Rhodium plating offers superior corrosion resistance and a brighter, more reflective finish compared to chromium plating, making it ideal for high-end jewelry and automotive parts. Chromium plating provides excellent hardness and wear resistance, commonly used for industrial applications requiring durable, scratch-resistant surfaces.
Table of Comparison
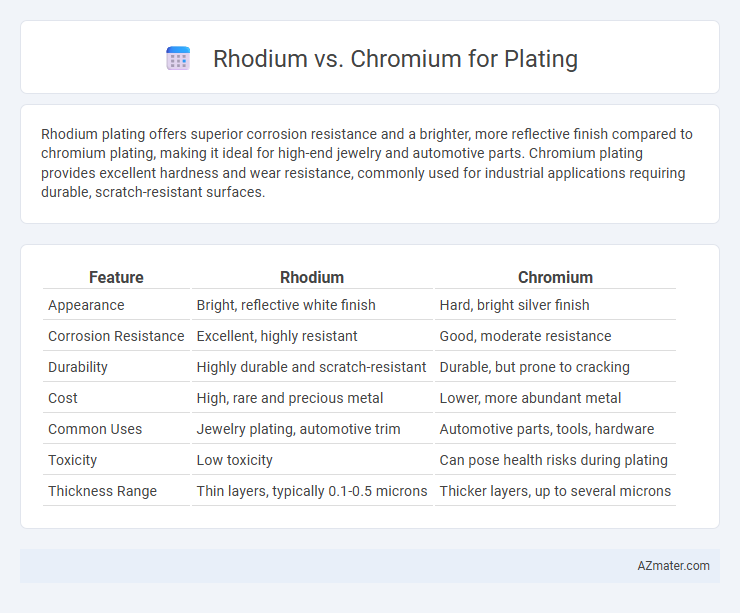
| Feature | Rhodium | Chromium |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Bright, reflective white finish | Hard, bright silver finish |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, highly resistant | Good, moderate resistance |
| Durability | Highly durable and scratch-resistant | Durable, but prone to cracking |
| Cost | High, rare and precious metal | Lower, more abundant metal |
| Common Uses | Jewelry plating, automotive trim | Automotive parts, tools, hardware |
| Toxicity | Low toxicity | Can pose health risks during plating |
| Thickness Range | Thin layers, typically 0.1-0.5 microns | Thicker layers, up to several microns |
Introduction to Rhodium and Chromium Plating
Rhodium plating is valued for its exceptional hardness, corrosion resistance, and brilliant reflective finish, making it ideal for jewelry and automotive trim applications. Chromium plating offers excellent durability and wear resistance, commonly used in industrial tools, automotive parts, and decorative surfaces. Both metals serve to enhance appearance and protect substrates, with rhodium providing superior tarnish resistance while chromium excels in hardness and cost-effectiveness.
Chemical Properties and Composition
Rhodium, a rare platinum-group metal with atomic number 45, exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance and high reflectivity due to its dense, chemically inert surface, making it ideal for durable, bright plating. Chromium, atomic number 24, forms a hard, oxidation-resistant oxide layer (Cr2O3) that enhances surface hardness and corrosion defense but lacks the exceptional reflectivity of rhodium. The chemical stability of rhodium in aggressive environments contrasts with chromium's tendency to oxidize, influencing their respective applications in jewelry and automotive plating processes.
Plating Process: Rhodium vs Chromium
Rhodium plating involves an electroplating process that deposits a thin layer of rhodium onto a substrate, offering superior corrosion resistance and a highly reflective, bright white finish. Chromium plating uses a similar electroplating method but typically provides a harder surface with excellent wear resistance and a characteristic shiny, metallic appearance. Rhodium plating requires precise control of solution chemistry and current density to achieve uniform coverage, while chromium plating involves a hexavalent chromium bath that demands strict environmental and safety protocols.
Durability and Hardness Comparison
Rhodium plating offers superior hardness, typically around 1000 Vickers hardness (HV), compared to chromium's hardness of approximately 700 HV, making rhodium more resistant to scratches and wear. In terms of durability, rhodium provides excellent corrosion resistance and maintains its bright, reflective finish longer under harsh environmental conditions than chromium, which can tarnish and dull over time. The higher hardness and better corrosion resistance of rhodium make it an ideal choice for high-end jewelry and precision instruments requiring long-lasting protection.
Aesthetic Finish and Appearance
Rhodium plating provides a brilliant, mirror-like white finish with exceptional brightness and a high level of reflectivity, making it ideal for enhancing the aesthetic appeal of jewelry and luxury items. Chromium plating offers a durable, shiny silver-gray appearance that resists tarnishing and corrosion, commonly used for automotive parts and household fixtures. The choice between rhodium and chromium plating hinges on desired glossiness and color tone, with rhodium favored for a sharper, more lustrous white shine and chromium for a sleek, metallic durability.
Resistance to Corrosion and Tarnishing
Rhodium offers superior resistance to corrosion and tarnishing compared to chromium, making it ideal for high-end jewelry and automotive parts exposed to harsh environments. Chromium provides a durable, corrosion-resistant coating but tends to develop surface oxidation and tarnish over time, especially under acidic or humid conditions. The exceptional chemical inertness of rhodium ensures lasting brilliance and protection against oxidation, whereas chromium may require regular maintenance to preserve its appearance.
Common Applications in Industry
Rhodium plating is extensively used in the automotive and jewelry industries for its exceptional corrosion resistance and brilliant, reflective finish, enhancing both durability and aesthetic appeal. Chromium plating, favored in manufacturing and construction, provides a hard, wear-resistant surface ideal for tools, machinery parts, and decorative elements on household appliances. Both metals serve critical roles, with rhodium preferred for precision electronics and fine jewelry, while chromium dominates heavy-duty and industrial applications.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Rhodium plating offers superior corrosion resistance and is non-toxic, posing minimal environmental hazards during application and disposal compared to chromium plating. Hexavalent chromium used in traditional chromium plating is highly toxic, carcinogenic, and requires rigorous safety measures and waste treatment protocols to prevent environmental contamination. Emerging alternatives and regulations are driving the industry towards rhodium and trivalent chromium plating, which are significantly safer and more environmentally sustainable.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Rhodium plating commands a significantly higher price per gram compared to chromium due to its rarity and superior corrosion resistance, making it less affordable for large-scale or budget-conscious projects. Chromium plating offers a cost-effective alternative, providing durable protection and aesthetic appeal at a fraction of rhodium's expense, ideal for automotive and industrial applications. Cost analysis reveals that while rhodium ensures premium quality and longevity, chromium remains the preferred choice when balancing affordability and performance.
Choosing the Right Plating for Your Needs
Rhodium plating offers superior corrosion resistance, a bright white finish, and excellent durability, making it ideal for fine jewelry and high-wear applications. Chromium plating provides a cost-effective solution with good hardness and a reflective silver appearance, suitable for automotive parts and decorative items. Selecting between rhodium and chromium plating depends on desired aesthetics, budget, and the level of durability required for the specific use case.
Infographic: Rhodium vs Chromium for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com