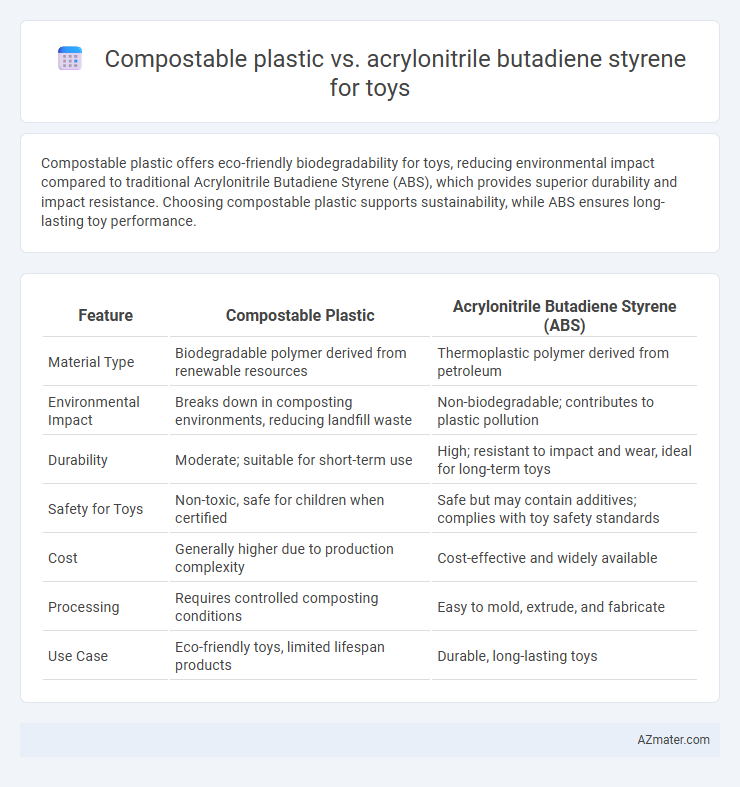
Compostable plastic offers eco-friendly biodegradability for toys, reducing environmental impact compared to traditional Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which provides superior durability and impact resistance. Choosing compostable plastic supports sustainability, while ABS ensures long-lasting toy performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Compostable Plastic | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Biodegradable polymer derived from renewable resources | Thermoplastic polymer derived from petroleum |
| Environmental Impact | Breaks down in composting environments, reducing landfill waste | Non-biodegradable; contributes to plastic pollution |
| Durability | Moderate; suitable for short-term use | High; resistant to impact and wear, ideal for long-term toys |
| Safety for Toys | Non-toxic, safe for children when certified | Safe but may contain additives; complies with toy safety standards |
| Cost | Generally higher due to production complexity | Cost-effective and widely available |
| Processing | Requires controlled composting conditions | Easy to mold, extrude, and fabricate |
| Use Case | Eco-friendly toys, limited lifespan products | Durable, long-lasting toys |
Introduction to Sustainable Toy Materials
Compostable plastics offer an eco-friendly alternative to traditional Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) in toy manufacturing, reducing environmental impact through biodegradability and lower carbon footprint. ABS, a common thermoplastic polymer, provides durability and strength but poses challenges in recycling and long-term environmental sustainability. Choosing compostable plastics supports sustainable toy production by aligning with circular economy principles and minimizing plastic pollution.
Overview of Compostable Plastics
Compostable plastics for toys, primarily made from polylactic acid (PLA) or starch blends, offer an eco-friendly alternative that biodegrades under industrial composting conditions, reducing environmental impact. These materials are designed to break down into non-toxic components within months, making them suitable for short-life products such as toys. Compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), a durable petroleum-based plastic known for impact resistance and long lifespan, compostable plastics present a sustainable option with limitations in heat resistance and mechanical strength.
