Zinc provides superior corrosion resistance and durability for coating compared to tin, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial applications. Tin offers excellent solderability and non-toxic properties, commonly used in food-grade packaging and electronics.
Table of Comparison
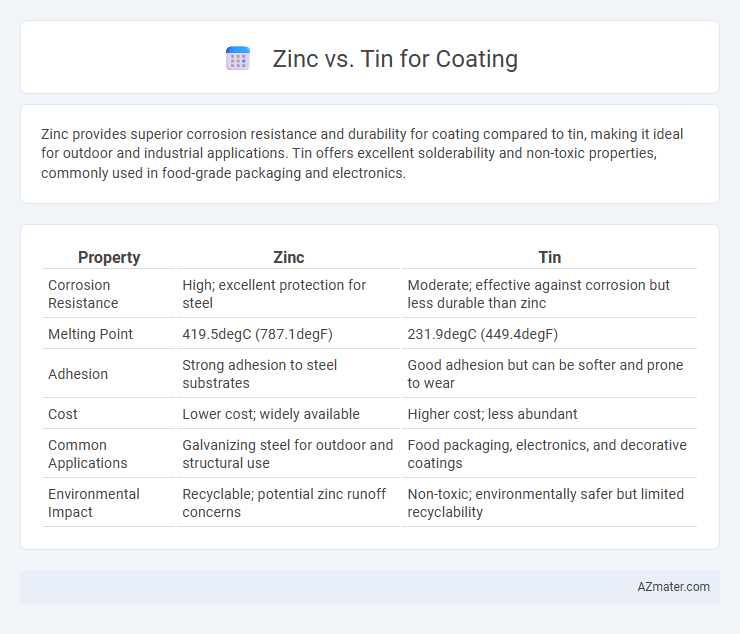
| Property | Zinc | Tin |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High; excellent protection for steel | Moderate; effective against corrosion but less durable than zinc |
| Melting Point | 419.5degC (787.1degF) | 231.9degC (449.4degF) |
| Adhesion | Strong adhesion to steel substrates | Good adhesion but can be softer and prone to wear |
| Cost | Lower cost; widely available | Higher cost; less abundant |
| Common Applications | Galvanizing steel for outdoor and structural use | Food packaging, electronics, and decorative coatings |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable; potential zinc runoff concerns | Non-toxic; environmentally safer but limited recyclability |
Introduction to Zinc and Tin Coatings
Zinc coatings serve as a primary corrosion-resistant layer by forming a protective oxide film, commonly used in galvanization for steel protection. Tin coatings provide excellent solderability and are highly effective for food-safe and electronic applications due to their non-toxic and conductive properties. Both metals enhance substrate durability but differ significantly in their corrosion resistance, adhesion characteristics, and industry-specific benefits.
Chemical Properties and Composition
Zinc exhibits high corrosion resistance due to its ability to form a stable, adherent oxide layer, making it ideal for galvanizing steel and protecting it from rust. Tin, characterized by its non-toxic, soft, and malleable nature, provides excellent corrosion resistance in mild environments and prevents oxidation in food and beverage containers. Both metals differ chemically; zinc is more reactive with a higher standard electrode potential (-0.76 V) than tin (-0.14 V), influencing their protective behavior and application in coatings.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Zinc offers superior corrosion resistance due to its ability to form a protective oxide layer that prevents rust and extends the lifespan of steel substrates. Tin coatings provide good corrosion resistance in mild environments, particularly against moisture and certain chemicals, but are less effective in harsh or outdoor conditions compared to zinc. Zinc's sacrificial anode properties make it ideal for protecting steel through galvanization, whereas tin primarily serves as a barrier coating without cathodic protection.
Industrial Applications of Zinc Coating
Zinc coating is extensively utilized in industrial applications due to its superior corrosion resistance, making it ideal for protecting steel structures, automotive parts, and construction materials. Unlike tin, zinc offers robust galvanic protection by sacrificially corroding to safeguard underlying metals, enhancing durability in harsh environments. This cost-effective coating method improves longevity and maintenance intervals for heavy machinery, infrastructure, and metal components exposed to moisture and chemicals.
Industrial Applications of Tin Coating
Tin coating provides excellent corrosion resistance and solderability, making it ideal for electronic components and food packaging industries. Its ability to form a protective oxide layer prevents metal degradation, enhancing the durability of steel in automotive and aerospace applications. Unlike zinc, tin's low toxicity and non-toxic nature offer safer usage in contact with consumables, promoting compliance with health regulations.
Cost Analysis: Zinc vs Tin
Zinc coatings generally offer a more cost-effective solution compared to tin due to lower material costs and abundant availability, making it ideal for large-scale industrial applications. Tin, while providing superior corrosion resistance and solderability, incurs higher expenses from both raw material prices and processing. Evaluating the total cost impact requires balancing zinc's economic advantage against tin's performance benefits in specific coating needs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Zinc coatings exhibit superior environmental sustainability due to their natural abundance, recyclability, and lower toxicity compared to tin, which is less abundant and often requires more energy-intensive extraction processes. Zinc's corrosion-resistant properties prolong the lifespan of coated materials, reducing waste and resource consumption over time. Tin coatings can contribute to environmental concerns related to mining and smelting, whereas zinc's eco-friendliness supports greener manufacturing practices and aligns better with circular economy principles.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Zinc coatings exhibit superior mechanical strength due to their ability to form a tough, adherent layer that resists cracking and deformation under stress. Tin coatings, while providing excellent corrosion resistance, generally have lower mechanical strength and are more prone to wear and abrasion. Zinc's durability in harsh environments makes it the preferred choice for structural applications requiring long-term protection and resilience.
Aesthetic and Finish Considerations
Zinc coatings provide a matte, silvery finish that offers a rugged, industrial aesthetic commonly preferred for outdoor and heavy-duty applications, resisting rust through a natural patina. Tin coatings deliver a bright, shiny, and smooth surface ideal for decorative and food-grade metal products, enhancing visual appeal and corrosion resistance with their non-toxic properties. The choice between zinc and tin depends on desired finish durability and visual impact, with tin favored for polished looks and zinc for robust, weathered appearances.
Choosing the Right Coating: Factors to Consider
When choosing between zinc and tin for coating, consider corrosion resistance, adhesion properties, and environmental conditions. Zinc offers superior galvanic protection, making it ideal for outdoor and marine applications, while tin provides excellent solderability and corrosion resistance in mild environments. Assess factors such as exposure to moisture, temperature variations, and compatibility with the substrate to ensure optimal performance.
Infographic: Zinc vs Tin for Coating
 azmater.com
azmater.com