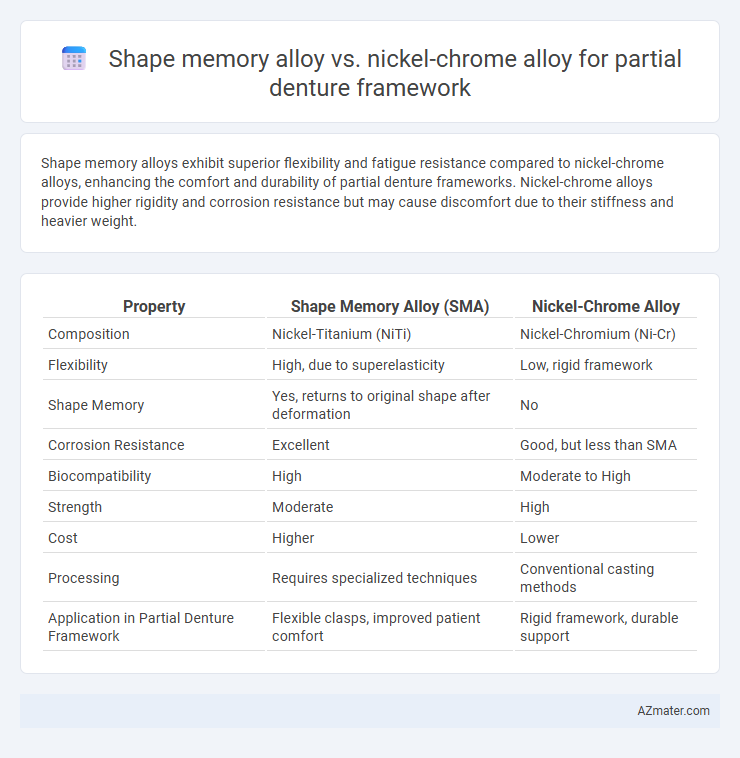
Shape memory alloys exhibit superior flexibility and fatigue resistance compared to nickel-chrome alloys, enhancing the comfort and durability of partial denture frameworks. Nickel-chrome alloys provide higher rigidity and corrosion resistance but may cause discomfort due to their stiffness and heavier weight.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) | Nickel-Chrome Alloy |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) | Nickel-Chromium (Ni-Cr) |
| Flexibility | High, due to superelasticity | Low, rigid framework |
| Shape Memory | Yes, returns to original shape after deformation | No |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good, but less than SMA |
| Biocompatibility | High | Moderate to High |
| Strength | Moderate | High |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Processing | Requires specialized techniques | Conventional casting methods |
| Application in Partial Denture Framework | Flexible clasps, improved patient comfort | Rigid framework, durable support |
Introduction to Partial Denture Framework Alloys
Partial denture frameworks require alloys with optimal strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility to ensure durability and patient comfort. Shape memory alloys, commonly based on nickel-titanium, offer flexibility and excellent elasticity, allowing for improved adaptation and retention in partial dentures. Nickel-chrome alloys provide high rigidity and corrosion resistance, making them a traditional choice for strong, stable frameworks in prosthodontics.
Overview of Shape Memory Alloys in Dentistry
Shape memory alloys (SMAs), primarily composed of nickel-titanium (NiTi), exhibit unique superelasticity and shape recovery properties ideal for partial denture frameworks. Their ability to undergo significant deformation and return to original shape enhances flexibility and retention compared to traditional nickel-chrome alloys, which are rigid and prone to fatigue over time. The biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and stress-induced phase transformation of SMAs improve patient comfort and framework longevity in dental applications.
Properties and Composition of Nickel-Chrome Alloys
Nickel-chrome alloys used in partial denture frameworks exhibit high corrosion resistance, excellent mechanical strength, and biocompatibility due to their primary composition of nickel, chromium, and minor amounts of molybdenum or beryllium. These alloys provide superior rigidity and durability compared to shape memory alloys, which are valued for their elasticity and ability to return to original shape after deformation. While nickel-chrome alloys ensure a stable and robust framework, their higher modulus of elasticity results in less flexibility than shape memory alloys, influencing prosthetic comfort and adaptation.
