Alloy steel offers superior strength, corrosion resistance, and durability compared to zinc, making it ideal for long-lasting roofing applications. Zinc provides excellent natural corrosion resistance and environmental sustainability but has lower tensile strength than alloy steel.
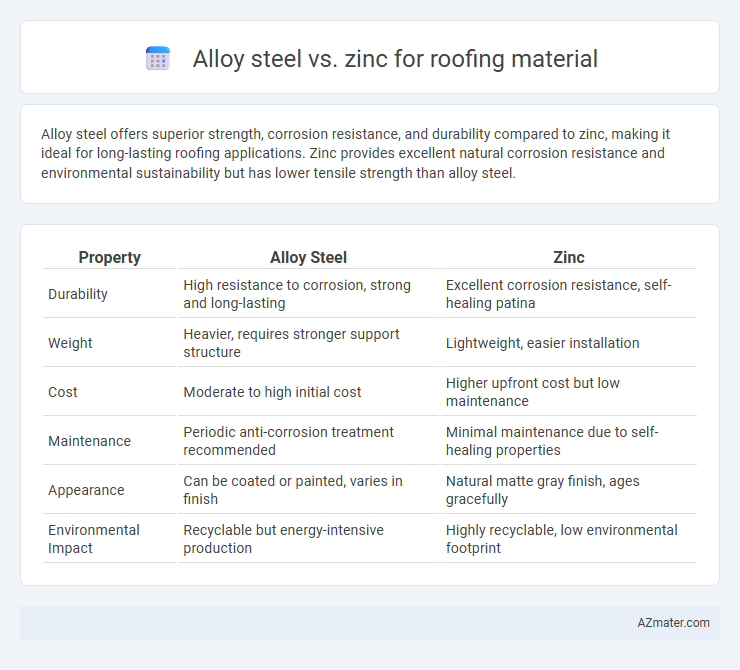
Table of Comparison
| Property | Alloy Steel | Zinc |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to corrosion, strong and long-lasting | Excellent corrosion resistance, self-healing patina |
| Weight | Heavier, requires stronger support structure | Lightweight, easier installation |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial cost | Higher upfront cost but low maintenance |
| Maintenance | Periodic anti-corrosion treatment recommended | Minimal maintenance due to self-healing properties |
| Appearance | Can be coated or painted, varies in finish | Natural matte gray finish, ages gracefully |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable but energy-intensive production | Highly recyclable, low environmental footprint |
Introduction to Alloy Steel and Zinc as Roofing Materials
Alloy steel roofing offers superior strength, corrosion resistance, and durability due to the combination of steel with elements like chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, making it ideal for harsh weather conditions. Zinc roofing is valued for its natural resistance to corrosion, self-healing patina, and eco-friendly properties, providing long-lasting protection with minimal maintenance. Both materials serve as reliable roofing options, but their performance depends on factors such as environmental exposure and maintenance requirements.
Composition and Properties of Alloy Steel Roofing
Alloy steel roofing is composed primarily of iron combined with controlled amounts of elements such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, enhancing its strength, corrosion resistance, and durability compared to standard steel or zinc roofing. Its high tensile strength and resistance to environmental factors like moisture and UV radiation make alloy steel an ideal choice for long-lasting roofing structures. Zinc roofing, while corrosion-resistant and lightweight due to its pure metallic nature, lacks the mechanical robustness and impact resistance provided by the reinforced composition of alloy steel.
Composition and Properties of Zinc Roofing
Zinc roofing is composed primarily of pure zinc with small amounts of titanium and copper, enhancing its durability and corrosion resistance. Its self-healing patina forms a protective layer that makes it highly resistant to environmental factors and reduces maintenance needs. Compared to alloy steel, zinc offers superior flexibility, lightweight characteristics, and excellent longevity, making it ideal for sustainable roofing solutions.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Alloy steel roofing offers superior durability and longevity compared to zinc, with higher resistance to corrosion, impact, and extreme weather conditions. Zinc roofs excel in self-healing properties due to their protective patina but generally have a lifespan of 80 to 100 years, whereas alloy steel can last up to 50 years with protective coatings. Overall, alloy steel provides enhanced strength and requires less maintenance under harsh environmental exposure.
Weather Resistance: Alloy Steel vs Zinc
Alloy steel offers superior weather resistance for roofing due to its enhanced corrosion resistance and strength when treated with protective coatings, making it ideal for harsh climates. Zinc naturally forms a protective patina that prevents rust and withstands extreme temperatures, providing long-lasting durability with minimal maintenance. While both materials excel in weather resistance, zinc typically outperforms alloy steel in coastal or highly acidic environments because of its self-healing surface properties.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Maintenance
Alloy steel roofing typically incurs higher initial installation costs due to specialized handling and fastening requirements, while zinc roofing offers moderate installation expenses with simpler techniques. Maintenance for alloy steel often involves regular inspections for corrosion and protective coatings, increasing long-term costs, whereas zinc's natural patina formation minimizes upkeep, resulting in lower maintenance expenses over time. When comparing lifecycle cost-effectiveness, zinc roofing usually provides better value through reduced maintenance and longer durability despite alloy steel's superior strength characteristics.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Alloy steel roofing offers superior durability and recyclability compared to zinc, which often requires intensive mining and processing that contribute to environmental degradation. The production of alloy steel typically involves higher energy consumption but benefits from well-established recycling infrastructure, reducing waste and lowering carbon footprint over the product lifecycle. Zinc roofing excels in corrosion resistance and longevity, yet its environmental sustainability is challenged by slow recycling rates and the ecological impact of zinc mining.
Aesthetic Options and Design Flexibility
Alloy steel roofing offers a wide range of aesthetic options with customizable finishes, colors, and textures that mimic natural materials like wood or stone, enhancing architectural creativity. Zinc roofing provides exceptional design flexibility due to its malleability, allowing complex shapes and intricate details that suit modern and historic restoration projects. Both materials support seamless installation, but zinc's natural patina evolves over time, adding unique visual character without additional coatings.
Common Applications and Suitability
Alloy steel is widely used in roofing for its high strength, corrosion resistance, and durability, making it suitable for industrial, commercial, and residential buildings exposed to harsh weather conditions. Zinc roofing offers excellent resistance to corrosion and algae growth, ideal for architectural applications requiring aesthetic appeal and longevity in moderate climates. Both materials provide long-term protection, but alloy steel is preferred for heavy-duty structures while zinc excels in decorative and historic roof restoration projects.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Roofing Material
Alloy steel offers superior strength, durability, and corrosion resistance compared to zinc, making it ideal for roofing in harsh weather conditions and industrial environments. Zinc roofs excel in aesthetic appeal and self-healing properties, which can extend longevity with minimal maintenance. For long-term investment and structural performance, alloy steel is preferable, while zinc suits projects prioritizing visual elegance and eco-friendly attributes.
Infographic: Alloy steel vs Zinc for Roofing material
 azmater.com
azmater.com