bonds, provides enhanced barrier properties and stability in harsh chemical applications.
Temperature Tolerance and Performance
Fluoropolymer pipes exhibit superior temperature tolerance, maintaining structural integrity in extreme heat up to 260degC (500degF) compared to polyethylene pipes, which typically withstand temperatures up to 80degC (176degF). The chemical stability of fluoropolymers ensures enhanced resistance to thermal degradation, making them ideal for high-temperature industrial applications. Polyethylene pipes, while more cost-effective and flexible, underperform in environments requiring prolonged heat exposure and exhibit higher thermal expansion than fluoropolymer alternatives.
Application Suitability in Various Industries
Fluoropolymer pipes excel in chemical processing and pharmaceutical industries due to their superior chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and non-stick properties, making them ideal for handling aggressive fluids and sterilization processes. Polyethylene pipes are widely used in water supply, gas distribution, and agriculture because of their flexibility, impact resistance, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for moderate temperature and pressure applications. The choice between fluoropolymer and polyethylene pipes depends on specific industry requirements such as chemical exposure, temperature range, and mechanical stress.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Fluoropolymer pipes offer superior chemical resistance and flexibility, reducing the need for frequent maintenance in harsh environments compared to polyethylene. Polyethylene pipes are easier to install with heat fusion techniques and have lower initial costs, but may require more regular inspections due to susceptibility to UV degradation and mechanical damage. Maintenance for fluoropolymer systems typically involves fewer repairs over time, making them suitable for long-term applications despite higher upfront installation complexity.
Cost Analysis and Economic Viability
Fluoropolymer pipes, characterized by high chemical resistance and temperature tolerance, typically incur costs three to five times higher than polyethylene pipes, which offer flexibility and lower initial investment. Polyethylene pipes dominate budget-conscious projects due to affordability and ease of installation, while fluoropolymer pipes justify their premium price in applications demanding exceptional durability and minimal maintenance. Evaluating long-term economic viability requires balancing upfront expenditure against lifespan benefits and operational savings in corrosive or high-temperature environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fluoropolymer pipes, known for their chemical resistance and durability, have a longer lifespan, reducing replacement frequency and waste generation compared to polyethylene pipes. Polyethylene pipes are more widely recyclable and derived from simpler hydrocarbon feedstocks, offering a smaller carbon footprint during production. The environmental impact of fluoropolymers is higher due to complex manufacturing processes and persistence in ecosystems, whereas polyethylene's biodegradability and recyclability enhance sustainability in water and gas pipeline applications.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Pipe Material
Fluoropolymer pipes offer superior chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and excellent lifespan, making them ideal for harsh industrial environments. Polyethylene pipes provide cost-effective, flexible, and corrosion-resistant solutions suitable for water, gas, and low-pressure applications. Selecting the right pipe material depends on specific project requirements including chemical exposure, temperature range, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Fluoropolymer vs Polyethylene for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com