Biocompatibility: Shape Memory vs. Nickel-Chrome Alloys
Shape memory alloys exhibit superior biocompatibility compared to nickel-chrome alloys due to their excellent corrosion resistance and reduced ion release, minimizing allergic reactions in patients. Nickel-chrome alloys often pose concerns related to nickel ion leaching, which can trigger hypersensitivity and cytotoxic effects in sensitive individuals. The enhanced biocompatibility of shape memory alloys, such as nickel-titanium (NiTi), supports safer long-term use in partial denture frameworks.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility Comparison
Shape memory alloys (SMAs), such as nickel-titanium, exhibit superior flexibility and excellent elastic recovery compared to nickel-chrome alloys, making them ideal for partial denture frameworks that require resilience under repeated stress. Nickel-chrome alloys provide higher mechanical strength and stiffness, offering better support and durability in frameworks but with less flexibility, which can increase the risk of framework fracture under cyclic loading. The choice between SMAs and nickel-chrome alloys depends on balancing the need for mechanical strength with the desired flexibility to accommodate functional movements in partial denture applications.
Corrosion Resistance in Oral Environments
Shape memory alloys (SMAs), particularly nickel-titanium (NiTi), exhibit superior corrosion resistance in oral environments compared to nickel-chrome (Ni-Cr) alloys due to the formation of a stable titanium oxide passive layer that prevents ion release and metal degradation. Nickel-chrome alloys are more prone to corrosion in the presence of saliva and acidic conditions, leading to potential metal ion leaching and allergic reactions in sensitive patients. The enhanced corrosion resistance of SMAs contributes to increased biocompatibility, longevity, and reduced risk of metallic taste or oral mucosal irritation in partial denture frameworks.
Clinical Performance and Longevity
Shape memory alloys (SMAs) used in partial denture frameworks exhibit superior flexibility and resilience compared to nickel-chrome alloys, enabling better adaptability to oral tissues and reducing the risk of framework deformation under masticatory forces. Clinical studies show that SMAs maintain consistent retention and comfort over extended periods, while nickel-chrome alloys, although offering high rigidity and corrosion resistance, may cause patient discomfort due to their stiffness and potential for localized stress concentrations. Longevity assessments indicate that nickel-chrome frameworks generally have a longer service life due to their durable material properties, but SMAs provide enhanced patient satisfaction and fewer adjustments during routine dental visits.
Patient Comfort and Adaptability
Shape memory alloys (SMAs) offer superior patient comfort in partial denture frameworks due to their flexibility and ability to return to their original shape, reducing pressure points and minimizing mucosal irritation. Nickel-chrome alloys, while rigid and durable, may cause discomfort from their stiffness and limited adaptability, leading to increased risk of soft tissue trauma. The adaptability of SMAs enhances accommodation to oral dynamics, providing a more secure and less intrusive fit, which significantly improves patient acceptance and compliance.
Cost-Efficiency and Accessibility
Shape memory alloys, such as nickel-titanium, offer superior flexibility and corrosion resistance for partial denture frameworks but often come at a higher cost compared to traditional nickel-chrome alloys. Nickel-chrome alloys provide a more cost-efficient option with widespread availability and established fabrication protocols, making them accessible for routine dental practice. The long-term cost-effectiveness of nickel-chrome stems from its durability and ease of repair, whereas shape memory alloys may reduce adjustments and improve patient comfort despite their initial expense.
Future Trends and Recommendations
Shape memory alloys (SMAs), such as nickel-titanium, offer superior flexibility and biocompatibility for partial denture frameworks compared to traditional nickel-chrome alloys, which provide rigidity and strength but may cause allergic reactions in some patients. Future trends in dental prosthetics emphasize the integration of SMAs due to their unique ability to adapt to oral movements, enhancing patient comfort and retention. Clinical recommendations advocate for the selective use of SMAs in cases requiring improved elasticity and reduced metal bulk, while nickel-chrome remains preferable for frameworks demanding high mechanical resistance.
Infographic: Shape memory alloy vs Nickel-chrome alloy for Partial denture framework
 azmater.com
azmater.com