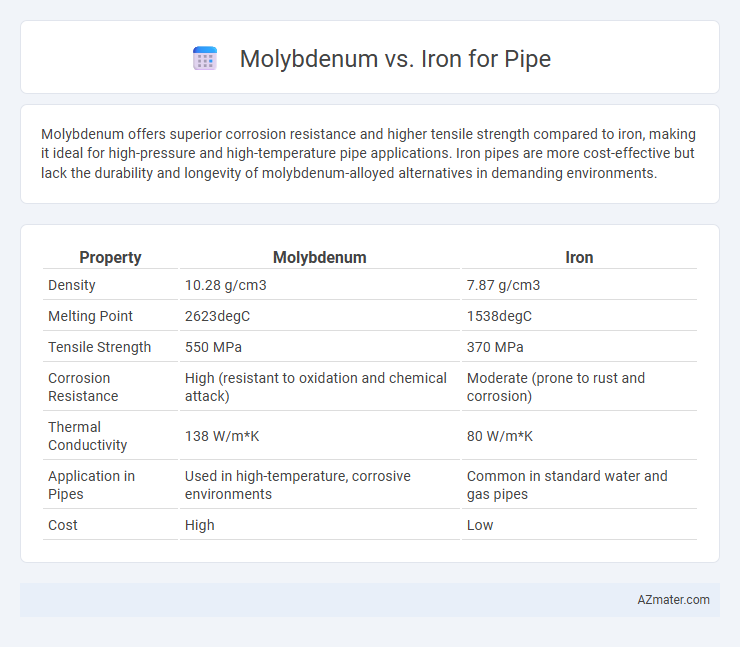
Molybdenum offers superior corrosion resistance and higher tensile strength compared to iron, making it ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature pipe applications. Iron pipes are more cost-effective but lack the durability and longevity of molybdenum-alloyed alternatives in demanding environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Molybdenum | Iron |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 10.28 g/cm3 | 7.87 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 2623degC | 1538degC |
| Tensile Strength | 550 MPa | 370 MPa |
| Corrosion Resistance | High (resistant to oxidation and chemical attack) | Moderate (prone to rust and corrosion) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 138 W/m*K | 80 W/m*K |
| Application in Pipes | Used in high-temperature, corrosive environments | Common in standard water and gas pipes |
| Cost | High | Low |
Introduction to Molybdenum and Iron in Pipe Manufacturing
Molybdenum enhances pipe manufacturing by providing exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature stability, making it ideal for demanding industrial applications. Iron, primarily used in carbon steel pipes, offers cost-effective durability and good tensile strength but lacks the superior corrosion resistance and heat tolerance provided by molybdenum alloys. The integration of molybdenum in steel pipes increases performance in aggressive environments such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation.
Chemical and Physical Properties Compared
Molybdenum exhibits higher corrosion resistance and a melting point of 2,623degC compared to iron's 1,538degC, making it ideal for high-temperature pipe applications. Its density is lower at 10.28 g/cm3 versus iron's 7.87 g/cm3, contributing to different mechanical strengths and weight considerations. Chemically, molybdenum is less reactive and forms stable oxides, enhancing durability in harsh environments where iron pipes may quickly oxidize and degrade.
Strength and Durability of Molybdenum vs Iron Pipes
Molybdenum pipes exhibit superior strength compared to iron pipes, with tensile strength often exceeding 600 MPa, making them ideal for high-pressure applications. The durability of molybdenum is enhanced by its excellent corrosion resistance and high melting point of 2,623degC, which prevents deformation under extreme temperatures. Iron pipes, generally less resistant to corrosion and wear, tend to have shorter lifespans in harsh environments compared to molybdenum's robust performance.
Corrosion Resistance: Which Metal Performs Better?
Molybdenum offers superior corrosion resistance compared to iron, especially in harsh environments involving acids, chlorides, and high temperatures. Its ability to form stable oxide layers significantly reduces the risk of rust and pitting, making it ideal for chemical processing and marine applications. Iron, while widely used for pipes, is more susceptible to oxidation and corrosion, requiring protective coatings or treatments to enhance durability.
Weight and Ease of Fabrication Differences
Molybdenum pipes are significantly lighter than iron pipes, offering an advantage in applications where weight reduction is critical. The fabrication of molybdenum is generally easier due to its superior corrosion resistance and ability to maintain strength at high temperatures, resulting in less frequent maintenance and welding. In contrast, iron pipes are heavier and require more intensive fabrication processes to prevent rust and ensure durability.
Cost Analysis: Molybdenum Pipes vs Iron Pipes
Molybdenum pipes typically incur higher upfront costs compared to iron pipes due to the rarity and advanced processing required for molybdenum. However, molybdenum's superior corrosion resistance and strength contribute to longer service life and reduced maintenance expenses, potentially offsetting initial expenditures. In contrast, iron pipes offer lower initial costs but may involve frequent replacements and higher maintenance in corrosive environments, increasing total lifetime costs.
Applications: Where Is Each Metal Preferred?
Molybdenum is preferred in high-temperature, corrosive environments such as chemical processing plants and power generation boilers due to its exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand extreme heat. Iron pipes, particularly cast and ductile iron, are commonly used in water, sewage, and gas distribution systems because of their cost-effectiveness, mechanical strength, and ease of fabrication. Applications requiring enhanced durability in aggressive environments favor molybdenum-alloyed pipes, while infrastructure projects with standard pressure and temperature demands typically utilize iron piping.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Molybdenum enhances steel pipes by improving corrosion resistance and extending lifespan, reducing the frequency of replacements and minimizing resource consumption. Iron pipes, while abundant and recyclable, often require more maintenance and replacement due to corrosion, leading to higher environmental impact over time. The integration of molybdenum in pipe alloys supports sustainability through durability and lower environmental footprint in manufacturing and lifecycle management.
Lifespan and Maintenance Requirements
Molybdenum-enhanced steel pipes exhibit superior corrosion resistance and higher strength compared to traditional iron pipes, significantly extending their lifespan in demanding environments. The enhanced durability reduces the frequency of maintenance, as these pipes resist pitting and stress corrosion cracking more effectively. Iron pipes require more frequent inspections and maintenance due to their susceptibility to rust and degradation, leading to shorter service life and higher long-term costs.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Metal for Pipes
Molybdenum enhances pipe resistance to corrosion, high temperatures, and mechanical stress, making it ideal for demanding industrial applications, while iron offers cost-effective strength for general plumbing and structural pipes. The choice between molybdenum and iron pipes depends on specific requirements such as environmental exposure, durability, and budget constraints. Selecting the right metal ensures optimal performance, longevity, and safety tailored to the intended pipe usage.
Infographic: Molybdenum vs Iron for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com