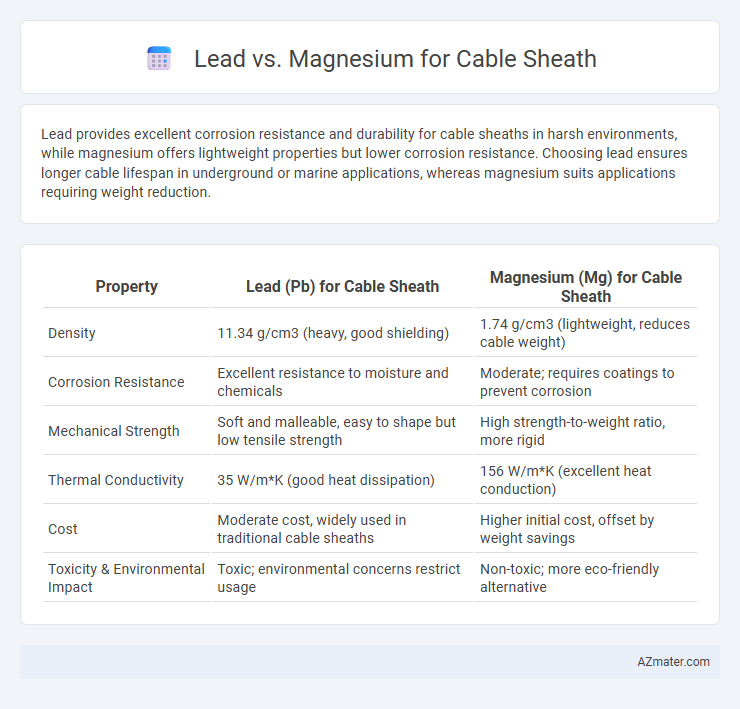
Lead provides excellent corrosion resistance and durability for cable sheaths in harsh environments, while magnesium offers lightweight properties but lower corrosion resistance. Choosing lead ensures longer cable lifespan in underground or marine applications, whereas magnesium suits applications requiring weight reduction.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lead (Pb) for Cable Sheath | Magnesium (Mg) for Cable Sheath |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 11.34 g/cm3 (heavy, good shielding) | 1.74 g/cm3 (lightweight, reduces cable weight) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent resistance to moisture and chemicals | Moderate; requires coatings to prevent corrosion |
| Mechanical Strength | Soft and malleable, easy to shape but low tensile strength | High strength-to-weight ratio, more rigid |
| Thermal Conductivity | 35 W/m*K (good heat dissipation) | 156 W/m*K (excellent heat conduction) |
| Cost | Moderate cost, widely used in traditional cable sheaths | Higher initial cost, offset by weight savings |
| Toxicity & Environmental Impact | Toxic; environmental concerns restrict usage | Non-toxic; more eco-friendly alternative |
Introduction to Cable Sheath Materials
Lead and magnesium are two commonly used materials for cable sheaths, each offering distinct advantages in protection and durability. Lead provides excellent corrosion resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for underground and submarine cables where moisture and chemical exposure are prevalent. Magnesium, although less traditional, offers a lightweight alternative with good mechanical strength and improved environmental sustainability, making it suitable for specific applications requiring reduced cable weight.
Overview of Lead and Magnesium Sheath Applications
Lead cable sheaths offer excellent corrosion resistance and long-term durability, making them ideal for underground and submarine power cables in harsh environments. Magnesium sheaths provide lightweight protection with good thermal conductivity and are often used in applications where weight reduction and heat dissipation are critical, such as aerospace and certain industrial cables. Both materials enhance cable lifespan and performance, with lead favored for its impermeability and magnesium chosen for its strength-to-weight ratio.
Physical Properties: Lead vs Magnesium
Lead offers high density and excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for durable cable sheaths in harsh environments. Magnesium, with its significantly lower density and high strength-to-weight ratio, provides lightweight protection but has less inherent corrosion resistance compared to lead. The choice between lead and magnesium for cable sheaths depends on the balance between weight requirements and environmental durability.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Magnesium offers superior corrosion resistance compared to lead in cable sheaths due to its naturally forming protective oxide layer that inhibits chemical degradation. Lead, while traditionally used, is more susceptible to corrosion in acidic or sulphide-rich environments, leading to potential sheath failures. Choosing magnesium enhances the durability and longevity of cable sheaths, particularly in aggressive or marine conditions.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Magnesium offers superior mechanical strength compared to lead in cable sheaths, providing enhanced resistance to impact and external mechanical stresses. Its higher tensile strength ensures better durability under bending and flexing conditions, making it ideal for flexible cable applications. Lead, while more malleable, lacks the structural rigidity of magnesium, resulting in lower overall mechanical performance and reduced flexibility in dynamic environments.
Weight and Density Differences
Lead's density of approximately 11.34 g/cm3 significantly exceeds magnesium's density of around 1.74 g/cm3, resulting in heavier cable sheaths when using lead. Magnesium offers a lightweight alternative, greatly reducing overall cable weight and improving handling and installation efficiency. The substantial weight difference impacts transportation costs and structural support requirements in cable design.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Lead cable sheaths pose significant environmental risks due to their toxicity and potential for soil and water contamination during corrosion and disposal. Magnesium offers a more sustainable alternative with its lower toxicity, better recyclability, and reduced environmental footprint throughout the cable lifecycle. Selecting magnesium over lead enhances cable sheath sustainability by minimizing hazardous waste and promoting eco-friendly materials management.
Cost Analysis: Lead vs Magnesium
Magnesium offers a significantly lower raw material cost compared to lead, making it a cost-effective option for cable sheaths in large-scale production. Lead's higher density and material price contribute to increased transportation and handling expenses, further elevating overall project costs. Considering long-term economic benefits, magnesium's lighter weight and better corrosion resistance reduce maintenance and replacement costs, enhancing its value over lead in cable sheath applications.
Safety Considerations and Health Risks
Lead cable sheaths pose significant health risks due to lead's toxicity, causing potential lead poisoning and environmental contamination during installation or disposal. Magnesium, while less toxic, requires careful handling to prevent fire hazards as it is highly reactive and flammable, especially in powdered or thin strip forms. Safety measures for lead include using protective gear and proper waste management, whereas magnesium demands stringent controls against ignition sources and adequate ventilation.
Industry Trends and Future Outlook
Lead cable sheaths have traditionally offered excellent corrosion resistance and durability, but industry trends are shifting towards magnesium due to its lighter weight and enhanced environmental sustainability. Advances in magnesium alloy formulations improve mechanical strength and protective qualities, promoting wider adoption in subsea and industrial cable applications. The future outlook indicates increased investment in magnesium sheath technologies driven by stricter environmental regulations and the demand for more efficient, eco-friendly cable solutions.
Infographic: Lead vs Magnesium for Cable Sheath
 azmater.com
azmater.com