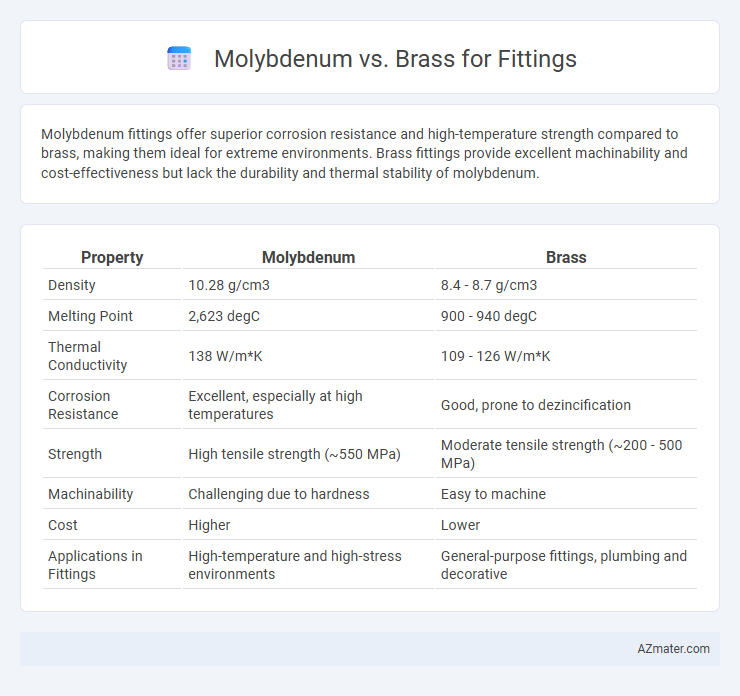
Molybdenum fittings offer superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength compared to brass, making them ideal for extreme environments. Brass fittings provide excellent machinability and cost-effectiveness but lack the durability and thermal stability of molybdenum.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Molybdenum | Brass |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 10.28 g/cm3 | 8.4 - 8.7 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 2,623 degC | 900 - 940 degC |
| Thermal Conductivity | 138 W/m*K | 109 - 126 W/m*K |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, especially at high temperatures | Good, prone to dezincification |
| Strength | High tensile strength (~550 MPa) | Moderate tensile strength (~200 - 500 MPa) |
| Machinability | Challenging due to hardness | Easy to machine |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Applications in Fittings | High-temperature and high-stress environments | General-purpose fittings, plumbing and decorative |
Introduction to Molybdenum and Brass Fittings
Molybdenum fittings offer exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature stability, making them ideal for demanding industrial applications such as aerospace and chemical processing. Brass fittings, composed primarily of copper and zinc, provide excellent machinability, corrosion resistance in water environments, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in plumbing and hydraulic systems. Understanding the distinct mechanical properties and environmental performance of molybdenum versus brass fittings ensures optimal material selection for specific engineering needs.
Chemical Properties and Composition
Molybdenum exhibits superior corrosion resistance and high melting point due to its atomic number 42 and placement in group 6 of the periodic table, making it ideal for fittings exposed to extreme chemical environments. Brass, an alloy primarily composed of copper and zinc, offers good machinability and moderate corrosion resistance but is susceptible to dezincification in acidic conditions. The chemical stability of molybdenum-based fittings surpasses brass fittings, especially in oxidizing and high-temperature applications, owing to molybdenum's robust metallic bonding and oxidation resistance.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Molybdenum fittings exhibit superior strength due to their high tensile strength of approximately 690 MPa, far exceeding brass fittings, which typically range around 300-400 MPa. The durability of molybdenum is enhanced by its excellent resistance to wear, corrosion, and high-temperature environments, making it ideal for demanding industrial applications. Brass fittings, while corrosion-resistant and easier to machine, generally offer lower longevity and mechanical performance under stress compared to molybdenum.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Molybdenum exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to brass, especially in harsh environments with high temperatures and acidic conditions, making it ideal for long-lasting fittings. Brass, composed primarily of copper and zinc, offers good resistance to corrosion in water and air but is more susceptible to dezincification and stress corrosion cracking over extended periods. The enhanced durability and resistance to chemical attack make molybdenum fittings a preferred choice in industrial applications demanding longevity and reliability.
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
Molybdenum exhibits significantly higher thermal conductivity, approximately 138 W/mK, compared to brass, which typically ranges between 100-130 W/mK, making molybdenum more efficient for heat dissipation in fittings. In terms of electrical conductivity, brass usually offers about 15-28% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard), whereas molybdenum has lower electrical conductivity around 19% IACS, implying brass is generally preferred for electrical conduction. The superior thermal stability and higher melting point of molybdenum also make it ideal for high-temperature fitting applications, while brass remains advantageous for moderate temperature and electrical uses.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Molybdenum fittings offer superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength but come with a significantly higher cost and limited availability compared to brass. Brass fittings provide excellent machinability, widespread availability, and cost efficiency, making them more suitable for general plumbing and low-pressure applications. For budget-conscious projects requiring readily available materials, brass remains the preferred choice over molybdenum.
Machinability and Ease of Fabrication
Molybdenum offers excellent strength and high-temperature resistance but poses significant challenges in machinability due to its hardness and tendency to cause tool wear. Brass, in contrast, exhibits superior machinability with easy chip removal and minimal tool wear, making it ideal for intricate fittings and rapid fabrication. Brass's ease of fabrication and lower manufacturing costs often outweigh molybdenum's performance benefits in standard fitting applications.
Typical Applications in Industry
Molybdenum fittings are predominantly used in high-temperature and corrosive environments such as aerospace, chemical processing, and power generation due to their excellent strength and resistance to oxidation. Brass fittings find widespread application in plumbing, HVAC systems, and instrumentation because of their superior machinability, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. The industrial choice between molybdenum and brass fittings depends on the operational conditions requiring either high durability under extreme conditions or economical performance in low-pressure environments.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Molybdenum fittings exhibit lower environmental impact due to their high durability and corrosion resistance, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing material waste. Brass fittings, while widely recyclable and composed primarily of copper and zinc, have a higher environmental footprint during extraction and processing phases. Both materials offer effective recyclability, but molybdenum's longer lifecycle enhances its sustainability advantages in fitting applications.
Choosing the Right Fitting: Key Considerations
Molybdenum fittings provide superior corrosion resistance, high-temperature strength, and durability, making them ideal for harsh industrial environments and chemical processing applications. Brass fittings offer excellent machinability, good corrosion resistance in low-pressure water systems, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for residential plumbing and hydraulic systems. When choosing the right fitting, consider factors such as operating temperature, pressure requirements, chemical exposure, and budget constraints to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Molybdenum vs Brass for Fitting
 azmater.com
azmater.com