Copper wire offers superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance compared to tin-coated wire, making it ideal for high-performance electrical applications. Tin coating on copper wires enhances solderability and protects against oxidation, extending wire lifespan in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
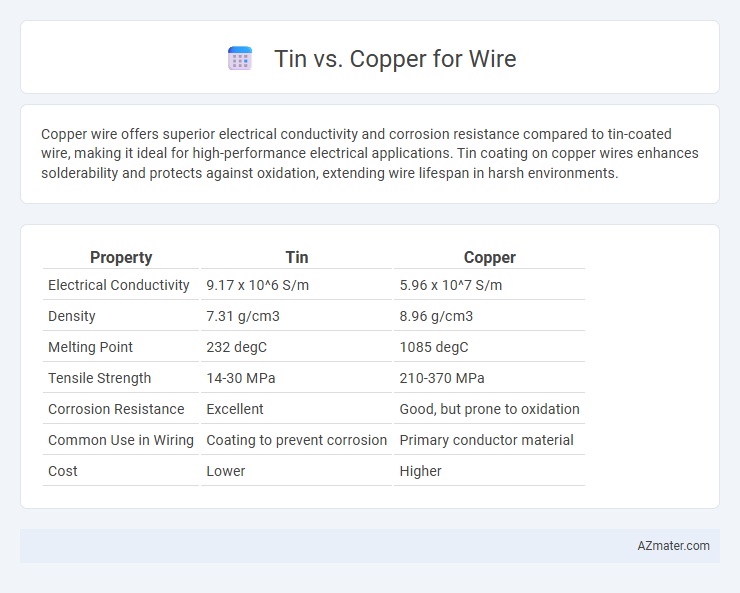
| Property | Tin | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 9.17 x 10^6 S/m | 5.96 x 10^7 S/m |
| Density | 7.31 g/cm3 | 8.96 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 232 degC | 1085 degC |
| Tensile Strength | 14-30 MPa | 210-370 MPa |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good, but prone to oxidation |
| Common Use in Wiring | Coating to prevent corrosion | Primary conductor material |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Tin and Copper Wires
Tin and copper wires serve crucial roles in electrical and electronic applications due to their conductive properties. Copper wires offer superior electrical conductivity and durability, making them ideal for high-performance and heavy-duty use. Tin-coated copper wires combine copper's conductivity with tin's corrosion resistance, enhancing longevity in harsh environments.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Copper offers superior electrical conductivity at approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m, making it the preferred choice for efficient electrical wiring. Tin, with a conductivity around 9.17 x 10^6 S/m, is significantly less conductive and is typically used as a protective coating rather than the primary conductive material. The higher conductivity of copper results in lower energy loss and improved performance in electrical systems compared to tin-coated wires.
Cost Differences: Tin vs. Copper
Tin-plated copper wire offers a cost-effective alternative to pure copper wire due to lower raw material expenses and improved corrosion resistance, which reduces maintenance costs over time. Although pure copper wire has higher electrical conductivity, tin plating extends the wire's lifespan by preventing oxidation, delivering better long-term value. Market prices show tin typically costs less per pound than copper, making tin-coated copper wire a preferred choice in budget-sensitive electrical and electronic applications.
Durability and Lifespan
Copper wire exhibits superior durability and longevity compared to tin-plated wire due to its inherent resistance to corrosion and excellent electrical conductivity. Tin plating on copper enhances corrosion resistance but may degrade faster under extreme environmental conditions, leading to reduced lifespan. The optimal choice depends on application requirements, with pure copper preferred for long-term durability and tin-plated variants suitable where environmental protection is critical.
Corrosion Resistance Factors
Tin-coated copper wire offers superior corrosion resistance compared to bare copper, as the tin layer acts as a protective barrier against oxidation and environmental contaminants. Copper, while an excellent conductor, is prone to tarnishing and developing copper oxide when exposed to moisture and air, which can degrade electrical performance over time. The tin plating enhances durability in harsh conditions, making tin-coated copper wire a preferred choice for applications requiring long-term reliability and exposure to corrosive environments.
Flexibility and Mechanical Strength
Copper wire offers superior mechanical strength and durability, making it ideal for applications requiring robust, long-lasting connections. Tin-coated copper wire enhances flexibility by providing corrosion resistance while maintaining much of copper's inherent strength. The tin layer reduces brittleness, allowing the wire to bend without breaking, which is essential for flexible electronic and automotive wiring.
Applications in Industry
Copper wires dominate industrial applications due to their excellent electrical conductivity, thermal stability, and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for power transmission, electronics, and telecommunication systems. Tin-plated copper wires are preferred in harsh environments for enhanced corrosion resistance and solderability, commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and marine industries. The combination of copper's conductivity and tin's protective properties ensures reliable performance in wiring harnesses, printed circuit boards, and electrical connectors across diverse industrial sectors.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Copper wire offers higher recyclability rates and lower environmental impact during extraction due to established mining regulations, while tin's mining often involves more energy-intensive processes and greater ecological disruption. Tin's limited supply and reliance on conflict-prone regions raise sustainability concerns compared to the abundant, widely recycled copper. Choosing copper wire supports circular economy principles through efficient reuse and reduced resource depletion, enhancing overall environmental sustainability.
Safety Considerations
Tin-coated copper wire offers enhanced corrosion resistance, reducing the risk of electrical faults and potential fire hazards compared to bare copper wire. Copper's superior conductivity makes pure copper wires preferable for high-current applications, but tin coating provides a safer barrier against oxidation in humid or marine environments. Proper insulation and regular inspection remain critical for both materials to ensure long-term electrical safety and performance.
Choosing the Right Wire for Your Needs
Tin-coated copper wire offers superior corrosion resistance and longevity, making it ideal for marine and outdoor applications where exposure to moisture is a concern. Pure copper wire provides excellent electrical conductivity and flexibility, suitable for general electrical wiring and high-performance electronic devices. Selecting the right wire depends on the environmental conditions, desired electrical performance, and budget constraints to ensure optimal functionality and durability.
Infographic: Tin vs Copper for Wire
 azmater.com
azmater.com