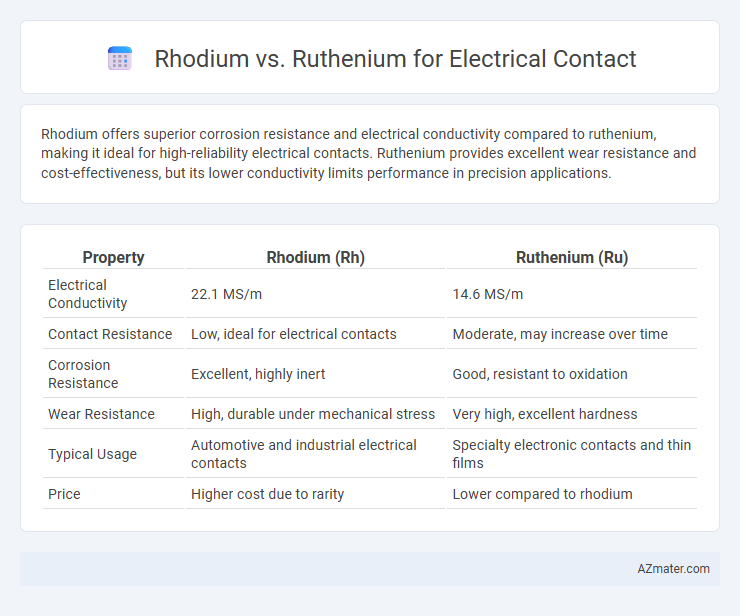
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity compared to ruthenium, making it ideal for high-reliability electrical contacts. Ruthenium provides excellent wear resistance and cost-effectiveness, but its lower conductivity limits performance in precision applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Rhodium (Rh) | Ruthenium (Ru) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 22.1 MS/m | 14.6 MS/m |
| Contact Resistance | Low, ideal for electrical contacts | Moderate, may increase over time |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, highly inert | Good, resistant to oxidation |
| Wear Resistance | High, durable under mechanical stress | Very high, excellent hardness |
| Typical Usage | Automotive and industrial electrical contacts | Specialty electronic contacts and thin films |
| Price | Higher cost due to rarity | Lower compared to rhodium |
Introduction to Rhodium and Ruthenium in Electrical Contacts
Rhodium and ruthenium, both members of the platinum group metals, are widely used in electrical contacts due to their exceptional corrosion resistance and high electrical conductivity. Rhodium offers superior oxidation resistance and hardness, making it ideal for high-performance, durable contacts in harsh environments. Ruthenium provides excellent wear resistance and oxidation stability, suitable for applications requiring long-term reliability and minimal electrical resistance.
Elemental Properties Relevant to Electrical Applications
Rhodium exhibits exceptional electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it highly suitable for durable electrical contacts in harsh environments. Ruthenium, while slightly less conductive, offers superior hardness and wear resistance, enhancing contact longevity under mechanical stress. Both elements belong to the platinum group metals, but rhodium's higher reflectivity and oxidation resistance typically give it an edge in high-performance electronic components.
Conductivity Comparison: Rhodium vs Ruthenium
Rhodium exhibits superior electrical conductivity compared to ruthenium, with a conductivity of approximately 21.8 million S/m versus ruthenium's 14.6 million S/m, making rhodium the preferred choice for high-efficiency electrical contacts. The higher conductivity of rhodium enhances signal transmission and reduces power loss in critical electronic components. Despite ruthenium's durability and corrosion resistance, rhodium remains dominant where optimal electrical performance is essential.
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Rhodium exhibits superior corrosion and oxidation resistance compared to ruthenium, making it highly effective for electrical contacts exposed to harsh environments. Ruthenium, while offering good conductivity, is more prone to oxidation, which can degrade contact performance over time. The enhanced stability of rhodium ensures longer-lasting, low-resistance connections in electrical systems.
Wear Resistance and Mechanical Durability
Rhodium exhibits superior wear resistance and exceptional mechanical durability, making it ideal for high-performance electrical contacts subjected to frequent switching and harsh environments. Ruthenium offers good wear resistance but generally falls short of rhodium in mechanical strength and longevity under repeated mechanical stress. The higher hardness and corrosion resistance of rhodium contribute to its preferred use in applications demanding long-term reliability and minimal contact degradation.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Rhodium exhibits higher market value and cost compared to ruthenium, driven by its rarity and extensive industrial demand, particularly in automotive catalysts and electrical contacts. Ruthenium provides a more cost-effective alternative with adequate conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for electrical contacts where budget constraints are critical. Market availability for rhodium is limited due to its scarcity and geopolitical supply risks, whereas ruthenium benefits from more stable supply chains derived primarily from platinum group metal mining.
Performance in High-Temperature Environments
Rhodium demonstrates superior corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity compared to ruthenium in high-temperature electrical contacts, maintaining stable performance up to 1000degC. Ruthenium offers excellent hardness and wear resistance but tends to oxidize more readily under elevated temperatures, potentially compromising contact reliability. Rhodium's stability and lower resistivity make it the preferred choice for critical high-temperature electrical contact applications in aerospace and automotive industries.
Applications in Modern Electronics
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and low electrical resistance, making it ideal for high-performance electrical contacts in connectors and switches used in modern electronics. Ruthenium excels in durability and hardness, providing enhanced wear resistance for contacts in demanding environments such as automotive sensors and memory devices. Both metals are favored in electronic applications due to their excellent conductivity and resistance to oxidation, ensuring long-lasting and reliable performance.
Environmental Impact and Recycling Considerations
Rhodium exhibits superior corrosion resistance and durability in electrical contacts, reducing frequent replacements and waste generation compared to ruthenium. Ruthenium, while less costly, tends to form oxides more readily, potentially increasing environmental burden through accelerated degradation and disposal needs. Both metals benefit from specialized recycling processes that recover precious materials, but rhodium's higher market value and lower chemical reactivity enhance its environmental sustainability in electrical applications.
Summary: Choosing Between Rhodium and Ruthenium for Electrical Contacts
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for high-reliability electrical contacts in harsh environments. Ruthenium provides greater hardness and wear resistance, which enhances durability in applications with frequent mechanical stress or switching cycles. Selecting between rhodium and ruthenium depends on balancing corrosion resistance with wear performance to optimize contact longevity and efficiency.
Infographic: Rhodium vs Ruthenium for Electrical Contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com