Zirconium-based media offer superior corrosion resistance and higher adsorption capacity for heavy metals compared to iron-based media in water treatment applications. Iron media, while cost-effective, are prone to oxidation and have lower efficiency in removing contaminants such as arsenic and phosphate.
Table of Comparison
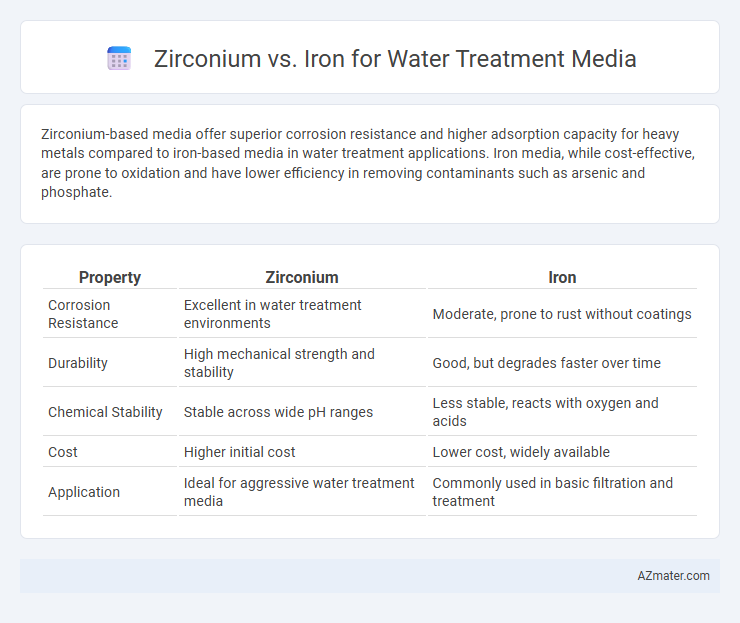
| Property | Zirconium | Iron |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in water treatment environments | Moderate, prone to rust without coatings |
| Durability | High mechanical strength and stability | Good, but degrades faster over time |
| Chemical Stability | Stable across wide pH ranges | Less stable, reacts with oxygen and acids |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost, widely available |
| Application | Ideal for aggressive water treatment media | Commonly used in basic filtration and treatment |
Introduction to Water Treatment Media
Zirconium-based water treatment media offer exceptional chemical stability and high resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for removing contaminants like heavy metals and radionuclides. Iron media, widely used due to its affordability and strong adsorption capacity, excels in reducing iron, manganese, and arsenic from water sources. Selecting appropriate media depends on specific water chemistry and treatment goals to ensure optimized contaminant removal and system longevity.
Overview of Zirconium in Water Treatment
Zirconium in water treatment serves as a high-performance media due to its exceptional chemical stability, resistance to corrosion, and strong affinity for removing contaminants such as arsenic, fluoride, and heavy metals. Compared to iron-based media, zirconium offers superior durability and can maintain efficiency across a wider range of pH levels, making it ideal for challenging water conditions. Its fine particle size and high surface area enhance adsorption capacity, leading to improved purification and extended media lifespan in filtration systems.
Overview of Iron-Based Media in Water Treatment
Iron-based media in water treatment primarily function as effective oxidizing agents and adsorbents, excelling in the removal of contaminants such as arsenic, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide. These media typically include forms like granular ferric hydroxide and greensand, which facilitate redox reactions to convert dissolved pollutants into insoluble particles that are easily filtered. Their cost-effectiveness and wide availability make iron-based media a prevalent choice for municipal and industrial water purification systems.
Comparative Adsorption Capacities
Zirconium-based media exhibit superior adsorption capacities for heavy metals like arsenic and lead compared to iron-based media, due to their higher surface area and greater chemical stability. Iron oxides, while effective in removing contaminants such as phosphorus and manganese, often show lower affinity and faster saturation under similar conditions. The enhanced adsorption efficiency of zirconium compounds is linked to their strong affinity for oxyanions and resistance to pH fluctuations during water treatment processes.
Removal Efficiency: Contaminants Targeted
Zirconium-based media exhibit superior removal efficiency for fluoride, arsenic, and phosphate due to their high affinity for oxyanions and strong ion-exchange properties, outperforming iron-based media in targeting these specific contaminants. Iron media, particularly iron oxide and hydroxide forms, effectively remove heavy metals like lead, chromium, and manganese through adsorption and redox reactions. Both media types play critical roles in water treatment, but zirconium excels in anion removal, while iron is more versatile for metal cations and oxidation processes.
Durability and Regeneration Potential
Zirconium-based water treatment media exhibit significantly higher durability compared to iron-based media, resisting corrosion and breakdown over extended use. The superior chemical stability of zirconium compounds enables more efficient regeneration cycles, maintaining filtration performance without substantial loss of media integrity. In contrast, iron media often suffer from reduced lifespan due to oxidation and limited regeneration capacity, leading to frequent replacement and increased maintenance costs.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Zirconium-based media often exhibit higher initial costs compared to iron-based media but provide longer service life and superior contaminant removal efficiency, reducing overall operational expenses. Iron media, while cheaper upfront, may require more frequent replacement and maintenance, potentially increasing long-term costs. Cost-effectiveness analysis reveals that zirconium's durability and performance can offset its initial price, making it a viable choice for water treatment facilities aiming for sustained economic benefits.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Zirconium-based media in water treatment exhibit lower toxicity and reduced leaching of harmful metals compared to iron-based media, minimizing environmental contamination. Iron media may contribute to increased sludge generation and residual iron, which can affect aquatic ecosystems and require more frequent disposal management. The inert nature of zirconium enhances safety in handling and disposal, making it a more environmentally friendly option for sustainable water treatment applications.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Zirconium-based media in water treatment systems require careful handling during installation due to their higher density and abrasive nature compared to iron media, necessitating robust vessel integrity and precise bed layering to ensure optimal performance. Maintenance of zirconium media often involves less frequent backwashing cycles because of its superior resistance to fouling and chemical degradation, reducing downtime and operational costs. Iron media, while easier to install due to its lighter weight, demands more frequent maintenance and backwashing to prevent media compaction and microbial growth, impacting system efficiency over time.
Choosing the Right Media: Zirconium vs Iron
Zirconium-based media offers superior filtration efficiency and chemical resistance compared to iron-based media, making it ideal for treating water with high levels of contaminants like heavy metals and organic compounds. Iron media excels in oxygen removal and manganese filtration but can degrade faster and may require more frequent replacement. Selecting between zirconium and iron depends on water quality parameters, treatment goals, and maintenance considerations to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Zirconium vs Iron for Water Treatment Media
 azmater.com
azmater.com