Platinum offers superior corrosion resistance and conductivity, making it ideal for precision industrial tools requiring durability in harsh environments. Steel provides higher tensile strength and cost-effectiveness, suitable for heavy-duty applications where wear resistance is critical.
Table of Comparison
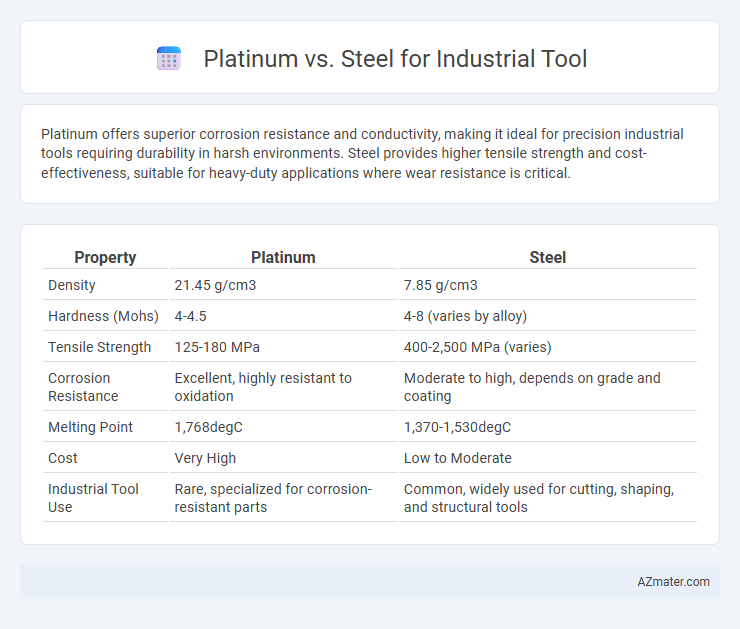
| Property | Platinum | Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 21.45 g/cm3 | 7.85 g/cm3 |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 4-4.5 | 4-8 (varies by alloy) |
| Tensile Strength | 125-180 MPa | 400-2,500 MPa (varies) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, highly resistant to oxidation | Moderate to high, depends on grade and coating |
| Melting Point | 1,768degC | 1,370-1,530degC |
| Cost | Very High | Low to Moderate |
| Industrial Tool Use | Rare, specialized for corrosion-resistant parts | Common, widely used for cutting, shaping, and structural tools |
Introduction: Platinum vs Steel in Industrial Tools
Platinum offers exceptional corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability, making it ideal for industrial tools used in harsh chemical environments or precision applications. Steel, especially tool-grade alloys like high-speed steel (HSS), provides superior hardness, strength, and cost-effectiveness for heavy-duty machining and cutting operations. Selecting between platinum and steel depends on specific tool requirements, balancing durability, resistance, and economic considerations in industrial settings.
Material Composition and Properties
Platinum, a dense and corrosion-resistant metal with a melting point of 1,768degC, offers exceptional chemical stability and excellent wear resistance, making it suitable for precision industrial tools exposed to harsh environments. Steel, primarily composed of iron and carbon with varying alloying elements such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, provides superior tensile strength, toughness, and cost-effectiveness, ideal for heavy-duty tooling applications requiring durability and impact resistance. The material composition of steel enables customization for specific mechanical properties, whereas platinum's unique properties deliver long-lasting performance in specialized industrial processes.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Platinum exhibits exceptional resistance to corrosion and high-temperature oxidation, making it highly durable for specialized industrial tools, though its relatively lower hardness limits wear resistance compared to steel. Steel, particularly alloy and tool steels, offers superior strength, hardness, and impact resistance, enabling longer tool life under heavy mechanical stress and abrasive conditions. For tools demanding extreme toughness and wear resistance, steel remains the preferred choice due to its balance of strength and durability.
Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
Platinum offers exceptional corrosion resistance and chemical inertness, making it ideal for industrial tools exposed to aggressive environments and harsh chemicals. Steel, while strong and cost-effective, is more susceptible to corrosion and requires additional coatings or treatments to withstand chemical exposure. Choosing platinum significantly extends tool lifespan and reliability in applications where chemical resistance is critical.
Thermal Conductivity and Heat Tolerance
Platinum exhibits superior thermal conductivity at approximately 72 W/m*K, enabling efficient heat dissipation in industrial tools compared to steel, which ranges between 15-50 W/m*K depending on the alloy. The heat tolerance of platinum significantly surpasses steel, with a melting point of 1,768degC versus roughly 1,370degC for common steel grades, making platinum ideal for high-temperature applications. This enhanced thermal performance and heat resistance contribute to improved tool longevity and consistent performance under extreme operational conditions.
Manufacturing and Machinability
Platinum offers superior resistance to corrosion and high temperatures, making it ideal for precision molds and specialized tooling in chemical and aerospace manufacturing. Steel's excellent machinability, combined with its strength and cost-effectiveness, dominates general industrial tool production for cutting, shaping, and forming operations. Selecting platinum enhances durability in extreme environments, whereas steel provides versatile and efficient manufacturing adaptability.
Cost-Effectiveness and Economic Impact
Steel remains the preferred material for industrial tools due to its superior cost-effectiveness, offering high durability and strength at a fraction of platinum's price. Platinum, though highly corrosion-resistant and conductive, is significantly more expensive, making it less viable for large-scale industrial applications where budget constraints are critical. The economic impact of choosing steel over platinum translates into lower production costs and increased accessibility for manufacturing sectors reliant on reliable, cost-efficient tooling solutions.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Platinum offers superior corrosion resistance and recyclability, reducing the environmental impact associated with frequent tool replacement in industrial applications. Steel, widely used due to its strength and cost-effectiveness, has a higher carbon footprint from mining and production processes but remains recyclable, contributing to resource efficiency. Choosing between platinum and steel for industrial tools depends on balancing durability, lifecycle emissions, and material sourcing sustainability.
Common Applications in Industry
Platinum is preferred in chemical processing industries for its exceptional corrosion resistance and catalytic properties, especially in sensors and laboratory equipment. Steel, particularly stainless steel, dominates in manufacturing tools, construction, and heavy machinery due to its high strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Both materials are selected based on application-specific requirements such as temperature resistance, mechanical stress, and exposure to corrosive environments.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Industrial Tool
Platinum offers exceptional corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability, making it ideal for specialized industrial tools operating in extreme environments. Steel provides superior strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness for most general industrial applications, including cutting, shaping, and heavy-duty tasks. Selecting the right material depends on operational conditions, required tool longevity, and budget constraints, with steel favored for durability and platinum chosen for chemical resistance and heat tolerance.
Infographic: Platinum vs Steel for Industrial Tool
 azmater.com
azmater.com