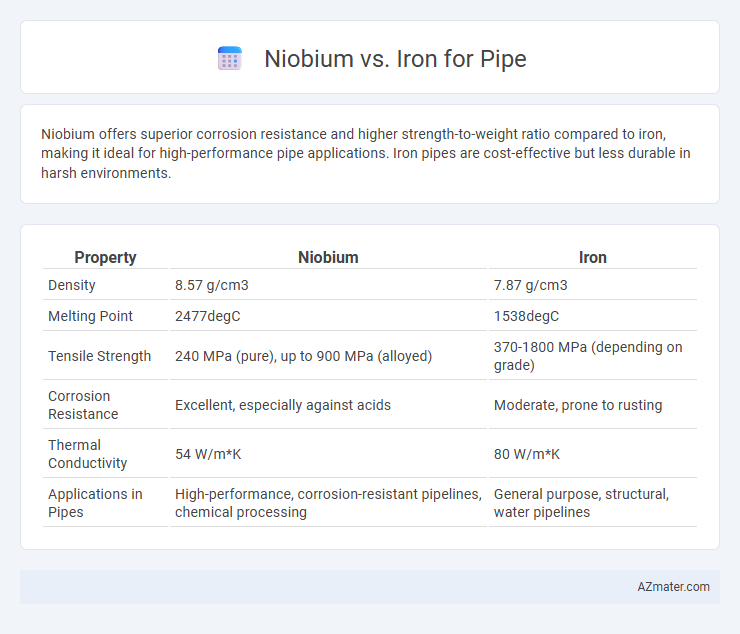
Niobium offers superior corrosion resistance and higher strength-to-weight ratio compared to iron, making it ideal for high-performance pipe applications. Iron pipes are cost-effective but less durable in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Niobium | Iron |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 8.57 g/cm3 | 7.87 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 2477degC | 1538degC |
| Tensile Strength | 240 MPa (pure), up to 900 MPa (alloyed) | 370-1800 MPa (depending on grade) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, especially against acids | Moderate, prone to rusting |
| Thermal Conductivity | 54 W/m*K | 80 W/m*K |
| Applications in Pipes | High-performance, corrosion-resistant pipelines, chemical processing | General purpose, structural, water pipelines |
Introduction to Niobium and Iron in Piping
Niobium and iron serve distinct roles in piping applications, with niobium primarily used as an alloying element to enhance steel's strength, corrosion resistance, and weldability. Iron, the base metal in most pipes, offers excellent structural integrity and cost-effectiveness but can be prone to rust and lower mechanical properties without alloying. Incorporating niobium into iron-based pipes improves durability and performance in high-pressure and corrosive environments, making it essential for advanced industrial piping solutions.
Material Composition: Niobium vs Iron
Niobium is a transition metal known for its high strength, corrosion resistance, and excellent ductility, often alloyed with iron to enhance mechanical properties in pipes. Iron, primarily composed of elemental Fe, offers good tensile strength but lacks the corrosion resistance and lightweight characteristics of niobium. The addition of niobium in iron-based pipes improves structural integrity, resistance to oxidation, and thermal stability, making niobium-containing alloys ideal for high-performance piping applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Niobium exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to iron for pipe applications, offering higher tensile strength and enhanced resistance to brittle fracture, which is critical in high-pressure environments. Its excellent ductility and toughness at low temperatures outperform traditional iron pipes, reducing the risk of failure under thermal stress. Niobium's ability to maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions makes it a preferred choice in demanding industries such as aerospace and chemical processing.
Corrosion Resistance in Piping Applications
Niobium exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to iron in piping applications, particularly in harsh chemical environments and high-temperature conditions. The addition of niobium enhances the formation of stable, protective oxide layers, significantly reducing susceptibility to pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking. Iron pipes, while cost-effective, are more prone to corrosion-related failures without extensive protective coatings or treatments.
Strength and Durability Factors
Niobium-enhanced steel pipes exhibit significantly higher tensile strength and improved resistance to corrosion compared to standard iron pipes, making them ideal for high-pressure and harsh environment applications. The addition of niobium refines the grain structure, enhancing toughness and fatigue resistance, which contributes to longer service life and reduced maintenance costs. Iron pipes, while cost-effective, generally offer lower durability and strength, limiting their use in critical infrastructure projects where safety and longevity are paramount.
Cost Analysis: Niobium vs Iron Pipes
Niobium pipes typically have a higher upfront cost compared to iron pipes due to niobium's scarcity and advanced manufacturing processes. However, niobium offers superior corrosion resistance and strength-to-weight ratio, potentially reducing long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. Iron pipes are more affordable initially but may incur higher lifecycle costs due to susceptibility to rust and lower durability.
Weldability and Fabrication Ease
Niobium-enhanced steel pipes offer superior weldability compared to traditional iron pipes due to niobium's ability to increase strength and toughness without compromising weld quality. The addition of niobium refines the grain structure, reducing weld cracking and enhancing fabrication ease by allowing faster cooling rates and improved mechanical properties. Iron pipes, while easier to source, generally require more caution during welding to avoid brittleness and reduced durability.
Applications in Various Industries
Niobium-enhanced steel pipes exhibit superior strength, corrosion resistance, and fatigue durability, making them ideal for aerospace, oil and gas, and chemical processing industries. Iron pipes, while cost-effective and widely used in water supply and construction, lack the high-performance attributes needed for extreme environments. Industries demanding advanced mechanical properties and long-term reliability increasingly prefer niobium alloys for critical pipeline applications.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Niobium-enhanced steel pipes exhibit superior strength and corrosion resistance compared to conventional iron pipes, reducing the frequency of replacements and lowering environmental impact through decreased resource extraction. Niobium's ability to enable thinner, lighter pipes means less raw material usage and energy consumption during manufacturing and transportation. Iron pipes require more maintenance and have a shorter lifespan, leading to higher carbon emissions and waste generation over time.
Choosing the Right Material: Niobium or Iron?
Niobium offers superior corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent weldability, making it ideal for pipes in aggressive environments or high-pressure systems. Iron pipes, while cost-effective and widely available, are more prone to corrosion and have lower strength, limiting their use in demanding industrial applications. Selecting niobium over iron ensures longer service life and reliability in critical infrastructure where durability and performance are paramount.
Infographic: Niobium vs Iron for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com