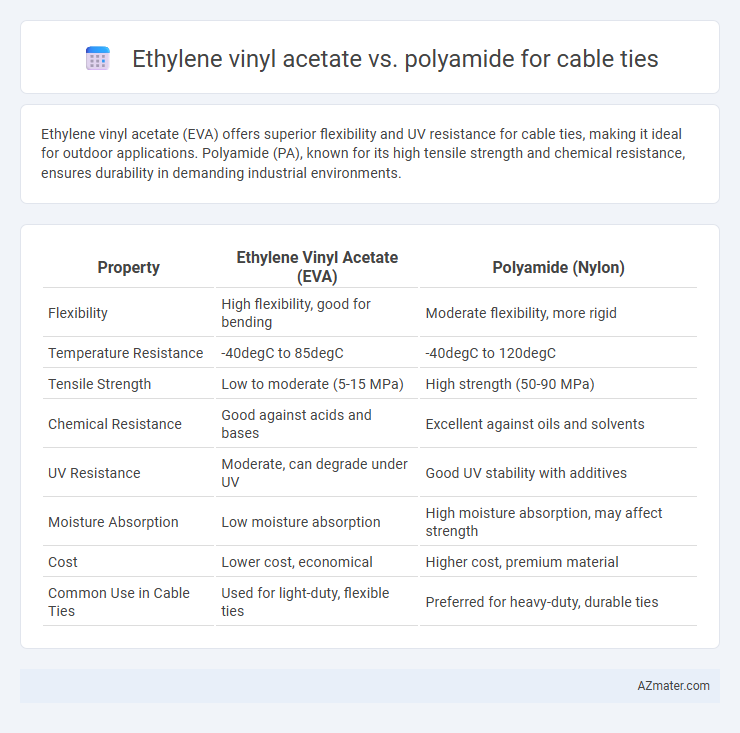
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility and UV resistance for cable ties, making it ideal for outdoor applications. Polyamide (PA), known for its high tensile strength and chemical resistance, ensures durability in demanding industrial environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Polyamide (Nylon) |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High flexibility, good for bending | Moderate flexibility, more rigid |
| Temperature Resistance | -40degC to 85degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Tensile Strength | Low to moderate (5-15 MPa) | High strength (50-90 MPa) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against acids and bases | Excellent against oils and solvents |
| UV Resistance | Moderate, can degrade under UV | Good UV stability with additives |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption | High moisture absorption, may affect strength |
| Cost | Lower cost, economical | Higher cost, premium material |
| Common Use in Cable Ties | Used for light-duty, flexible ties | Preferred for heavy-duty, durable ties |
Introduction to Cable Tie Materials
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) and polyamide (PA) are two common materials used in cable ties, each offering distinct properties suited for various applications. EVA provides excellent flexibility, UV resistance, and weather durability, making it ideal for outdoor and temporary cable management. Polyamide, known for its high tensile strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance, is preferred in heavy-duty industrial settings requiring long-term secure bundling.
Overview of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA)
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) offers excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and UV stability, making it a popular choice for cable ties in outdoor and industrial applications. EVA's lightweight nature and strong adhesion properties enhance cable management by providing a secure yet gentle hold on wires without damaging insulation. Compared to polyamide, EVA exhibits superior resistance to environmental stress cracking and maintains performance in low temperatures, ensuring reliable use in varied conditions.
Properties of Polyamide (Nylon)
Polyamide (Nylon) cable ties exhibit exceptional mechanical strength, high abrasion resistance, and excellent resistance to chemicals and UV radiation, making them ideal for demanding environments. Their superior thermal stability allows use in temperatures ranging from -40degC to 85degC, ensuring long-term durability without deformation. Compared to Ethylene vinyl acetate, Nylon offers greater tensile strength and rigidity, providing secure and reliable cable management in industrial and outdoor applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers flexibility and moderate tensile strength, typically ranging from 10 to 25 MPa, making it suitable for applications requiring some elasticity in cable ties. Polyamide (PA), particularly nylon 6/6, demonstrates superior mechanical strength with tensile values between 70 to 85 MPa, providing enhanced durability and resistance to breakage under stress. The higher crystallinity and molecular structure of polyamide result in better load-bearing capacity and long-term mechanical stability compared to EVA in cable tie applications.
Flexibility and Durability Factors
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility for cable ties, maintaining elasticity in low temperatures and resisting cracking under repeated bending, making it ideal for dynamic applications. Polyamide (PA), commonly known as nylon, demonstrates excellent durability with high tensile strength and resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and UV exposure, ensuring long-lasting performance in harsh environments. While EVA excels in flexibility, polyamide provides enhanced durability, making material selection dependent on specific application requirements for cable management.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers excellent chemical resistance against a wide range of acids, alkalis, and oils, making it suitable for environments with moderate chemical exposure, while providing good UV and weather resistance. Polyamide (PA), commonly known as nylon, exhibits superior mechanical strength and exceptional resistance to hydrocarbons, solvents, and higher temperatures, but can absorb moisture, potentially affecting its performance in humid or wet conditions. In terms of environmental resistance, EVA is favored for flexibility and resistance to ozone degradation, whereas polyamide is preferred for durability in harsh chemical and thermal applications where tensile strength and abrasion resistance are critical.
Temperature Performance and Stability
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility and impact resistance with temperature performance typically ranging from -40degC to 80degC, maintaining stability in moderate thermal conditions. Polyamide (PA), commonly known as nylon, demonstrates higher temperature resistance, usually operating effectively between -40degC and 120degC, with excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength under prolonged heat exposure. In applications requiring high thermal endurance and chemical resistance, polyamide cable ties outperform EVA, which is better suited for environments with lower thermal stress and higher elasticity needs.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers lower raw material and processing costs compared to polyamide, making it a cost-effective choice for cable tie production in high-volume manufacturing. Polyamide, while more expensive, provides superior mechanical strength and thermal resistance, justifying its higher price in demanding applications. Manufacturing EVA cable ties involves simpler extrusion processes with less energy consumption, whereas polyamide requires precise mold control and longer cycle times to achieve optimal material properties.
Typical Applications: EVA vs. Polyamide
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) cable ties are preferred for applications requiring flexibility, UV resistance, and chemical inertness, commonly used in outdoor settings, horticulture, and light bundling tasks. Polyamide (nylon) cable ties dominate in industrial environments due to their high tensile strength, heat resistance, and durability, making them suitable for heavy-duty wiring, automotive, and electrical installations. EVA excels in low-stress, weather-exposed scenarios, while polyamide is the choice for demanding mechanical and thermal conditions in cable management.
Choosing the Right Material for Cable Ties
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers flexibility, UV resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for general-purpose cable ties in indoor environments. Polyamide (PA), commonly known as nylon, provides superior strength, chemical resistance, and durability for demanding applications, particularly in outdoor or industrial settings. Selecting between EVA and polyamide cable ties depends on environmental exposure, tensile strength requirements, and expected lifespan of the installation.
Infographic: Ethylene vinyl acetate vs Polyamide for Cable tie
 azmater.com
azmater.com