Properties of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a durable thermoplastic known for its high impact resistance, toughness, and excellent dimensional stability, making it ideal for toy manufacturing. ABS offers superior strength, heat resistance, and ease of molding compared to compostable plastics, which often lack the same mechanical robustness and durability. Its chemical resistance and ability to retain vibrant colors enhance the safety and aesthetic appeal of toys, ensuring long-lasting playability.
Environmental Impact: Compostable Plastics vs ABS
Compostable plastics used in toys significantly reduce environmental impact by breaking down into non-toxic components within months under industrial composting conditions, unlike Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which persists in landfills for centuries due to its non-biodegradable, petroleum-based composition. ABS production involves high energy consumption and emits volatile organic compounds (VOCs), contributing to air pollution and greenhouse gas effects, whereas compostable plastics typically derive from renewable biomass sources, lowering carbon footprint. Disposal of ABS toys exacerbates microplastic pollution and soil contamination, while compostable alternatives support circular economy principles through enhanced biodegradability and reduced ecological toxicity.
Durability and Safety in Toy Applications
Compostable plastics offer eco-friendly advantages but generally lack the durability required for toys subjected to frequent impact and rough handling, unlike acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), which provides high impact resistance, rigidity, and toughness essential for long-lasting toy performance. ABS is non-toxic and widely approved for toy manufacturing, ensuring child safety through resistance to chemicals and heat, whereas compostable plastics may degrade under stress, potentially leading to safety hazards such as sharp edges or fragmented pieces. The superior mechanical properties and established safety standards of ABS make it the preferred material in toy applications where durability and child protection are paramount.
Manufacturing Processes and Feasibility
Compostable plastics are derived from renewable resources such as polylactic acid (PLA) or polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), requiring lower energy inputs during manufacturing and offering biodegradability under industrial composting conditions, which reduces environmental impact. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a petroleum-based thermoplastic known for its high impact resistance and ease of injection molding, facilitating complex toy designs with excellent durability and dimensional stability. The feasibility of compostable plastics in toy production is limited by their lower heat resistance and mechanical strength compared to ABS, making ABS more suitable for mass production despite its environmental drawbacks.
Cost Comparison: Compostable Plastics vs ABS
Compostable plastics for toys generally incur higher material costs compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), with prices ranging from $3 to $6 per kilogram versus ABS's $1.50 to $3 per kilogram. Manufacturing using compostable plastics often requires specialized processing to maintain biodegradability, increasing production expenses by 10-20%. Despite higher upfront costs, compostable plastics offer potential savings in waste management and environmental compliance, which can offset initial investments over time.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Consumer perception of compostable plastic toys is increasingly positive due to growing environmental awareness and demand for sustainable products, while Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) remains favored for its durability and safety in high-quality toys. Market trends indicate a rising shift towards eco-friendly materials, with compostable plastics gaining traction among eco-conscious parents, though ABS still dominates in conventional toy manufacturing due to established safety standards and cost-effectiveness. The toy industry's innovation focuses on balancing biodegradability with performance to meet evolving consumer preferences and regulatory pressures.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Compostable plastics for toys must meet ASTM D6400 and EN 13432 standards to ensure biodegradability and safety for children, whereas Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) complies with stringent regulations such as CPSIA and REACH for chemical toxicity and mechanical safety. Certification bodies like TUV and UL provide eco-labels for compostable plastics, while ABS materials often undergo ASTM F963 testing for mechanical integrity and heavy metal content. Regulatory compliance impacts market acceptance, with compostable plastics favored for environmentally conscious consumers and ABS preferred for durability and stringent safety approvals.
Future Outlook for Eco-Friendly Toy Materials
Compostable plastics offer significant potential in the toy industry by reducing long-term environmental impact through biodegradability and lower carbon footprints compared to conventional materials like Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). Innovations in biopolymer composites are driving improved durability and safety standards, making compostable plastics increasingly viable for sustainable toy manufacturing. Market trends indicate a growing preference for eco-friendly toy materials, supported by stricter environmental regulations and consumer demand for green products.
Infographic: Compostable plastic vs Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene for Toy
 azmater.com
azmater.com