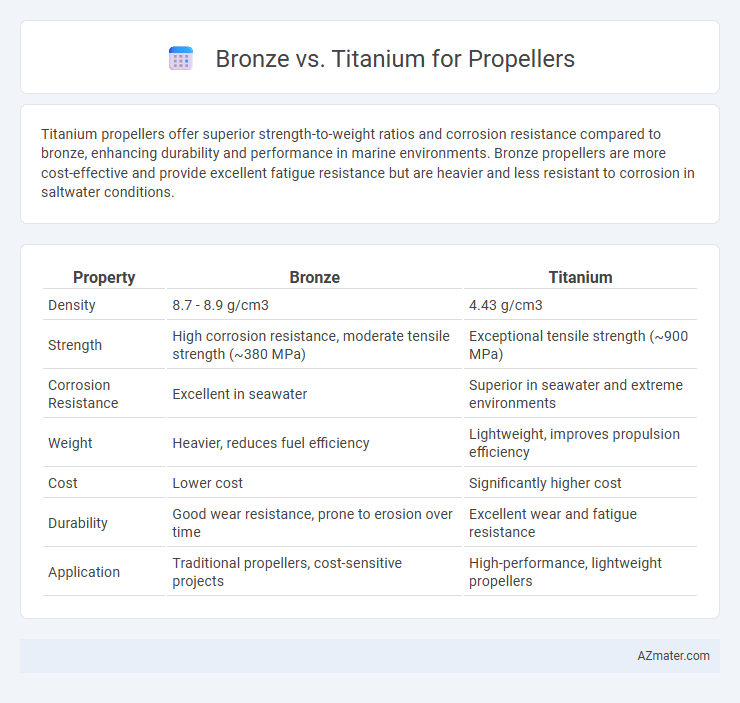
Titanium propellers offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance compared to bronze, enhancing durability and performance in marine environments. Bronze propellers are more cost-effective and provide excellent fatigue resistance but are heavier and less resistant to corrosion in saltwater conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bronze | Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 8.7 - 8.9 g/cm3 | 4.43 g/cm3 |
| Strength | High corrosion resistance, moderate tensile strength (~380 MPa) | Exceptional tensile strength (~900 MPa) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in seawater | Superior in seawater and extreme environments |
| Weight | Heavier, reduces fuel efficiency | Lightweight, improves propulsion efficiency |
| Cost | Lower cost | Significantly higher cost |
| Durability | Good wear resistance, prone to erosion over time | Excellent wear and fatigue resistance |
| Application | Traditional propellers, cost-sensitive projects | High-performance, lightweight propellers |
Introduction to Propeller Materials
Bronze and titanium are two popular materials used in manufacturing marine propellers due to their distinct mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. Bronze propellers, commonly made from manganese or nickel-aluminum bronze alloys, offer excellent durability in saltwater environments and are known for their affordability and ease of casting. Titanium propellers deliver superior strength-to-weight ratios and outstanding corrosion resistance, making them ideal for high-performance vessels and applications requiring lightweight yet robust components.
Overview of Bronze Propellers
Bronze propellers are widely favored in marine applications due to their excellent corrosion resistance, durability, and ability to withstand harsh saltwater environments. These propellers provide superior strength and fatigue resistance, making them ideal for both recreational and commercial vessels. Their dense material composition also contributes to improved propulsion efficiency and reduced vibration compared to other metals.
Overview of Titanium Propellers
Titanium propellers offer superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to bronze, providing enhanced durability and corrosion resistance in marine environments. Their lightweight nature improves fuel efficiency and maneuverability while maintaining excellent fatigue resistance under high stress. While titanium propellers command a higher initial cost, their longevity and reduced maintenance needs deliver significant long-term performance benefits for advanced marine applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Titanium propellers offer superior strength compared to bronze, with a tensile strength of approximately 950 MPa versus bronze's 350-750 MPa range, making them more resistant to deformation under high stress. In terms of durability, titanium exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance in marine environments, significantly reducing maintenance and extending service life, whereas bronze, although corrosion-resistant, is more prone to erosion and fatigue over time. The combined strength and corrosion resistance of titanium result in a propeller that maintains optimal performance and reliability over a longer operational lifespan.
Corrosion Resistance: Bronze vs Titanium
Titanium exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to bronze, making it highly effective in harsh marine environments where saltwater exposure is constant. Bronze, while corrosion-resistant and traditionally used for propellers, is more susceptible to dezincification and galvanic corrosion when in contact with dissimilar metals. The enhanced corrosion resistance of titanium ensures longer propeller lifespan and reduced maintenance costs in saltwater applications.
Weight and Performance Differences
Bronze propellers are heavier than titanium ones, typically weighing about 20-30% more, which affects overall vessel weight and fuel efficiency. Titanium offers superior strength-to-weight ratio, providing enhanced performance through reduced rotational inertia and improved acceleration. The lighter titanium propellers also resist corrosion better, maintaining peak efficiency longer than bronze in marine environments.
Cost Analysis: Bronze vs Titanium
Bronze propellers generally cost 30-50% less than titanium due to the abundance and lower processing expenses of copper alloys compared to titanium's complex manufacturing requirements. The long-term investment in titanium propellers can be justified by their superior corrosion resistance and strength-to-weight ratio, potentially reducing maintenance and replacement costs over time. Evaluating lifecycle expenses, bronze remains budget-friendly initially, while titanium offers better value for high-performance or harsh marine environments.
Maintenance and Longevity
Bronze propellers exhibit excellent corrosion resistance and durability in marine environments, requiring periodic cleaning and occasional polishing to maintain optimal performance. Titanium propellers offer superior strength and resistance to corrosion, significantly reducing maintenance frequency and extending lifespan compared to bronze. The lightweight nature of titanium also contributes to lower wear and tear, enhancing overall longevity in demanding marine applications.
Suitability for Marine Environments
Titanium offers superior corrosion resistance compared to bronze, making it highly suitable for marine environments with high salinity and varying pH levels. Bronze, while durable and cost-effective, is more prone to galvanic corrosion and biofouling, requiring regular maintenance in seawater applications. Titanium's lightweight and strength-to-weight ratio enhance propeller efficiency and longevity in harsh oceanic conditions, outperforming traditional bronze alloys.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Propeller
Bronze propellers offer exceptional corrosion resistance and are highly durable, making them ideal for saltwater applications, while titanium propellers provide superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced fatigue resistance, ideal for high-performance or racing boats. Choosing the right material depends on factors such as operating environment, budget, and performance requirements, with bronze favored for its cost-effectiveness and titanium valued for lightweight strength and longevity. Understanding the differences in mechanical properties and corrosion resistance ensures optimal propulsion efficiency and lifespan for your vessel.
Infographic: Bronze vs Titanium for Propeller
 azmater.com
azmater.com