Aluminum wheels offer excellent corrosion resistance and durability, while magnesium wheels provide superior lightweight performance and enhanced acceleration. Choosing between aluminum and magnesium depends on balancing weight reduction with cost and strength requirements for optimal wheel performance.
Table of Comparison
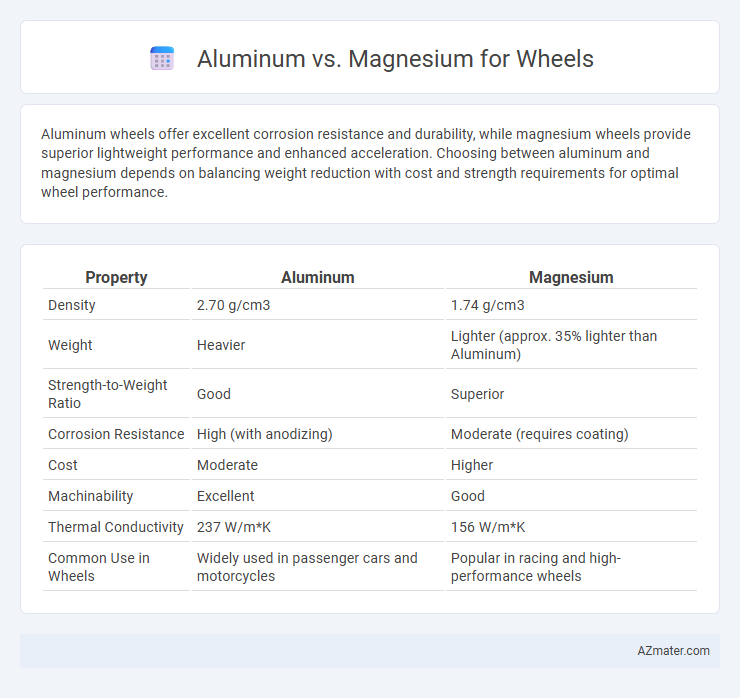
| Property | Aluminum | Magnesium |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 2.70 g/cm3 | 1.74 g/cm3 |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter (approx. 35% lighter than Aluminum) |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Good | Superior |
| Corrosion Resistance | High (with anodizing) | Moderate (requires coating) |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
| Machinability | Excellent | Good |
| Thermal Conductivity | 237 W/m*K | 156 W/m*K |
| Common Use in Wheels | Widely used in passenger cars and motorcycles | Popular in racing and high-performance wheels |
Introduction: Choosing the Right Material for Wheels
Aluminum wheels offer excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight properties, and strong durability, making them a popular choice for everyday driving and performance vehicles. Magnesium wheels are even lighter than aluminum, providing superior weight reduction and enhanced handling, though they require careful maintenance due to their susceptibility to corrosion. Selecting between aluminum and magnesium wheels depends on balancing weight savings, strength, cost, and environmental exposure for specific driving needs.
Overview of Aluminum and Magnesium Wheels
Aluminum wheels are widely preferred for their excellent balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and affordability, making them a practical choice for everyday vehicles. Magnesium wheels, known for their significantly lighter weight and superior performance in racing applications, offer enhanced acceleration and handling but come at a higher cost and require more maintenance due to susceptibility to corrosion. The choice between aluminum and magnesium wheels depends on factors such as vehicle type, budget, and performance requirements.
Weight Comparison: Aluminum vs Magnesium
Magnesium wheels weigh approximately 30-40% less than aluminum wheels, offering significant weight reduction for improved vehicle performance. The density of magnesium is about 1.74 g/cm3 compared to aluminum's 2.70 g/cm3, making magnesium the lighter choice for wheel manufacturing. This weight difference directly contributes to better acceleration, braking, and fuel efficiency in vehicles equipped with magnesium wheels.
Strength and Durability Differences
Magnesium wheels offer a higher strength-to-weight ratio compared to aluminum, making them ideal for performance applications where weight reduction is critical. Aluminum wheels generally provide superior corrosion resistance and long-term durability under various road conditions. While magnesium wheels excel in lightweight strength, aluminum wheels are often preferred for their enhanced toughness and maintenance benefits over time.
Performance and Handling Impact
Magnesium wheels offer superior performance with reduced weight, enhancing acceleration, braking, and cornering responsiveness compared to aluminum wheels. Aluminum wheels provide greater durability and corrosion resistance, but their increased weight can slightly compromise handling precision. Racing and high-performance vehicles often prefer magnesium alloys for optimized handling impact due to their lightweight properties and rigidity.
Corrosion Resistance and Maintenance
Aluminum wheels demonstrate superior corrosion resistance due to the natural formation of a protective oxide layer that prevents rust and reduces maintenance efforts. Magnesium wheels, while lighter and stronger, are more prone to corrosion, requiring specialized coatings and frequent upkeep to maintain durability. Choosing aluminum wheels minimizes long-term maintenance costs and improves longevity in harsh environmental conditions.
Cost and Affordability Analysis
Aluminum wheels generally offer a more cost-effective option compared to magnesium wheels due to lower raw material and manufacturing expenses. Magnesium wheels, while lightweight and high-performance, tend to be significantly pricier because of complex production processes and limited availability. For budget-conscious consumers, aluminum wheels provide superior affordability without compromising durability, making them the preferred choice in most automotive markets.
Style, Customization, and Aesthetics
Magnesium wheels offer a lightweight advantage and exhibit a distinctive rugged texture that appeals to enthusiasts seeking a vintage or racing-inspired style, while aluminum wheels provide a smoother finish and a wider array of polished, painted, or machined customization options. Customization on aluminum wheels extends to intricate spoke designs and vibrant color palettes, enhancing the vehicle's visual appeal and allowing for precise alignment with personal aesthetics. Both materials support aesthetic upgrades, but aluminum's corrosion resistance ensures a longer-lasting shine, maintaining style integrity under various weather conditions.
Safety Considerations for Each Material
Aluminum wheels offer superior corrosion resistance and a higher melting point, enhancing durability and safety under extreme braking conditions. Magnesium wheels are lighter, improving vehicle handling and reducing unsprung weight, but they are more prone to corrosion and can ignite under intense heat, posing potential fire hazards. Proper maintenance and protective coatings are essential for magnesium wheels to mitigate safety risks compared to aluminum alternatives.
Final Verdict: Which Wheel Material Is Better?
Aluminum wheels offer superior corrosion resistance and durability, making them ideal for long-term use and rough conditions. Magnesium wheels provide unmatched lightweight performance, enhancing acceleration and handling but require more maintenance due to their susceptibility to corrosion. For most drivers, aluminum wheels deliver a balanced combination of strength, affordability, and longevity, while magnesium wheels suit high-performance applications where weight savings are critical.
Infographic: Aluminum vs Magnesium for Wheel
 azmater.com
azmater.com