Iridium pigments offer superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to cadmium pigments, which are known for their vibrant yellow and red hues but pose significant toxicity concerns. Iridium-based pigments provide long-lasting color stability in high-temperature and harsh environmental conditions, making them preferable for industrial and artistic applications.
Table of Comparison
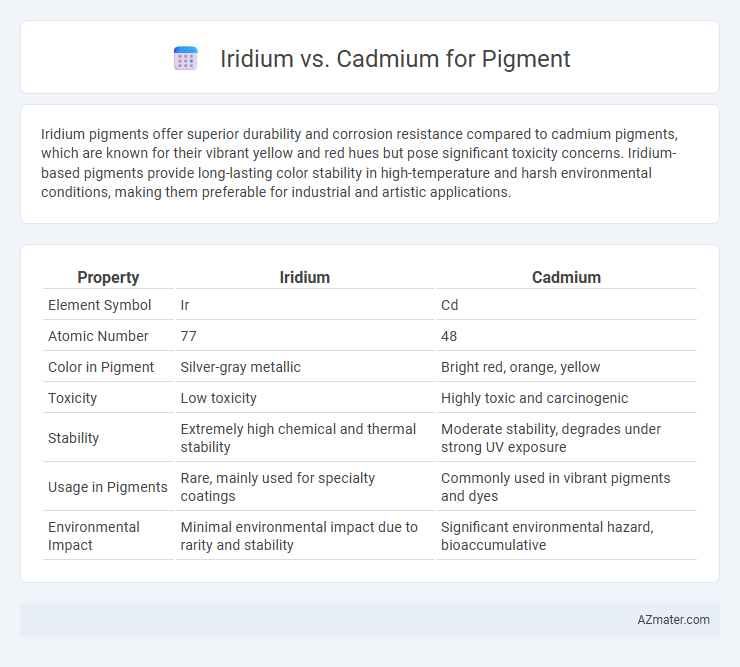
| Property | Iridium | Cadmium |
|---|---|---|
| Element Symbol | Ir | Cd |
| Atomic Number | 77 | 48 |
| Color in Pigment | Silver-gray metallic | Bright red, orange, yellow |
| Toxicity | Low toxicity | Highly toxic and carcinogenic |
| Stability | Extremely high chemical and thermal stability | Moderate stability, degrades under strong UV exposure |
| Usage in Pigments | Rare, mainly used for specialty coatings | Commonly used in vibrant pigments and dyes |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal environmental impact due to rarity and stability | Significant environmental hazard, bioaccumulative |
Introduction to Iridium and Cadmium Pigments
Iridium pigments are valued for their exceptional durability, corrosion resistance, and unique metallic luster, making them ideal for high-performance coatings and specialized applications. Cadmium pigments offer vibrant, highly stable colors with excellent lightfastness and weather resistance, commonly used in automotive and industrial coatings. Both iridium and cadmium pigments provide distinct advantages in color intensity and longevity, influencing their selection based on specific application requirements.
Chemical Properties: Iridium vs Cadmium
Iridium exhibits exceptional chemical stability and resistance to oxidation, making it ideal for high-durability pigment applications where longevity and color retention under harsh conditions are critical. Cadmium, by contrast, has moderate chemical stability but poses toxicity concerns, limiting its use despite its vibrant pigment qualities and excellent lightfastness. The inertness of iridium compounds offers superior resistance to chemical degradation compared to the more reactive cadmium compounds, which are prone to environmental leaching and degradation.
Color Range and Hue Comparison
Iridium-based pigments offer a narrower color range with predominantly metallic silver and gray hues, providing excellent stability and brightness in high-temperature applications. Cadmium pigments deliver a vibrant spectrum of reds, oranges, and yellows, known for their intense opacity and rich hues, especially in artistic and industrial coatings. While cadmium pigments excel in vivid, saturated colors, iridium pigments are prized for their unique reflective qualities and durability in extreme conditions.
Lightfastness and Durability in Pigments
Iridium pigments exhibit superior lightfastness and durability compared to cadmium pigments, maintaining color stability under prolonged exposure to UV light and harsh environmental conditions. Cadmium pigments, while vibrant, tend to degrade faster and show noticeable fading or discoloration over time when exposed to sunlight. The exceptional corrosion resistance of iridium compounds further enhances their longevity in both artistic and industrial applications.
Toxicity and Environmental Impact
Iridium pigments exhibit low toxicity and minimal environmental impact due to their inert nature and stability, making them preferable for sensitive applications. Cadmium pigments, while vibrant and durable, pose significant health risks, including carcinogenicity and organ toxicity, and contribute to environmental pollution through heavy metal contamination. Regulatory restrictions on cadmium usage highlight the importance of safer alternatives like iridium for sustainable pigment production.
Cost and Availability of Iridium and Cadmium Pigments
Iridium pigments are significantly more expensive than cadmium pigments due to the rarity and high extraction costs of iridium, which is one of the rarest elements in the Earth's crust. Cadmium pigments, derived from more abundant and cost-effective zinc and sulfur ores, offer greater availability and affordability, making them widely used in industrial applications despite toxicity concerns. The limited supply chain and geopolitical factors further constrain iridium pigment availability, while cadmium pigments benefit from established production infrastructure and global distribution networks.
Performance in Artistic Applications
Iridium pigments offer exceptional lightfastness and chemical stability, maintaining vibrant color intensity in artistic applications over time. Cadmium pigments provide rich opacity and brilliant hues, especially in reds and yellows, but may exhibit moderate toxicity and less long-term durability compared to iridium-based options. Artists prioritize iridium pigments when permanence and resistance to fading are critical, whereas cadmium pigments are favored for their strong covering power and vivid color spectrum.
Industrial Uses Beyond Art
Iridium pigments exhibit exceptional durability and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for high-temperature coatings and specialized electronics in industrial applications. Cadmium pigments, valued for their vibrant color and stability, are widely used in plastics, ceramics, and automotive coatings but face restrictions due to toxicity concerns. Industrial sectors increasingly favor iridium-infused materials for performance-critical environments, while cadmium remains regulated under environmental guidelines controlling occupational exposure.
Regulations and Safety Standards
Iridium pigments, known for their high stability and non-toxicity, comply with stringent international regulations such as REACH and RoHS, making them safer for use in cosmetics and industrial applications compared to cadmium pigments. Cadmium pigments are classified as toxic and carcinogenic under OSHA and EPA standards, leading to restricted use in many countries due to their environmental and health hazards. Regulatory bodies mandate strict exposure limits for cadmium, whereas iridium-based pigments face fewer restrictions, reflecting their superior safety profile in pigment manufacturing.
Future Trends in Pigment Innovation
Iridium pigments are gaining attention for their exceptional durability and vibrant color stability, making them a promising alternative to traditional cadmium-based pigments, which face regulatory restrictions due to toxicity concerns. Future trends in pigment innovation emphasize the development of environmentally friendly and non-toxic materials, positioning iridium as a key element in sustainable pigment chemistry. Advances in nanotechnology and material science are driving enhanced optical properties and longer-lasting pigments, with iridium compounds at the forefront of these innovations.
Infographic: Iridium vs Cadmium for Pigment
 azmater.com
azmater.com