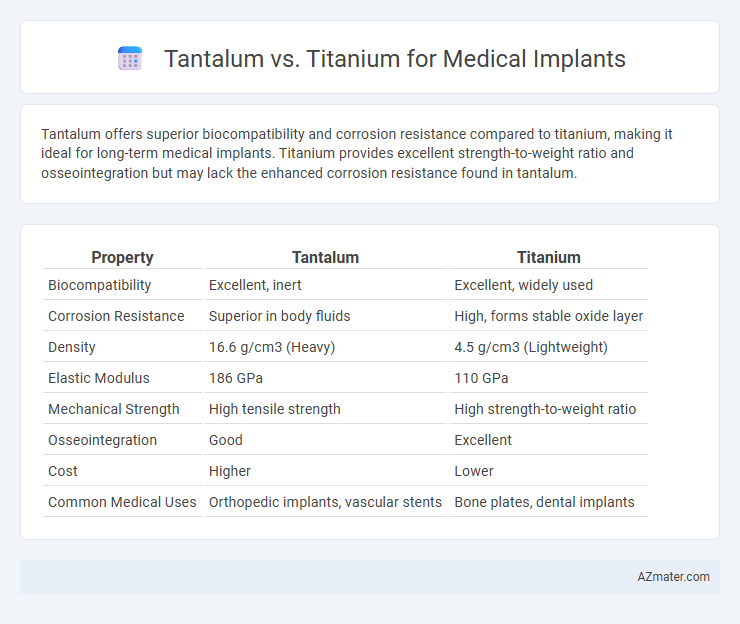
Tantalum offers superior biocompatibility and corrosion resistance compared to titanium, making it ideal for long-term medical implants. Titanium provides excellent strength-to-weight ratio and osseointegration but may lack the enhanced corrosion resistance found in tantalum.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tantalum | Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Biocompatibility | Excellent, inert | Excellent, widely used |
| Corrosion Resistance | Superior in body fluids | High, forms stable oxide layer |
| Density | 16.6 g/cm3 (Heavy) | 4.5 g/cm3 (Lightweight) |
| Elastic Modulus | 186 GPa | 110 GPa |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength | High strength-to-weight ratio |
| Osseointegration | Good | Excellent |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Common Medical Uses | Orthopedic implants, vascular stents | Bone plates, dental implants |
Introduction to Tantalum and Titanium in Medical Implants
Tantalum and titanium are prominent metals used in medical implants due to their exceptional biocompatibility and corrosion resistance. Tantalum exhibits outstanding osteointegration owing to its porous structure, making it ideal for bone-related applications. Titanium is favored for its high strength-to-weight ratio and ability to form a stable oxide layer, ensuring long-term durability and compatibility with human tissue.
Biocompatibility Comparison: Tantalum vs Titanium
Tantalum exhibits superior biocompatibility compared to titanium due to its exceptional corrosion resistance and excellent osteointegration properties, which minimize inflammatory responses and promote bone growth. Titanium, while also highly biocompatible and widely used in medical implants, can occasionally cause metal ion release leading to localized allergic reactions. Studies highlight tantalum's porous structure that enhances cell attachment and vascularization, making it advantageous for long-term implant stability over titanium.
Mechanical Properties and Strength Differences
Tantalum exhibits superior corrosion resistance and exceptional biocompatibility, making it highly suitable for long-term medical implants, with a tensile strength typically around 200-300 MPa. Titanium, specifically Ti-6Al-4V alloy, offers a higher tensile strength of approximately 900 MPa and excellent fatigue resistance, which is crucial for load-bearing applications. Despite titanium's greater mechanical strength, tantalum's excellent ductility and elasticity modulus closer to human bone reduce stress shielding, improving implant integration and longevity.
Corrosion Resistance in Biological Environments
Tantalum exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to titanium in biological environments due to its stable oxide layer that prevents ion release and material degradation. Titanium also forms a protective oxide layer but is more susceptible to localized corrosion such as pitting in chloride-rich bodily fluids. The enhanced biocompatibility and longevity of tantalum implants stem from their exceptional resistance to bio-corrosion, making them ideal for long-term medical implant applications.
Osseointegration: Implant Integration with Bone
Tantalum exhibits exceptional osseointegration due to its porous structure that mimics cancellous bone, enhancing osteoblast adhesion and vascularization. Titanium, widely used in medical implants, offers excellent biocompatibility and forms a stable oxide layer that promotes bone cell attachment and mineralization. Clinical studies demonstrate that tantalum's superior bone ingrowth and integration often result in faster healing times and improved implant stability compared to titanium.
Imaging Compatibility: MRI and X-Ray Considerations
Tantalum offers superior imaging compatibility in MRI due to its non-ferromagnetic properties, resulting in minimal artifact production and clearer images, crucial for accurate diagnosis and follow-up. Titanium, while also biocompatible and widely used, generates more pronounced artifacts during MRI scans but provides excellent radiopacity for X-rays, facilitating easy implant localization. Choosing between tantalum and titanium hinges on balancing MRI clarity with X-ray visibility based on clinical imaging requirements.
Allergic Reactions and Patient Safety
Tantalum exhibits superior biocompatibility with a lower incidence of allergic reactions compared to titanium, making it a preferred choice for patients sensitive to metal allergies. Titanium, while widely used due to its strength and corrosion resistance, can occasionally cause hypersensitivity in some patients, potentially leading to implant rejection or complications. Patient safety is enhanced by choosing tantalum implants in cases where allergy testing indicates titanium sensitivity, ensuring minimized immune response and improved implant integration.
Longevity and Durability of Implants
Tantalum and titanium are both highly regarded for medical implants due to their exceptional biocompatibility and corrosion resistance. Tantalum offers superior longevity with its extreme durability, resistance to wear, and excellent osseointegration, making it ideal for implants requiring long-term stability. Titanium provides excellent strength-to-weight ratio and fatigue resistance, ensuring durable performance under physiological stress, though its longevity can be slightly less than tantalum in highly demanding environments.
Cost and Availability in the Medical Market
Tantalum and titanium are prominent materials in the medical implant market, with titanium generally favored due to its lower cost and greater availability. Titanium offers excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance while being significantly more abundant and less expensive than tantalum. The high cost and limited availability of tantalum restrict its use primarily to specialized implants where superior radiopacity or osseointegration properties justify the expense.
Clinical Applications and Future Trends
Tantalum exhibits exceptional biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and osteointegration, making it ideal for orthopedic and dental implants, particularly in load-bearing applications where bone ingrowth is critical. Titanium, renowned for its strength-to-weight ratio and widespread clinical use, dominates in cardiovascular stents, dental implants, and joint replacements due to its proven durability and favorable biomechanical properties. Emerging trends in medical implants emphasize surface modification and 3D printing technologies to optimize tantalum and titanium constructs, enhancing personalized treatment and accelerating recovery times.
Infographic: Tantalum vs Titanium for Medical Implant
 azmater.com
azmater.com